Page 1086 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1086
1050 ParT EighT Immunology of Neoplasia
often contains a translocation that fuses the E2A(TCF3) gene
Immunological and Molecular Classification of ALL on chromosome 19 with the PBX1 gene on chromosome 1.
Immunological Classification Leukemic cells that express both cytoplasmic and surface Ig
ALL subtypes are typically identified by their immunophenotype. heavy chains have been designated transitional preB-cell ALL.
They are positioned by the lymphoid developmental stage at The surface µ chains on these leukemic cells are noncovalently
which the leukemic cell appears to have been arrested (Table 78.1). associated with surrogate light chain (VpreB λ5[λ14.1]), CD79a,
and CD79b.
B-Cell Precursor Leukemias
B-cell precursor ALLs are the most common childhood leukemias.
ProB-cell ALL is characterized by expression of CD19 and CD34 CLiNiCaL PEarLS
without CD10. This is the most common leukemia of infants Mature Versus Precursor B-Cell Acute
that contains rearrangements of the MLL(KMT2A) gene on Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
chromosome 11q23. It is associated with a poor outcome.
Leukemic blast cells of early preB-cell ALL resemble normal Since the treatment of mature B-cell leukemia (the leukemic form of
B-lymphoid cell precursors. They express CD19, CD22, and Burkitt lymphoma) is vastly different from the treatment of B-cell precursor
ALL, it is critical to distinguish between the two. Burkitt leukemia is
CD79a. CD10 and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) characterized by mature B-cell phenotype and by the presence of
are detectable in 90% of cases. CD34 is detected in >75% of chromosomal translocations involving the cMyc gene (Chapter 79).
cases. Early preB-cell ALL is the most prevalent type of ALL and
is thus often called “common ALL” (cALL).
In preB-cell ALL lymphoblasts accumulate cytoplasmic Mature B-cell ALL is the leukemic form of Burkitt lymphoma
immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy chains but have no detectable surface (Chapter 79). As treatment is dramatically different from that
Igs. This subtype also expresses CD19, CD22, and CD79a. It for B-cell precursor ALL, this subtype must be specifically ruled
out as part of the immunophenotypic evaluation of ALL. Mature
B-cell ALL cells express surface Ig µ heavy chains in association
with either κ or λ light chains. In most cases, cells have L3
2 hit morphology and express CD19, CD22, and CD20. CD10 and
nd
st
1 hit mutation in cell of ALL CD23 are frequently expressed, whereas CD34 is absent.
transformed clone
T-Cell ALL
T-cell ALL is more prevalent in less affluent countries, which is
likely a reflection of a lower incidence of the common B-lineage
early childhood peak. In affluent countries, T-cell ALL occurs in
latent period 10–15% of children with ALL. It is also more common in adults.
In many treatment protocols, T-cell ALL is considered to have
a less favorable prognosis compared with B-cell precursor ALL.
In T-cell ALL, the cells express surface CD7 and cytoplasmic
-9 months Birth 3 years CD3 (cCD3) antigens. More than 90% of the T lymphoblasts
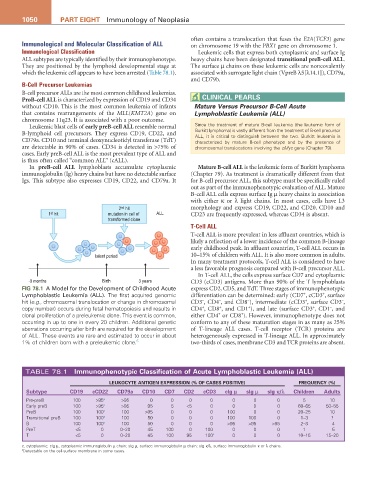
Fig 78.1 A Model for the Development of Childhood Acute express CD2, CD5, and TdT. Three stages of immunophenotypic
+
+
Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL). The first acquired genomic differentiation can be determined: early (CD7 , cCD3 , surface
−
−
−
+
−
hit (e.g., chromosomal translocation or change in chromosomal CD3 , CD4 , and CD8 ), intermediate (cCD3 , surface CD3 ,
−
+
+
+
+
copy number) occurs during fetal hematopoiesis and results in CD4 , CD8 , and CD1 ), and late (surface CD3 , CD1 , and
+
+
clonal proliferation of a preleukemic clone. This event is common, either CD4 or CD8 ). However, immunophenotype does not
occurring in up to one in every 20 children. Additional genetic conform to any of these maturation stages in as many as 25%
aberrations occurring after birth are required for the development of T-lineage ALL cases. T-cell receptor (TCR) proteins are
of ALL. These events are rare and estimated to occur in about heterogeneously expressed in T-lineage ALL. In approximately
5
1% of children born with a preleukemic clone. two-thirds of cases, membrane CD3 and TCR proteins are absent.
TABLE 78.1 immunophenotypic Classification of acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (aLL)
LEUKOCYTE aNTigEN EXPrESSiON (% OF CaSES POSiTiVE) FrEQUENCY (%)
Subtype CD19 cCD22 CD79a CD10 CD7 CD2 cCD3 cig µ sig µ sig κ/λ Children adults
Pre-preB 100 >95 a >95 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5 10
Early preB 100 >95 a >95 95 5 <5 0 0 0 0 60–65 50–55
PreB 100 100 a 100 >95 0 0 0 100 0 0 20–25 10
Transitional preB 100 100 a 100 50 0 0 0 100 100 0 1–3 ?
B 100 100 a 100 50 0 0 0 >95 >95 >95 2–3 4
PreT <5 0 0–20 45 100 0 100 0 0 0 1 5
T <5 0 0–20 45 100 95 100 a 0 0 0 10–15 15–20
c, cytoplasmic; cIg µ, cytoplasmic immunoglobulin µ chain; sIg µ, surface immunoglobulin µ chain; sIg κ/λ, surface immunoglobulin κ or λ chains.
a Detectable on the cell-surface membrane in some cases.