Page 127 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 127
110 ParT ONE Principles of Immune Response
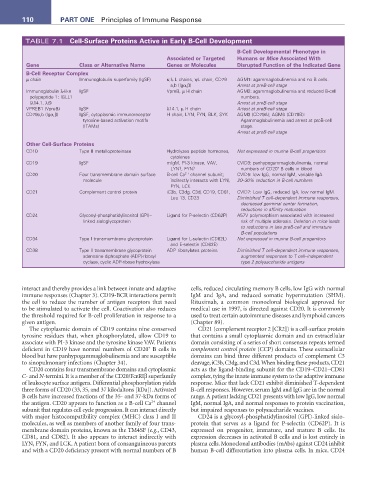
TABLE 7.1 Cell-Surface Proteins active in Early B-Cell Development
B-Cell Developmental Phenotype in
associated or Targeted Humans or Mice associated With
Gene Class or alternative Name Genes or Molecules Disrupted Function of the Indicated Gene
B-Cell receptor Complex
µ chain Immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) κ,λ L chains, ψL chain, CD79 AGM1: agammaglobulinemia and no B cells.
a,b (Igα,β) Arrest at preB-cell stage
Immunoglobulin λ-like IgSF VpreB, µ H chain AGM2: agammaglobulinemia and reduced B-cell
polypeptide 1; IGLL1 numbers.
(λ14.1, λ5) Arrest at preB-cell stage
VPREB1 (VpreB) IgSF λ14.1, µ H chain Arrest at preB-cell stage
CD79a,b (Igα,β) IgSF, cytoplasmic immunoreceptor H chain, LYN, FYN, BLK, SYK AGM3 (CD79A); AGM6 (CD79B):
tyrosine-based activation motifs Agammaglobulinemia and arrest at proB-cell
(ITAMs) stage.
Arrest at proB-cell stage
Other Cell-Surface Proteins
CD10 Type II metalloproteinase Hydrolyzes peptide hormones, Not expressed in murine B-cell progenitors
cytokines
CD19 IgSF mIgM, PI-3 kinase, VAV, CVID3: panhypogammaglobulinemia, normal
+
LYN?, FYN? numbers of CD20 B cells in blood
2 +
CD20 Four transmembrane domain surface B-cell Ca channel subunit; CVID5: low IgG, normal IgM, variable IgA
molecule indirectly interacts with LYN, 20–30% reduction in B-cell numbers
FYN, LCK
CD21 Complement control protein iC3b, C3dg, C3d, CD19, CD81, CVID7: Low IgG, reduced IgA, low normal IgM.
Leu 13, CD23 Diminished T cell–dependent immune responses,
decreased germinal center formation,
reductions in affinity maturation
CD24 Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI)– Ligand for P-selectin (CD62P) A57V polymorphism associated with increased
linked sialoglycoprotein risk of multiple sclerosis. Deletion in mice leads
to reductions in late preB-cell and immature
B-cell populations
CD34 Type I transmembrane glycoprotein Ligand for L-selectin (CD62L) Not expressed in murine B-cell progenitors
and E-selectin (CD62E)
CD38 Type II transmembrane glycoprotein ADP ribosylates proteins Diminished T cell–dependent immune responses,
adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribosyl augmented responses to T cell–independent
cyclase, cyclic ADP-ribose hydroxylase type 2 polysaccharide antigens
interact and thereby provides a link between innate and adaptive cells, reduced circulating memory B cells, low IgG with normal
immune responses (Chapter 3). CD19-BCR interactions permit IgM and IgA, and reduced somatic hypermutation (SHM).
the cell to reduce the number of antigen receptors that need Rituximab, a common monoclonal biological approved for
to be stimulated to activate the cell. Coactivation also reduces medical use in 1997, is directed against CD20. It is commonly
the threshold required for B-cell proliferation in response to a used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and lymphoid cancers
given antigen. (Chapter 89).
The cytoplasmic domain of CD19 contains nine conserved CD21 (complement receptor 2 [CR2]) is a cell-surface protein
tyrosine residues that, when phosphorylated, allow CD19 to that contains a small cytoplasmic domain and an extracellular
associate with PI-3 kinase and the tyrosine kinase VAV. Patients domain consisting of a series of short consensus repeats termed
+
deficient in CD19 have normal numbers of CD20 B cells in complement control protein (CCP) domains. These extracellular
blood but have panhypogammaglobulinemia and are susceptible domains can bind three different products of complement C3
to sinopulmonary infections (Chapter 34). cleavage, iC3b, C3dg, and C3d. When binding these products, CD21
CD20 contains four transmembrane domains and cytoplasmic acts as the ligand-binding subunit for the CD19–CD21–CD81
C- and N-termini. It is a member of the CD20/FcεRIβ superfamily complex, tying the innate immune system to the adaptive immune
of leukocyte surface antigens. Differential phosphorylation yields response. Mice that lack CD21 exhibit diminished T-dependent
three forms of CD20 (33, 35, and 37 kilodaltons [kDa]). Activated B-cell responses. However, serum IgM and IgG are in the normal
B cells have increased fractions of the 35- and 37-kDa forms of range. A patient lacking CD21 presents with low IgG, low normal
2+
the antigen. CD20 appears to function as a B-cell Ca channel IgM, normal IgA, and normal responses to protein vaccination,
subunit that regulates cell cycle progression. It can interact directly but impaired responses to polysaccharide vaccines.
with major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and II CD24 is a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked sialo-
molecules, as well as members of another family of four trans- protein that serves as a ligand for P-selectin (CD62P). It is
membrane domain proteins, known as the TM4SF (e.g., CD43, expressed on progenitor, immature, and mature B cells. Its
CD81, and CD82). It also appears to interact indirectly with expression decreases in activated B cells and is lost entirely in
LYN, FYN, and LCK. A patient born of consanguineous parents plasma cells. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) against CD24 inhibit
and with a CD20 deficiency present with normal numbers of B human B-cell differentiation into plasma cells. In mice, CD24