Page 1307 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1307
CHaPter 93 Assessment of Functional Immune Responses in Lymphocytes 1269
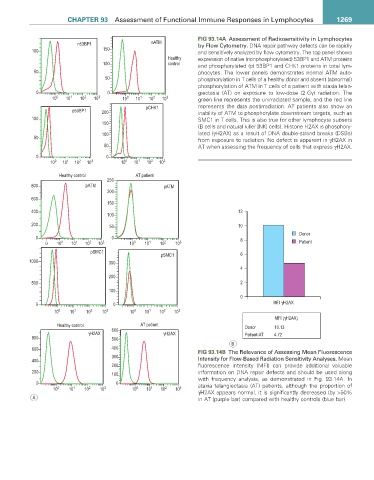
FIG 93.14a Assessment of Radiosensitivity in Lymphocytes
Q %3 Q$70 by Flow Cytometry. DNA repair pathway defects can be rapidly
and sensitively analyzed by flow cytometry. The top panel shows
+HDOWK\ expression of native (nonphosphorylated) 53BP1 and ATM proteins
FRQWURO and phosphorylated (p) 53BP1 and CHK1 proteins in total lym-
phocytes. The lower panels demonstrates normal ATM auto-
phosphorylation in T cells of a healthy donor and absent (abnormal)
phosphorylation of ATM in T cells of a patient with ataxia telan-
giectasia (AT) on exposure to low-dose (2 Gy) radiation. The
green line represents the unirradiated sample, and the red line
S&+. represents the data postirradiation. AT patients also show an
S %3 inability of ATM to phosphorylate downstream targets, such as
SMC1 in T cells. This is also true for other lymphocyte subsets
(B cells and natural killer [NK] cells). Histone H2AX is phosphory-
lated (γH2AX) as a result of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs)
from exposure to radiation. No defect is apparent in γH2AX in
AT when assessing the frequency of cells that express γH2AX.
+HDOWK\ FRQWURO $7 SDWLHQW
S$70 S$70
'RQRU
3DWLHQW
S60&
S60&
0), γ+ $;
0), γ+ $;
+HDOWK\ FRQWURO $7 SDWLHQW 'RQRU
γ+ $; γ+ $; 3DWLHQW $7
%
FIG 93.14B The Relevance of Assessing Mean Fluorescence
Intensity for Flow-Based Radiation Sensitivity Analyses. Mean
fluorescence intensity (MFI) can provide additional valuable
information on DNA repair defects and should be used along
with frequency analysis, as demonstrated in Fig. 93.14A. In
ataxia telangiectasia (AT) patients, although the proportion of
γH2AX appears normal, it is significantly decreased (by >50%
$ in AT (purple bar) compared with healthy controls (blue bar).