Page 1019 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1019
982 Part seven Organ-Specific Inflammatory Disease
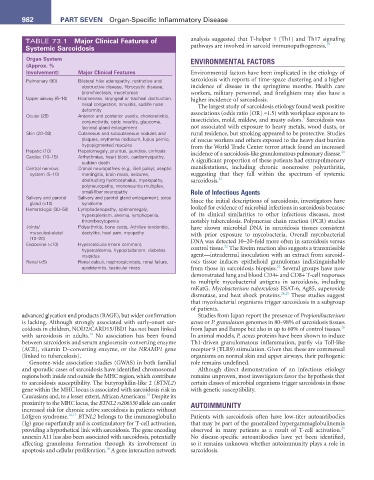
TABLE 73.1 Major Clinical Features of analysis suggested that T-helper 1 (Th1) and Th17 signaling
19
systemic sarcoidosis pathways are involved in sarcoid immunopathogenesis.
Organ system ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
(approx. %
Involvement) Major Clinical Features Environmental factors have been implicated in the etiology of
Pulmonary (90) Bilateral hilar adenopathy, restrictive and sarcoidosis with reports of time–space clustering and a higher
obstructive disease, fibrocystic disease, incidence of disease in the springtime months. Health care
bronchiectasis, mycetomas workers, military personnel, and firefighters may also have a
Upper airway (5–10) Hoarseness, laryngeal or tracheal obstruction, higher incidence of sarcoidosis.
nasal congestion, sinusitis, saddle nose The largest study of sarcoidosis etiology found weak positive
deformity
Ocular (25) Anterior and posterior uveitis, chorioretinitis, associations (odds ratio [OR] ≈1.5) with workplace exposure to
3
conjunctivitis, optic neuritis, glaucoma, insecticides, mold, mildew, and musty odors. Sarcoidosis was
lacrimal gland enlargement not associated with exposure to heavy metals, wood dusts, or
Skin (20–30) Cutaneous and subcutaneous nodules and rural residence, but smoking appeared to be protective. Studies
plaques, erythema nodosum, lupus pernio, of rescue workers and others exposed to the heavy dust burden
hypopigmented macules from the World Trade Center terror attack found an increased
Hepatic (10) Hepatomegaly, pruritus, jaundice, cirrhosis incidence of a sarcoidosis-like granulomatous pulmonary disease.
20
Cardiac (10–15) Arrhythmias, heart block, cardiomyopathy,
sudden death A significant proportion of these patients had extrapulmonary
Central nervous Cranial neuropathies (e.g., Bell palsy), aseptic manifestations, including chronic nonerosive polyarthritis,
system (5–10) meningitis, brain mass, seizures, suggesting that they fall within the spectrum of systemic
obstructing hydrocephalus, myelopathy, sarcoidosis. 21
polyneuropathy, mononeuritis multiplex,
small-fiber neuropathy Role of Infectious Agents
Salivary and parotid Salivary and parotid gland enlargement, sicca
gland (<10) syndrome Since the initial descriptions of sarcoidosis, investigators have
Hematologic (30–50) Lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, looked for evidence of microbial infections in sarcoidosis because
hypersplenism, anemia, lymphopenia, of its clinical similarities to other infectious diseases, most
thrombocytopenia notably tuberculosis. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) studies
Joints/ Polyarthritis, bone cysts, Achilles tendonitis, have shown microbial DNA in sarcoidosis tissues consistent
musculoskeletal dactylitis, heel pain, myopathy with prior exposure to mycobacteria. Overall mycobacterial
(10–20)
Endocrine (<10) Hypercalciuria (more common), DNA was detected 10–20-fold more often in sarcoidosis versus
22
hypercalcemia, hypopituitarism, diabetes control tissue. The Kveim reaction also suggests a transmissible
insipidus agent—intradermal inoculation with an extract from sarcoid-
Renal (<5) Renal calculi, nephrocalcinosis, renal failure, osis tissue induces epithelioid granulomas indistinguishable
23
epididymitis, testicular mass from those in sarcoidosis biopsies. Several groups have now
demonstrated lung and blood CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses
to multiple mycobacterial antigens in sarcoidosis, including
mKatG, Mycobacterium tuberculosis ESAT-6, Ag85, superoxide
dismutase, and heat shock proteins. 24,25 These studies suggest
that mycobacterial organisms trigger sarcoidosis in a subgroup
of patients.
advanced glycation end products (RAGE), but wider confirmation Studies from Japan report the presence of Propionibacterium
is lacking. Although strongly associated with early-onset sar- acnes or P. granulosum genomes in 80–98% of sarcoidosis tissues
26
coidosis in children, NOD2/CARD15/IBD1 has not been linked from Japan and Europe but also in up to 60% of control tissues.
14
with sarcoidosis in adults. No association has been found In animal models, P. acnes proteins have been shown to induce
between sarcoidosis and serum angiotensin-converting enzyme Th1-driven granulomatous inflammation, partly via Toll-like
(ACE), vitamin D–converting enzyme, or the NRAMP1 gene receptor 9 (TLR9) stimulation. Given that these are commensal
(linked to tuberculosis). organisms on normal skin and upper airways, their pathogenic
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in both familial role remains undefined.
and sporadic cases of sarcoidosis have identified chromosomal Although direct demonstration of an infectious etiology
regions both inside and outside the MHC region, which contribute remains unproven, most investigators favor the hypothesis that
to sarcoidosis susceptibility. The butyrophilin-like 2 (BTNL2) certain classes of microbial organisms trigger sarcoidosis in those
gene within the MHC locus is associated with sarcoidosis risk in with genetic susceptibility.
15
Caucasians and, to a lesser extent, African Americans. Despite its
proximity to the MHC locus, the BTNL2 rs206530 allele can confer AUTOIMMUNITY
increased risk for chronic active sarcoidosis in patients without
Löfgren syndrome. 16,17 BTNL2 belongs to the immunoglobulin Patients with sarcoidosis often have low-titer autoantibodies
(Ig) gene superfamily and is costimulatory for T-cell activation, that may be part of the generalized hypergammaglobulinemia
27
providing a hypothetical link with sarcoidosis. The gene encoding observed in many patients as a result of T-cell activation.
annexin A11 has also been associated with sarcoidosis, potentially No disease-specific autoantibodies have yet been identified,
affecting granuloma formation through its involvement in so it remains unknown whether autoimmunity plays a role in
18
apoptosis and cellular proliferation. A gene interaction network sarcoidosis.