Page 1159 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1159
1124 Part NINE Transplantation
More limited data are available about reconstitution of NK
−
3000 cell function. In patients with NK SCID, NK cells are often the
first cells to appear after haploidentical HSCT. Lower NK-cell
counts are observed at long-term follow-up after HSCT in patients
CD3 + lymphocytes/µl 2000 with γc or JAK3 defects.
2500
HSCT for Combined Immunodeficiencies Other Than SCID
1500
The Primary Immune Deficiency Treatment Consortium (PIDTC)
related HLA-identical
1000
MUD
forms of combined immunodeficiency characterized by residual
Related HLA-mismatched has established criteria to distinguish typical SCID from other
500 (although lower than normal) T cell–mediated immunity.
23
Omenn syndrome is a fatal disorder, unless treated with HSCT.
0
0 1 3 6 12 15 24 Satisfactory results have been obtained with transplantation from
related HLA-identical donors, but less so from haploidentical
Months since HSCT donors. However, an improved outcome has been observed in
+
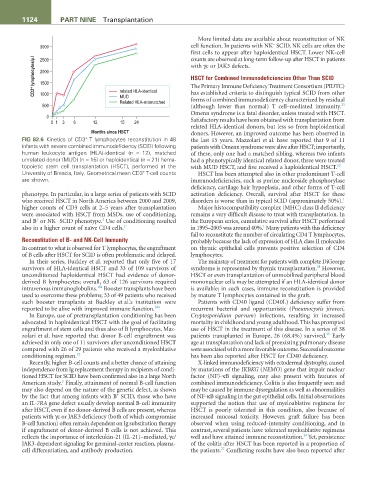
FIG 82.6 Kinetics of CD3 T lymphocytes reconstitution in 48 the last 15 years. Mazzolari et al. have reported that 9 of 11
infants with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) following patients with Omenn syndrome were alive after HSCT; importantly,
human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-identical (n = 12), matched of these, only one had a matched sibling, whereas two infants
unrelated donor (MUD) (n = 15) or haploidentical (n = 21) hema- had a phenotypically identical related donor, three were treated
topoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), performed at the with MUD HSCT, and five received a haploidentical HSCT. 22
+
University of Brescia, Italy. Geometrical mean CD3 T-cell counts HSCT has been attempted also in other predominant T-cell
are shown. immunodeficiencies, such as purine nucleoside phosphorylase
deficiency, cartilage hair hypoplasia, and other forms of T-cell
phenotype. In particular, in a large series of patients with SCID activation deficiency. Overall, survival after HSCT for these
who received HSCT in North America between 2000 and 2009, disorders is worse than in typical SCID (approximately 50%). 1
higher counts of CD3 cells at 2–5 years after transplantation Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II deficiency
were associated with HSCT from MSDs, use of conditioning, remains a very difficult disease to treat with transplantation. In
+
−
2
and B or NK SCID phenotype. Use of conditioning resulted the European series, cumulative survival after HSCT performed
1
also in a higher count of naïve CD4 cells. 2 in 1995–2005 was around 40%. Many patients with this deficiency
fail to reconstitute the number of circulating CD4 T lymphocytes,
Reconstitution of B- and NK-Cell Immunity probably because the lack of expression of HLA class II molecules
In contrast to what is observed for T lymphocytes, the engraftment on thymic epithelial cells prevents positive selection of CD4
of B cells after HSCT for SCID is often problematic and delayed. lymphocytes.
In their series, Buckley et al. reported that only five of 17 The mainstay of treatment for patients with complete DiGeorge
24
survivors of HLA-identical HSCT and 33 of 109 survivors of syndrome is represented by thymic transplantation. However,
unconditioned haploidentical HSCT had evidence of donor- HSCT or even transplantation of unmobilized peripheral blood
derived B lymphocytes; overall, 63 of 126 survivors required mononuclear cells may be attempted if an HLA-identical donor
18a
intravenous immunoglobulins. Booster transplants have been is available; in such cases, immune reconstitution is provided
used to overcome these problems; 33 of 49 patients who received by mature T lymphocytes contained in the graft.
such booster transplants at Buckley et al.’s institution were Patients with CD40 ligand (CD40L) deficiency suffer from
reported to be alive with improved immune function. 18a recurrent bacterial and opportunistic (Pneumocystis jiroveci,
In Europe, use of pretransplantation conditioning has been Cryptosporidium parvum) infections, resulting in increased
advocated in haploidentical HSCT with the goal of facilitating mortality in childhood and young adulthood. This has prompted
engraftment of stem cells and thus also of B lymphocytes. Maz- use of HSCT in the treatment of this disease. In a series of 38
25
zolari et al. have reported that donor B-cell engraftment was patients transplanted in Europe, 26 (68.4%) survived. Early
achieved in only one of 11 survivors after unconditioned HSCT age at transplantation and lack of preexisting pulmonary disease
compared with 26 of 29 patients who received a myeloablative were associated with a more favorable outcome. Successful outcome
conditioning regimen. 22 has been also reported after HSCT for CD40 deficiency.
Recently, higher B-cell counts and a better chance of attaining X-linked immunodeficiency with ectodermal dystrophy, caused
independence from Ig replacement therapy in recipients of condi- by mutations of the IKBKG (NEMO) gene that impair nuclear
tioned HSCT for SCID have been confirmed also in a large North factor (NF)-κB signaling, may also present with features of
2
American study. Finally, attainment of normal B-cell function combined immunodeficiency. Colitis is also frequently seen and
may also depend on the nature of the genetic defect, as shown may be caused by immune dysregulation as well as abnormalities
+
by the fact that among infants with B SCID, those who have of NF-κB signaling in the gut epithelial cells. Initial observations
an IL-7RA gene defect usually develop normal B-cell immunity supported the notion that use of myeloablative regimens for
after HSCT, even if no donor-derived B cells are present, whereas HSCT is poorly tolerated in this condition, also because of
patients with γc or JAK3 deficiency (both of which compromise increased mucosal toxicity. However, graft failure has been
B-cell function) often remain dependent on Ig substitution therapy observed when using reduced-intensity conditioning, and in
if engraftment of donor-derived B cells is not achieved. This contrast, several patients have tolerated myeloablative regimens
26
reflects the importance of interleukin-21 (IL-21)–mediated, γc/ well and have attained immune reconstitution. Yet, persistence
JAK3-dependent signaling for germinal-center reaction, plasma- of the colitis after HSCT has been reported in a proportion of
27
cell differentiation, and antibody production. the patients. Conflicting results have also been reported after