Page 1133 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1133
CHaPter 81 Concepts and Challenges in Organ Transplantation 1099
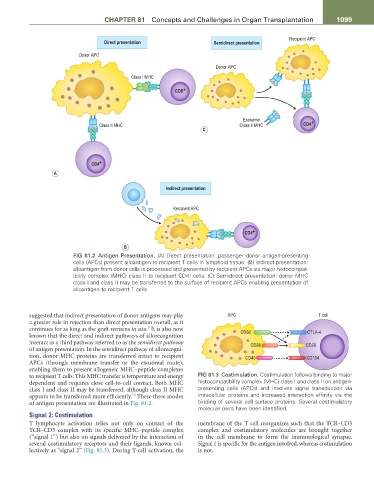
Recipient APC
Direct presentation Semidirect presentation
Donor APC
Donor APC
Class I MHC
CD8 +
Exosome +
Class II MHC Class II MHC CD4
C
CD4 +
A
Indirect presentation
Recipient APC
CD4 +
B
FiG 81.2 Antigen Presentation. (A) Direct presentation: passenger donor antigen-presenting
cells (APCs) present alloantigen to recipient T cells in lymphoid tissue. (B) Indirect presentation:
alloantigen from donor cells is processed and presented by recipient APCs via major histocompat-
ibility complex (MHC) class II to recipient CD4 cells. (C) Semidirect presentation: donor MHC
+
class I and class II may be transferred to the surface of recipient APCs enabling presentation of
alloantigen to recipient T cells.
suggested that indirect presentation of donor antigens may play APC T cell
a greater role in rejection than direct presentation overall, as it
9
continues for as long as the graft remains in situ. It is also now CD80 CTLA-4
known that the direct and indirect pathways of allorecognition
interact as a third pathway referred to as the semidirect pathway CD86 CD28
of antigen presentation. In the semidirect pathway of allorecogni-
tion, donor MHC proteins are transferred intact to recipient CD40 CD154
APCs (through membrane transfer or the exosomal route),
enabling them to present allogeneic MHC–peptide complexes
to recipient T cells. This MHC transfer is temperature and energy FiG 81.3 Costimulation. Costimulation follows binding to major
dependent and requires close cell-to-cell contact. Both MHC histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II on antigen-
class I and class II may be transferred, although class II MHC presenting cells (APCs) and involves signal transduction via
10
appears to be transferred more efficiently. These three modes intracellular proteins and increased interaction affinity via the
of antigen presentation are illustrated in Fig. 81.2. binding of several cell surface proteins. Several costimulatory
molecule pairs have been identified.
Signal 2: Costimulation
T lymphocyte activation relies not only on contact of the membrane of the T cell reorganizes such that the TCR–CD3
TCR–CD3 complex with its specific MHC–peptide complex complex and costimulatory molecules are brought together
(“signal 1”) but also on signals delivered by the interaction of in the cell membrane to form the immunological synapse.
several costimulatory receptors and their ligands, known col- Signal 1 is specific for the antigen involved, whereas costimulation
lectively as “signal 2” (Fig. 81.3). During T-cell activation, the is not.