Page 1161 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1161
1126 Part NINE Transplantation
remains a severe disorder with a rather high risk of complications However, a subgroup of these patients fail to respond to G-CSF,
37
and death, especially in patients with oxidase-null phenotype. and some of them are at high risk for development of myelogenous
Therefore there has been a renewed interest in HSCT for CGD. leukemia. A retrospective multicenter study of 136 patients with
In a survey of the European experience in 1985–2000, 27 patients SCN who underwent allogeneic HSCT between 1990 and 2012
with CGD were treated with HSCT; most of them received reported a 3-year overall survival rate of 82%, with 17%
41
unmodified bone marrow from an HLA-identical sibling after transplantation-related mortality. Transplantation at a younger
myeloablative conditioning. Overall, 23 of the 27 patients were age (<10 years) and use of matched related or unrelated donors
reported to have survived, and the disease had been cured in 22 were associated with an improved outcome.
38
of them. In this study, all 18 patients who were infection-free
at the time of transplantation survived. However, a real break- Other Primary Immune Deficiencies
through in the treatment of CGD was provided by a prospective IFN-γ receptor 1 deficiency leads to severe mycobacterial
multicenter study in 56 patients with CGD, 42 of whom had infections, with a high rate of mortality early in life. Although
high-risk features, including treatment-refractory infections and HSCT should theoretically correct the disease, results have been
39
severe inflammatory complications. In this study, reduced- disappointing, with few exceptions. An international survey of
intensity conditioning (with low-dose or targeted busulfan eight transplanted patients showed that only two were in full
administration, high-dose fludarabine, and serotherapy) and remission 5 years after transplantation. The high level of IFN-γ
transplantation from matched related (n = 21) or unrelated (n in these patients inhibits engraftment of donor-derived HSCs,
= 35) donors resulted in a 2-year overall survival rate of 96% accounting for the high rejection rate. Correction of the disease
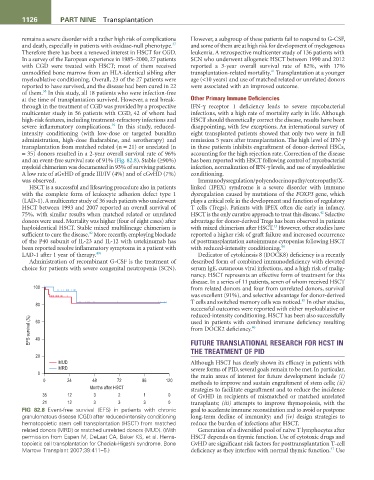
and an event-free survival rate of 91% (Fig. 82.8). Stable (≥90%) has been reported with HSCT following control of mycobacterial
myeloid chimerism was documented in 93% of surviving patients. infection, normalization of IFN-γ levels, and use of myeloablative
A low rate of aGvHD of grade III/IV (4%) and of cGvHD (7%) conditioning.
was observed. Immunodysregulation/polyendocrinopathy/enteropathy/X-
HSCT is a successful and lifesaving procedure also in patients linked (IPEX) syndrome is a severe disorder with immune
with the complete form of leukocyte adhesion defect type 1 dysregulation caused by mutations of the FOXP3 gene, which
(LAD-1). A multicenter study of 36 such patients who underwent plays a critical role in the development and function of regulatory
HSCT between 1993 and 2007 reported an overall survival of T cells (Tregs). Patients with IPEX often die early in infancy.
42
75%, with similar results when matched related or unrelated HSCT is the only curative approach to treat this disease. Selective
donors were used. Mortality was higher (four of eight cases) after advantage for donor-derived Tregs has been observed in patients
43
haploidentical HSCT. Stable mixed multilineage chimerism is with mixed chimerism after HSCT. However, other studies have
40
sufficient to cure the disease. More recently, employing blockade reported a higher risk of graft failure and increased occurrence
of the P40 subunit of IL-23 and IL-12 with ustekinumab has of posttransplantation autoimmune cytopenias following HSCT
been reported resolve inflammatory symptoms in a patient with with reduced-intensity conditioning. 44
LAD-1 after 1 year of therapy. 40a Dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (DOCK8) deficiency is a recently
Administration of recombinant G-CSF is the treatment of described form of combined immunodeficiency with elevated
choice for patients with severe congenital neutropenia (SCN). serum IgE, cutaneous viral infections, and a high risk of malig-
nancy. HSCT represents an effective form of treatment for this
disease. In a series of 11 patients, seven of whom received HSCT
100 from related donors and four from unrelated donors, survival
was excellent (91%), and selective advantage for donor-derived
45
80 T cells and switched memory cells was noticed. In other studies,
successful outcomes were reported with either myeloablative or
reduced-intensity conditioning. HSCT has been also successfully
EFS survival (%) 60 used in patients with combined immune deficiency resulting
46
from DOCK2 deficiency.
40
FUTURE TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH FOR HCST IN
THE TREATMENT OF PID
20
MUD Although HSCT has clearly shown its efficacy in patients with
MRD severe forms of PID, several goals remain to be met. In particular,
0 the main areas of interest for future development include (i)
0 24 48 72 96 120 methods to improve and sustain engraftment of stem cells; (ii)
Months after HSCT strategies to facilitate engraftment and to reduce the incidence
35 12 3 2 1 0 of GvHD in recipients of mismatched or matched unrelated
21 12 3 3 3 0 transplants; (iii) attempts to improve thymopoiesis, with the
FIG 82.8 Event-free survival (EFS) in patients with chronic goal to accelerate immune reconstitution and to avoid or postpone
granulomatous disease (CGD) after reduced-intensity conditioning long-term decline of immunity; and (iv) design strategies to
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) from matched reduce the burden of infections after HSCT.
related donors (MRD) or matched unrelated donors (MUD). (With Generation of a diversified pool of naïve T lymphocytes after
permission from Eapen M, DeLaat CA, Baker KS, et al. Hema- HSCT depends on thymic function. Use of cytotoxic drugs and
topoietic cell transplantation for Chediak-Higashi syndrome. Bone GvHD are significant risk factors for posttransplantation T-cell
47
Marrow Transplant 2007;39:411–5.) deficiency as they interfere with normal thymic function. Use