Page 1260 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1260
CHaPter 90 Vaccines 1221
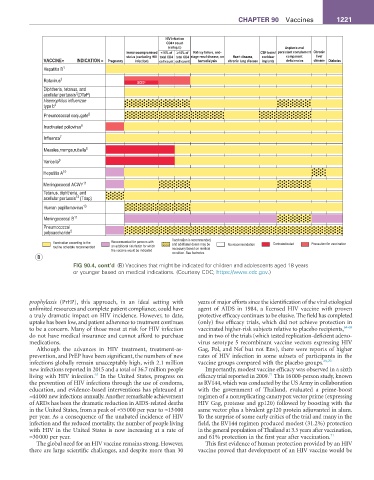
HIV infection
CD4+ count
µ
(cells/ L) Asplenia and
Immunocompromised <15% of ≥15% of Kidney failure, end- CSF leaks/ persistent complement Chronic
status (excluding HIV total CD4 total CD4 stage renal disease, on Heart disease, cochlear component liver
VACCINE INDICATION Pregnancy infection) cell count cell count hemodialysis chronic lung disease implants deficiencies disease Diabetes
Hepatitis B 1
Rotavirus 2 SCID*
Diphtheria, tetanus, and
3
acellular pertussis (DTaP)
Haemophilus influenzae
type b 4
Pneumococcal conjugate 5
Inactivated poliovirus 6
Influenza 7
Measles,mumps,rubella 8
Varicella 9
Hepatitis A 10
Meningococcal ACWY 11
Tetanus, diphtheria, and
12
acellular pertussis (Tdap)
Human papillomavirus 13
Meningococcal B 11
Pneumococcal
polysaccharide 5
Vaccination is recommended,
Vaccination according to the Recommended for persons with and additional doses may be No recommendation Contraindicated Precaution for vaccination
routine schedule recommended an additional risk factor for which necessary based on medical
the vaccine would be indicated
condition. See footnotes.
B
FIG 90.4, cont’d (B) Vaccines that might be indicated for children and adolescents aged 18 years
or younger based on medical indications. (Courtesy CDC; https://www.cdc.gov.)
prophylaxis (PrEP), this approach, in an ideal setting with years of major efforts since the identification of the viral etiological
unlimited resources and complete patient compliance, could have agent of AIDS in 1984, a licensed HIV vaccine with proven
a truly dramatic impact on HIV incidence. However, to date, protective efficacy continues to be elusive. The field has completed
uptake has been low, and patient adherence to treatment continues (only) five efficacy trials, which did not achieve protection in
to be a concern. Many of those most at risk for HIV infection vaccinated higher-risk subjects relative to placebo recipients, 64-68
do not have medical insurance and cannot afford to purchase and in two of the trials (which tested replication-deficient adeno-
medications. virus serotype 5 recombinant vaccine vectors expressing HIV
Although the advances in HIV treatment, treatment-as- Gag, Pol, and Nef but not Env), there were reports of higher
prevention, and PrEP have been significant, the numbers of new rates of HIV infection in some subsets of participants in the
infections globally remain unacceptably high, with 2.1 million vaccine groups compared with the placebo groups. 69,70
new infections reported in 2015 and a total of 36.7 million people Importantly, modest vaccine efficacy was observed in a sixth
63
71
living with HIV infection. In the United States, progress on efficacy trial reported in 2009. This 16 000-person study, known
the prevention of HIV infections through the use of condoms, as RV144, which was conducted by the US Army in collaboration
education, and evidence-based interventions has plateaued at with the government of Thailand, evaluated a prime-boost
≈44 000 new infections annually. Another remarkable achievement regimen of a nonreplicating canarypox vector prime (expressing
of ARDs has been the dramatic reduction in AIDS-related deaths HIV Gag, protease and gp120) followed by boosting with the
in the United States, from a peak of ≈55 000 per year to ≈13 000 same vector plus a bivalent gp120 protein adjuvanted in alum.
per year. As a consequence of the unabated incidence of HIV To the surprise of some early critics of the trial and many in the
infection and the reduced mortality, the number of people living field, the RV144 regimen produced modest (31.2%) protection
with HIV in the United States is now increasing at a rate of in the general population of Thailand at 3.5 years after vaccination,
≈30 000 per year. and 61% protection in the first year after vaccination. 71
The global need for an HIV vaccine remains strong. However, This first evidence of human protection provided by an HIV
there are large scientific challenges, and despite more than 30 vaccine proved that development of an HIV vaccine would be