Page 1071 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1071
1036 ParT EighT Immunology of Neoplasia
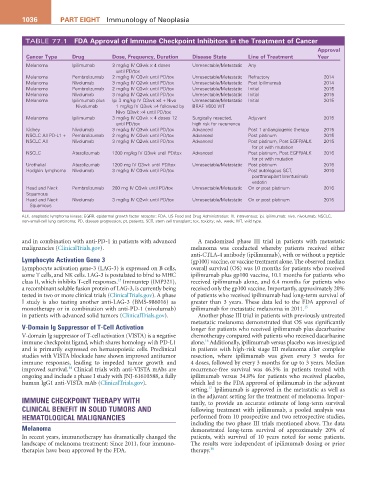
TABLE 77.1 FDa approval of immune Checkpoint inhibitors in the Treatment of Cancer
approval
Cancer Type Drug Dose, Frequency, Duration Disease State Line of Treatment Year
Melanoma Ipilimumab 3 mg/kg IV Q3wk × 4 doses Unresectable/Metastatic Any
until PD/tox
Melanoma Pembrolizumab 2 mg/kg IV Q3wk until PD/tox Unresectable/Metastatic Refractory 2014
Melanoma Nivolumab 3 mg/kg IV Q2wk until PD/tox Unresectable/Metastatic Post ipilimumab 2014
Melanoma Pembrolizumab 2 mg/kg IV Q3wk until PD/tox Unresectable/Metastatic Initial 2015
Melanoma Nivolumab 3 mg/kg IV Q2wk until PD/tox Unresectable/Metastatic Initial 2015
Melanoma Ipilimumab plus Ipi 3 mg/kg IV Q3wk ×4 + Nivo Unresectable/Metastatic Initial 2015
Nivolumab 1 mg/kg IV Q3wk ×4 followed by BRAF V600 WT
Nivo Q3wk ×4 until PD/tox
Melanoma Ipilimumab 3 mg/kg IV Q3wk × 4 doses 12 Surgically resected, Adjuvant 2015
until PD/tox high risk for recurrence
Kidney Nivolumab 3 mg/kg IV Q3wk until PD/tox Advanced Post 1 antiangiogenic therapy 2015
NSCLC All PD-L1 + Pembrolizumab 2 mg/kg IV Q3wk until PD/tox Advanced Post platinum 2015
NSCLC All Nivolumab 3 mg/kg IV Q2wk until PD/tox Advanced Post platinum, Post EGFR/ALK 2015
for pt with mutation
NSCLC Atezolizumab 1200 mg/kg IV Q3wk until PD/tox Advanced Post platinum, Post EGFR/ALK 2016
for pt with mutation
Urothelial Atezolizumab 1200 mg IV Q3wk until PD/tox Unresectable/Metastatic Post platinum 2016
Hodgkin lymphoma Nivolumab 3 mg/kg IV Q3wk until PD/tox Post autologous SCT, 2016
posttransplant brentuximab
vedotin
Head and Neck Pembrolizumab 200 mg IV Q3wk until PD/tox Unresectable/Metastatic On or post platinum 2016
Squamous
Head and Neck Nivolumab 3 mg/kg IV Q2wk until PD/tox Unresectable/Metastatic On or post platinum 2016
Squamous
ALK, anaplastic lymphoma kinase; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; FDA, US Food and Drug Administration; IV, intravenous; ipi, ipilimumab; nivo, nivolumab; NSCLC,
non–small-cell lung carcinoma; PD, disease progression; pt, patients; SCT, stem cell transplant; tox, toxicity; wk, week; WT, wild type.
and in combination with anti-PD-1 in patients with advanced A randomized phase III trial in patients with metastatic
malignancies (ClinicalTrials.gov). melanoma was conducted whereby patients received either
anti-CTLA-4 antibody (ipilimumab), with or without a peptide
Lymphocyte Activation Gene 3 (gp100) vaccine, or vaccine treatment alone. The observed median
Lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3) is expressed on B cells, overall survival (OS) was 10 months for patients who received
some T cells, and NK cells. LAG-3 is postulated to bind to MHC ipilimumab plus gp100 vaccine, 10.1 months for patients who
13
class II, which inhibits T-cell responses. Immuntep (IMP321), received ipilimumab alone, and 6.4 months for patients who
a recombinant soluble fusion protein of LAG-3, is currently being received only the gp100 vaccine. Importantly, approximately 20%
tested in two or more clinical trials (ClinicalTrials.gov). A phase of patients who received ipilimumab had long-term survival of
I study is also testing another anti-LAG-3 (BMS-986016) as greater than 3 years. These data led to the FDA approval of
monotherapy or in combination with anti-PD-1 (nivolumab) ipilimumab for metastatic melanoma in 2011. 15
in patients with advanced solid tumors (ClinicalTrials.gov). Another phase III trial in patients with previously untreated
metastatic melanoma demonstrated that OS was significantly
V-Domain Ig Suppressor of T-Cell Activation longer for patients who received ipilimumab plus dacarbazine
V-domain Ig suppressor of T-cell activation (VISTA) is a negative chemotherapy compared with patients who received dacarbazine
16
immune checkpoint ligand, which shares homology with PD-L1 alone. Additionally, ipilimumab versus placebo was investigated
and is primarily expressed on hematopoietic cells. Preclinical in patients with high-risk stage III melanoma after complete
studies with VISTA blockade have shown improved antitumor resection, where ipilimumab was given every 3 weeks for
immune responses, leading to impeded tumor growth and 4 doses, followed by every 3 months for up to 3 years. Median
14
improved survival. Clinical trials with anti-VISTA mAbs are recurrence-free survival was 46.5% in patients treated with
ongoing and include a phase I study with JNJ-61610588, a fully ipilimumab versus 34.8% for patients who received placebo,
human IgG1 anti-VISTA mAb (ClinicalTrials.gov). which led to the FDA approval of ipilimumab in the adjuvant
17
setting. Ipilimumab is approved in the metastatic as well as
IMMUNE CHECKPOINT THERAPY WITH in the adjuvant setting for the treatment of melanoma. Impor-
tantly, to provide an accurate estimate of long-term survival
CLINICAL BENEFIT IN SOLID TUMORS AND following treatment with ipilimumab, a pooled analysis was
HEMATOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES performed from 10 prospective and two retrospective studies,
including the two phase III trials mentioned above. The data
Melanoma demonstrated long-term survival of approximately 20% of
In recent years, immunotherapy has dramatically changed the patients, with survival of 10 years noted for some patients.
landscape of melanoma treatment: Since 2011, four immuno- The results were independent of ipilimumab dosing or prior
therapies have been approved by the FDA. therapy. 18