Page 1258 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1258
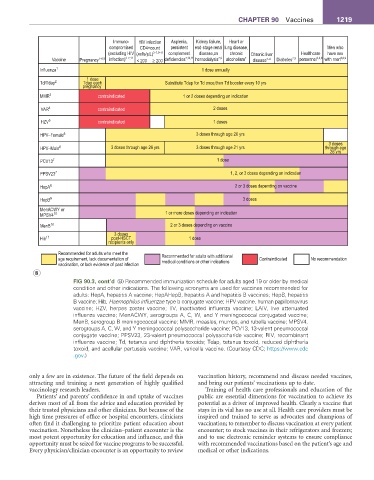
CHaPter 90 Vaccines 1219
Immuno- HIV infection Asplenia, Kidney failure, Heart or
compromised CD4+count persistent end-stage renal lung disease, Men who
(excluding HIV (xells/µL) 3–7,9–11 complement disease,on chronic Chronic liver Healthcare have sex
Vaccine Pregnancy 1–6,9 infection) 3–7,11 < 200 ≥ 200 deficiencies 7,10,11 hemodialysis 7,9 alcoholism 7 disease 7–9 Diabetes 7,9 personnel 3,4,9 with men 6,8,9
Influenza 1 1 dose annually
1 dose
Td/Tdap 2 Tdap each Substitute Tdap for Td once,then Td booster every 10 yrs
pregnancy
MMR 3 contraindicated 1 or 2 doses depending on indication
VAR 4 contraindicated 2 doses
HZV 5 contraindicated 1 doses
HPV–Female 6 3 doses through age 26 yrs
3 doses
HPV–Male 6 3 doses through age 26 yrs 3 doses through age 21 yrs through age
26 yrs
PCV13 7 1 dose
PPSV23 7 1, 2, or 3 doses depending on indication
HepA 8 2 or 3 doses depending on vaccine
HepB 9 3 doses
MenACWY or
MPSV4 10 1 or more doses depending on indication
MenB 10 2 or 3 doses depending on vaccine
3 doses
Hib 11 post-HSCT 1 dose
recipients only
Recommended for adults who meet the Recommended for adults with additional
age requirement, lack documentation of medical conditions or other indications Contraindicated No recommendation
vaccination, or lack evidence of past infection
B
FIG 90.3, cont’d (B) Recommended immunization schedule for adults aged 19 or older by medical
condition and other indications. The following acronyms are used for vaccines recommended for
adults: HepA, hepatitis A vaccine; HepAHepB, hepatitis A and hepatitis B vaccines; HepB, hepatitis
B vaccine; Hib, Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine; HPV vaccine, human papillomavirus
vaccine; HZV, herpes zoster vaccine; IIV, inactivated influenza vaccine; LAIV, live attenuated
influenza vaccine; MenACWY, serogroups A, C, W, and Y meningococcal conjugated vaccine;
MenB, serogroup B meningococcal vaccine; MMR, measles, mumps, and rubella vaccine; MPSV4,
serogroups A, C, W, and Y meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine; PCV13, 13-valent pneumococcal
conjugate vaccine; PPSV23, 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine; RIV, recombinant
influenza vaccine; Td, tetanus and diphtheria toxoids; Tdap, tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria
toxoid, and acellular pertussis vaccine; VAR, varicella vaccine. (Courtesy CDC; https://www.cdc
.gov.)
only a few are in existence. The future of the field depends on vaccination history, recommend and discuss needed vaccines,
attracting and training a next generation of highly qualified and bring our patients’ vaccinations up to date.
vaccinology research leaders. Training of health care professionals and education of the
Patients’ and parents’ confidence in and uptake of vaccines public are essential dimensions for vaccination to achieve its
derives most of all from the advice and education provided by potential as a driver of improved health. Clearly a vaccine that
their trusted physicians and other clinicians. But because of the stays in its vial has no use at all. Health care providers must be
high time pressures of office or hospital encounters, clinicians inspired and trained to serve as advocates and champions of
often find it challenging to prioritize patient education about vaccination; to remember to discuss vaccination at every patient
vaccination. Nonetheless the clinician–patient encounter is the encounter; to stock vaccines in their refrigerators and freezers;
most potent opportunity for education and influence, and this and to use electronic reminder systems to ensure compliance
opportunity must be seized for vaccine programs to be successful. with recommended vaccinations based on the patient’s age and
Every physician/clinician encounter is an opportunity to review medical or other indications.