Page 1070 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1070
ChaPTEr 77 Immunotherapy of Cancer 1035
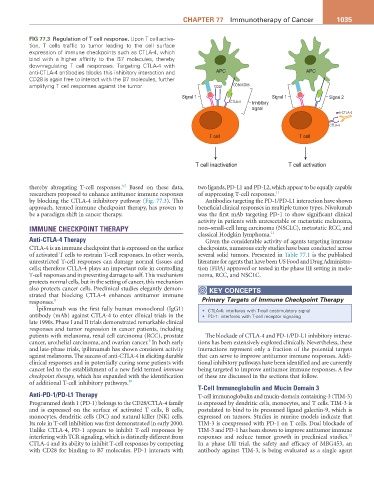
Fig 77.3 Regulation of T cell response. Upon T cell activa-
tion, T cells traffic to tumor leading to the cell surface
expression of immune checkpoints such as CTLA-4, which
bind with a higher affinity to the B7 molecules, thereby
downregulating T cell responses. Targeting CTLA-4 with
anti-CTLA-4 antibodies blocks this inhibitory interaction and APC APC
CD28 is again free to interact with the B7 molecules, further
amplifying T cell responses against the tumor. CD28 CD80/CD86
Signal 1 Signal 1 Signal 2
CTLA-4 Inhibitory
signal
anti-CTLA-4
CTLA-4
T cell T cell
T cell inactivation T cell activation
6,7
thereby abrogating T-cell responses. Based on these data, two ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, which appear to be equally capable
researchers proposed to enhance antitumor immune responses of suppressing T-cell responses. 11
by blocking the CTLA-4 inhibitory pathway (Fig. 77.3). This Antibodies targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction have shown
approach, termed immune checkpoint therapy, has proven to beneficial clinical responses in multiple tumor types. Nivolumab
be a paradigm shift in cancer therapy. was the first mAb targeting PD-1 to show significant clinical
activity in patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma,
IMMUNE CHECKPOINT THERAPY non–small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC), metastatic RCC, and
classical Hodgkin lymphoma. 11
Anti-CTLA-4 Therapy Given the considerable activity of agents targeting immune
CTLA-4 is an immune checkpoint that is expressed on the surface checkpoints, numerous early studies have been conducted across
of activated T cells to restrain T-cell responses. In other words, several solid tumors. Presented in Table 77.1 is the published
unrestricted T-cell responses can damage normal tissues and literature for agents that have been US Food and Drug Administra-
cells; therefore CTLA-4 plays an important role in controlling tion (FDA) approved or tested in the phase III setting in mela-
T-cell responses and in preventing damage to self. This mechanism noma, RCC, and NSCLC.
protects normal cells, but in the setting of cancer, this mechanism
also protects cancer cells. Preclinical studies elegantly demon- KEY CONCEPTS
strated that blocking CTLA-4 enhances antitumor immune
responses. 8 Primary Targets of Immune Checkpoint Therapy
Ipilimumab was the first fully human monoclonal (IgG1) • CTLA-4: interferes with T-cell costimulatory signal
antibody (mAb) against CTLA-4 to enter clinical trials in the • PD-1: interferes with T-cell receptor signaling
late 1990s. Phase I and II trials demonstrated remarkable clinical
responses and tumor regression in cancer patients, including
patients with melanoma, renal cell carcinoma (RCC), prostate The blockade of CTLA-4 and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory interac-
9
cancer, urothelial carcinoma, and ovarian cancer. In both early tions has been extensively explored clinically. Nevertheless, these
and late-phase trials, ipilimumab has shown consistent activity interactions represent only a fraction of the potential targets
against melanoma. The success of anti-CTLA-4 in eliciting durable that can serve to improve antitumor immune responses. Addi-
clinical responses and in potentially curing some patients with tional inhibitory pathways have been identified and are currently
cancer led to the establishment of a new field termed immune being targeted to improve antitumor immune responses. A few
checkpoint therapy, which has expanded with the identification of these are discussed in the sections that follow.
of additional T-cell inhibitory pathways. 10
T-Cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin Domain 3
Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Therapy T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3 (TIM-3)
Programmed death 1 (PD-1) belongs to the CD28/CTLA-4 family is expressed by dendritic cells, monocytes, and T cells. TIM-3 is
and is expressed on the surface of activated T cells, B cells, postulated to bind to its presumed ligand galectin-9, which is
monocytes, dendritic cells (DC) and natural killer (NK) cells. expressed on tumors. Studies in murine models indicate that
Its role in T-cell inhibition was first demonstrated in early 2000. TIM-3 is coexpressed with PD-1 on T cells. Dual blockade of
Unlike CTLA-4, PD-1 appears to inhibit T-cell responses by TIM-3 and PD-1 has been shown to improve antitumor immune
12
interfering with TCR signaling, which is distinctly different from responses and reduce tumor growth in preclinical studies.
CTLA-4 and its ability to inhibit T-cell responses by competing In a phase I/II trial, the safety and efficacy of MBG453, an
with CD28 for binding to B7 molecules. PD-1 interacts with antibody against TIM-3, is being evaluated as a single agent