Page 1229 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1229
1192 PART TEN Prevention and Therapy of Immunological Diseases
kinases. These mAbs include and target the designated RTK: identifying mutations in patients with immunodeficiencies.
bevacizumab (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Specifically, mutation of JAK3 results in a severe combined
[VEGFR]), ranibizumab (VEGFR), cetuximab (epidermal growth immune deficiency (SCID), characterized by an almost complete
factor receptor [EGFR]), pertuzumab (human epidermal growth absence of T cells and NK cells with defective B cells. This
factor receptor [HER]), and trastuzumab (HER2/neu). phenocopies deficiency of the cognate receptor that associates
with JAK3, the IL-2 receptor common γ chain, cγc (encoded by
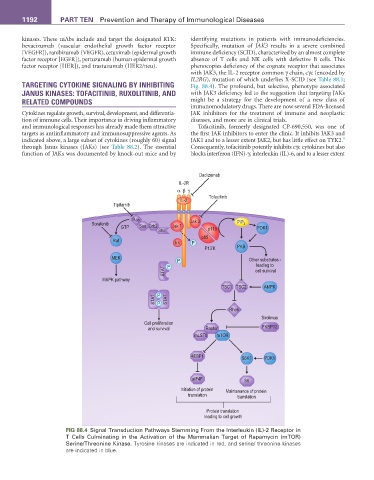
IL2RG), mutation of which underlies X-SCID (see Table 88.1;
TARGETING CYTOKINE SIGNALING BY INHIBITING Fig. 88.4). The profound, but selective, phenotype associated
JANUS KINASES: TOFACITINIB, RUXOLITINIB, AND with JAK3 deficiency led to the suggestion that targeting JAKs
RELATED COMPOUNDS might be a strategy for the development of a new class of
immunomodulatory drugs. There are now several FDA-licensed
Cytokines regulate growth, survival, development, and differentia- JAK inhibitors for the treatment of immune and neoplastic
tion of immune cells. Their importance in driving inflammatory diseases, and more are in clinical trials.
and immunological responses has already made them attractive Tofacitinib, formerly designated CP-690,550, was one of
targets as antiinflammatory and immunosuppressive agents. As the first JAK inhibitors to enter the clinic. It inhibits JAK3 and
9
indicated above, a large subset of cytokines (roughly 60) signal JAK1 and to a lesser extent JAK2, but has little effect on TYK2.
through Janus kinases (JAKs) (see Table 88.2). The essential Consequently, tofacitinib potently inhibits cγc cytokines but also
function of JAKs was documented by knock-out mice and by blocks interferon (IFN)-γ, interleukin (IL)-6, and to a lesser extent
Daclizumab
IL-2R
αβ γ
Tofacitinib
IL-2
Tipifarnib
Ras Jak 3
Sorafenib PIP 3
GTP Sos Grb2 Jak 1 PDK1
Shc p110
p85
Raf Ick P
P13’K PKB
MEK
P Other substrates -
leading to
STAT P cell survival
MAPK pathway
TSC1 TSC2 AMPK
STAT P P STAT
Rheb
Sirolimus
Cell proliferation
and survival Raptor FKBP12
mLST8 mTOR
4EBP1 S6K1 PDK1
eIF4F S6
Initiation of protein Maintenance of protein
translation translation
Protein translation
leading to cell growth
FIG 88.4 Signal Transduction Pathways Stemming From the Interleukin (IL)-2 Receptor in
T Cells Culminating in the Activation of the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR)
Serine/Threonine Kinase. Tyrosine kinases are indicated in red, and serine/ threonine kinases
are indicated in blue.