Page 1160 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1160
CHaPtEr 82 Immune Reconstitution Therapy for Immunodeficiency 1125
HSCT in patients with hypermorphic mutations of the IKBA 1
gene, another cause of combined immune deficiency with 0.9
ectodermal dystrophy. 28 0.8
Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome 0.7
Bone marrow transplantation for correction of WAS was 0.6
attempted as early as 1968, with partial success. Full correction Survival 0.5
following HSCT was first reported in 1978 when a more robust 0.4
conditioning regimen was used. Since then, results of related 0.3
HLA-identical HSCT in WAS have been consistently good, with
continuous improvement in recent years, and excellent results 0.2
have been also achieved with HSCT from MUDs. A multiinsti- 0.1
tutional study of 194 patients with WAS treated with HSCT 0
showed an overall survival of 84%, and a 5-year survival as high 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000
29
as 89.1% for transplantations performed since year 2000. For Days following HCT
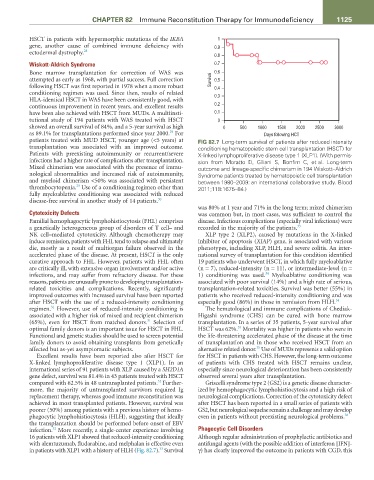
patients treated with MUD HSCT, younger age (<5 years) at FIG 82.7 Long-term survival of patients after reduced intensity
transplantation was associated with an improved outcome. conditioning hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for
Patients with preexisting autoimmunity or recurrent/severe X-linked lymphoproliferative disease type 1 (XLP1). (With permis-
infections had a higher rate of complications after transplantation. sion from Moratto D, Giliani S, Bonfim C, et al. Long-term
Mixed chimerism was associated with the presence of immu- outcome and lineage-specific chimerism in 194 Wiskott–Aldrich
nological abnormalities and increased risk of autoimmunity, Syndrome patients treated by hematopoietic cell transplantation
and myeloid chimerism <50% was associated with persistent between 1980–2009: an international collaborative study. Blood
29
thrombocytopenia. Use of a conditioning regimen other than 2011;118:1675–84.)
fully myeloablative conditioning was associated with reduced
disease-free survival in another study of 14 patients. 30
was 80% at 1 year and 71% in the long term; mixed chimerism
Cytotoxicity Defects was common but, in most cases, was sufficient to control the
Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL) comprises disease. Infectious complications (especially viral infections) were
a genetically heterogeneous group of disorders of T cell– and recorded in the majority of the patients. 33
NK cell–mediated cytotoxicity. Although chemotherapy may XLP type 2 (XLP2), caused by mutations in the X-linked
induce remission, patients with FHL tend to relapse and ultimately inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) gene, is associated with various
die, mostly as a result of multiorgan failure observed in the phenotypes, including XLP, HLH, and severe colitis. An inter-
accelerated phase of the disease. At present, HSCT is the only national survey of transplantation for this condition identified
curative approach to FHL. However, patients with FHL often 19 patients who underwent HSCT, in which fully myeloablative
are critically ill, with extensive organ involvement and/or active (n = 7), reduced-intensity (n = 11), or intermediate-level (n =
34
infections, and may suffer from refractory disease. For these 1) conditioning was used. Myeloablative conditioning was
reasons, patients are unusually prone to developing transplantation- associated with poor survival (14%) and a high rate of serious,
related toxicities and complications. Recently, significantly transplantation-related toxicities. Survival was better (55%) in
improved outcomes with increased survival have been reported patients who received reduced-intensity conditioning and was
after HSCT with the use of a reduced-intensity conditioning especially good (86%) in those in remission from HLH. 34
31
regimen. However, use of reduced-intensity conditioning is The hematological and immune complications of Chediak-
associated with a higher risk of mixed and recipient chimerism Higashi syndrome (CHS) can be cured with bone marrow
31
(65%), even for HSCT from matched donors. Selection of transplantation. In a series of 35 patients, 5-year survival after
35
optimal family donors is an important issue for HSCT in FHL. HSCT was 62%. Mortality was higher in patients who were in
Functional and genetic studies should be used to screen potential the life-threatening accelerated phase of the disease at the time
family donors to avoid obtaining transplants from genetically of transplantation and in those who received HSCT from an
35
affected but as-yet asymptomatic subjects. alternative related donor. Use of MUDs represents a valid option
Excellent results have been reported also after HSCT for for HSCT in patients with CHS. However, the long-term outcome
X-linked lymphoproliferative disease type 1 (XLP1). In an of patients with CHS treated with HSCT remains unclear,
international series of 91 patients with XLP caused by a SH2D1A especially since neurological deterioration has been consistently
gene defect, survival was 81.4% in 43 patients treated with HSCT observed several years after transplantation.
32
compared with 62.5% in 48 untransplanted patients. Further- Griscelli syndrome type 2 (GS2) is a genetic disease character-
more, the majority of untransplanted survivors required Ig ized by hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and a high risk of
replacement therapy, whereas good immune reconstitution was neurological complications. Correction of the cytotoxicity defect
achieved in most transplanted patients. However, survival was after HSCT has been reported in a small series of patients with
poorer (50%) among patients with a previous history of hemo- GS2, but neurological sequelae remain a challenge and may develop
phagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), suggesting that ideally even in patients without preexisting neurological problems. 36
the transplantation should be performed before onset of EBV
32
infection. More recently, a single-center experience involving Phagocytic Cell Disorders
16 patients with XLP1 showed that reduced-intensity conditioning Although regular administration of prophylactic antibiotics and
with alemtuzumab, fludarabine, and melphalan is effective even antifungal agents (with the possible addition of interferon [IFN]-
33
in patients with XLP1 with a history of HLH (Fig. 82.7). Survival γ) has clearly improved the outcome in patients with CGD, this