Page 1194 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1194
CHaPTEr 85 Gene Therapy for Primary Immune Deficiency Diseases 1159
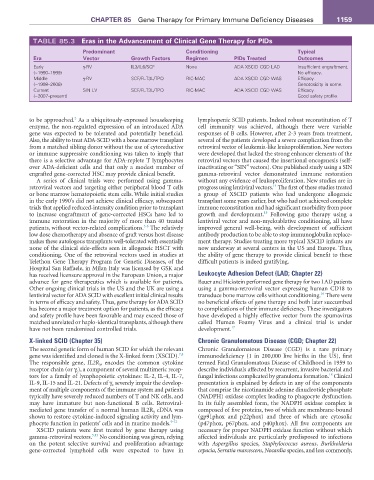
TABLE 85.3 Eras in the advancement of Clinical Gene Therapy for PIDs
Predominant Conditioning Typical
Era Vector Growth Factors regimen PIDs Treated Outcomes
Early γ-RV IL3/IL6/SCF None ADA XSCID CGD LAD Insufficient engraftment.
(~1990–1999) No efficacy.
Middle γ-RV SCF/FLT3L/TPO RIC-MAC ADA XSCID CGD WAS Efficacy.
(~1998–2006) Genotoxicity in some.
Current SIN LV SCF/FLT3L/TPO RIC-MAC ADA XSCID CGD WAS Efficacy.
(~2007–present) Good safety profile.
2
to be approached. As a ubiquitously-expressed housekeeping lymphopenic SCID patients. Indeed robust reconstitution of T
enzyme, the non-regulated expression of an introduced ADA cell immunity was achieved, although there were variable
gene was expected to be tolerated and potentially beneficial. responses of B cells. However, after 2-3 years from treatment,
Also, the ability to treat ADA-SCID with a bone marrow transplant several of the patients developed a severe complication from the
from a matched sibling donor without the use of cytoreductive retroviral vector of leukemia-like leukoproliferation. New vectors
or immune suppressive conditioning was taken to imply that were developed that lacked the strong enhancer elements of the
there is a selective advantage for ADA-replete T lymphocytes retroviral vectors that caused the insertional oncogenesis (self-
over ADA-deficient cells and that only a modest number of inactivating or “SIN” vectors). One published study using a SIN
engrafted gene-corrected HSC may provide clinical benefit. gamma-retroviral vector demonstrated immune restoration
A series of clinical trials were performed using gamma- without any evidence of leukoproliferation. New studies are in
14
retroviral vectors and targeting either peripheral blood T cells progress using lentiviral vectors. The first of these studies treated
or bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells. While initial studies a group of XSCID patients who had undergone allogeneic
in the early 1990’s did not achieve clinical efficacy, subsequent transplant some years earlier, but who had not achieved complete
trials that applied reduced-intensity condition prior to transplant immune reconstitution and had significant morbidity from poor
15
to increase engraftment of gene-corrected HSCs have led to growth and development. Following gene therapy using a
immune restoration in the majority of more than 40 treated lentiviral vector and non-myeloablative conditioning, all have
3-6
patients, without vector-related complications. The relatively improved general well-being, with development of sufficient
low dose chemotherapy and absence of graft versus host disease antibody production to be able to stop immunoglobulin replace-
makes these autologous transplants well-tolerated with essentially ment therapy. Studies treating more typical XSCID infants are
none of the clinical side-effects seen in allogeneic HSCT with now underway at several centers in the US and Europe. Thus,
conditioning. One of the retroviral vectors used in studies at the ability of gene therapy to provide clinical benefit to these
Telethon Gene Therapy Program for Genetic Diseases, of the difficult patients is indeed gratifying.
Hospital San Raffaele, in Milan Italy was licensed by GSK and
has received licensure approval in the European Union, a major Leukocyte Adhesion Defect (LAD; Chapter 22)
advance for gene therapeutics which is available for patients. Bauer and Hickstein performed gene therapy for two LAD patients
Other ongoing clinical trials in the US and the UK are using a using a gamma-retroviral vector expressing human CD18 to
16
lentiviral vector for ADA SCID with excellent initial clinical results transduce bone marrow cells without conditioning. There were
in terms of efficacy and safety. Thus, gene therapy for ADA SCID no beneficial effects of gene therapy and both later succumbed
has become a major treatment option for patients, as the efficacy to complications of their immune deficiency. These investigators
and safety profile have been favorable and may exceed those of have developed a highly effective vector from the spumavirus
matched unrelated or haplo-identical transplants, although there called Human Foamy Virus and a clinical trial is under
have not been randomized controlled trials. development. 17
X-linked SCID (Chapter 35) Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD; Chapter 22)
The second genetic form of human SCID for which the relevant Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD) is a rare primary
7,8
gene was identified and cloned is the X-linked form (XSCID). immunodeficiency (1 in 200,000 live births in the US), first
The responsible gene, IL2R γ , encodes the common cytokine termed Fatal Granulomatous Disease of Childhood in 1959 to
receptor chain (or γ c ), a component of several multimeric recep- describe individuals affected by recurrent, invasive bacterial and
18
tors for a family of lymphopoietic cytokines: IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, fungal infections complicated by granuloma formation. Clinical
IL-9, IL-15 and IL-21. Defects of γ c severely impair the develop- presentation is explained by defects in any of the components
ment of multiple components of the immune system and patients that comprise the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
typically have severely reduced numbers of T and NK cells, and (NADPH) oxidase complex leading to phagocyte dysfunction.
may have immature but non-functional B cells. Retroviral- In its fully assembled form, the NADPH oxidase complex is
mediated gene transfer of a normal human IL2R γ cDNA was composed of five proteins, two of which are membrane-bound
shown to restore cytokine-induced signaling activity and lym- (gp91phox and p22phox) and three of which are cytosolic
phocyte function in patients’ cells and in murine models. 9-12 (p47phox, p67phox, and p40phox). All five components are
XSCID patients were first treated by gene therapy using necessary for proper NADPH oxidase function without which
5,13
gamma-retroviral vectors. No conditioning was given, relying affected individuals are particularly predisposed to infections
on the potent selective survival and proliferation advantage with Aspergillus species, Staphylococcus aureus, Burkholderia
gene-corrected lymphoid cells were expected to have in cepacia, Serratia marcescens, Nocardia species, and less commonly,