Page 129 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 129
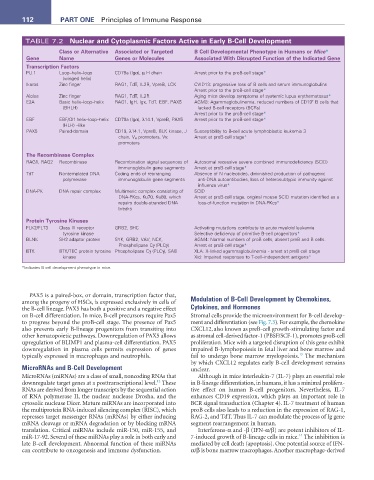
112 ParT ONE Principles of Immune Response
TABLE 7.2 Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Factors active in Early B-Cell Development
Class or alternative associated or Targeted B Cell Developmental Phenotype in Humans or Mice*
Gene Name Genes or Molecules associated With Disrupted Function of the Indicated Gene
Transcription Factors
PU.1 Loop–helix–loop CD79a (Igα), µ H chain Arrest prior to the proB-cell stage*
(winged helix)
Ikaros Zinc finger RAG1, TdT, IL2R, VpreB, LCK CVID13: progressive loss of B cells and serum immunoglobulins
Arrest prior to the proB-cell stage*
Aiolos Zinc finger RAG1, TdT, IL2R Aging mice develop symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus*
+
E2A Basic helix–loop–helix RAG1, IgH, Igκ, TdT, EBF, PAX5 AGM8: Agammaglobulinemia, reduced numbers of CD19 B cells that
(BHLH) lacked B-cell receptors (BCRs)
Arrest prior to the proB-cell stage*
EBF EBF/Olf helix–loop–helix CD79a (Igα), λ14.1, VpreB, PAX5 Arrest prior to the proB-cell stage*
(HLH) –like
PAX5 Paired-domain CD19, λ14.1, VpreB, BLK kinase, J Susceptibility to B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia 3
chain, V H promoters, Vκ Arrest at proB-cell stage*
promoters
The recombinase Complex
RAG1, RAG2 Recombinase Recombination signal sequences of Autosomal recessive severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)
immunoglobulin gene segments Arrest at proB-cell stage*
TdT Nontemplated DNA Coding ends of rearranging Absence of N nucleotides, diminished production of pathogenic
polymerase immunoglobulin gene segments anti-DNA autoantibodies, loss of heterosubtypic immunity against
influenza virus*
DNA-PK DNA repair complex Multimeric complex consisting of SCID
DNA-PKcs, Ku70, Ku80, which Arrest at proB-cell stage, original mouse SCID mutation identified as a
repairs double-stranded DNA loss-of-function mutation in DNA-PKcs*
breaks
Protein Tyrosine Kinases
FLK2/FLT3 Class III receptor GRB2, SHC Activating mutations contribute to acute myeloid leukemia
tyrosine kinase Selective deficiency of primitive B-cell progenitors*
BLNK SH2 adaptor protein SYK, GRB2, VAV, NCK, AGM4: Normal numbers of proB cells, absent preB and B cells.
Phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ) Arrest at proB-cell stage*
BTK BTK/TEC protein tyrosine Phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ), SAB XLA: X-linked agammaglobulinemia - arrest at preB cell stage
kinase Xid: Impaired responses to T-cell–independent antigens*
*Indicates B cell development phenotype in mice.
PAX5 is a paired-box, or domain, transcription factor that,
among the progeny of HSCs, is expressed exclusively in cells of Modulation of B-Cell Development by Chemokines,
the B-cell lineage. PAX5 has both a positive and a negative effect Cytokines, and Hormones
on B-cell differentiation. In mice, B-cell precursors require Pax5 Stromal cells provide the microenvironment for B-cell develop-
to progress beyond the proB-cell stage. The presence of Pax5 ment and differentiation (see Fig. 7.3). For example, the chemokine
also prevents early B-lineage progenitors from transiting into CXCL12, also known as preB-cell growth-stimulating factor and
other hematopoietic pathways. Downregulation of PAX5 allows as stromal cell-derived factor-1 (PBSF/SCF-1), promotes proB-cell
upregulation of BLIMP1 and plasma-cell differentiation. PAX5 proliferation. Mice with a targeted disruption of this gene exhibit
downregulation in plasma cells permits expression of genes impaired B-lymphopoiesis in fetal liver and bone marrow and
13
typically expressed in macrophages and neutrophils. fail to undergo bone marrow myelopoiesis. The mechanism
by which CXCL12 regulates early B-cell development remains
MicroRNAs and B-Cell Development unclear.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of small, noncoding RNAs that Although in mice interleukin-7 (IL-7) plays an essential role
12
downregulate target genes at a posttranscriptional level. These in B-lineage differentiation, in humans, it has a minimal prolifera-
RNAs are derived from longer transcripts by the sequential action tive effect on human B-cell progenitors. Nevertheless, IL-7
of RNA polymerase II, the nuclear nuclease Drosha, and the enhances CD19 expression, which plays an important role in
cytosolic nuclease Dicer. Mature miRNAs are incorporated into BCR signal transduction (Chapter 4). IL-7 treatment of human
the multiprotein RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which proB cells also leads to a reduction in the expression of RAG-1,
represses target messenger RNAs (mRNAs) by either inducing RAG-2, and TdT. Thus IL-7 can modulate the process of Ig gene
mRNA cleavage or mRNA degradation or by blocking mRNA segment rearrangement in human.
translation. Critical miRNAs include miR-150, miR-155, and Interferons-α and -β (IFN-α/β) are potent inhibitors of IL-
14
miR-17-92. Several of these miRNAs play a role in both early and 7-induced growth of B-lineage cells in mice. The inhibition is
late B-cell development. Abnormal function of these miRNAs mediated by cell death (apoptosis). One potential source of IFN-
can contribute to oncogenesis and immune dysfunction. α/β is bone marrow macrophages. Another macrophage-derived