Page 1304 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1304
1266 Part eleven Diagnostic Immunology
Mutations in BTK impair B-cell maturation and function,
ASSESSMENT OF SIGNALING AND DNA REPAIR and patients with XLA can have either no peripheral B cells (null
PATHWAYS IN LYMPHOCYTES VIA mutations) or reduced B cells (hypomorphic/leaky mutations),
PHOSPHOFLOW CYTOMETRY depending on the specific genetic defect (Chapter 34). Two
regulatory tyrosine residues in BTK undergo rapid phosphoryla-
A key aspect of studying lymphocyte responses is to assess tion upon B-cell receptor (BCR) cross-linking (Y551 within the
43
signaling in appropriate lymphocyte subsets and its alteration SH1 domain and Y223 in the SH3 domain). Y551 is transphos-
in pathological conditions. A versatile tool called phosphoflow is phorylated by Src family kinases whereas Y223 is autophosphory-
unique in its ability to allow the study of multiple intracellular lated. Phospho-BTK accounts for a small fraction (<5%) of the
signaling molecules in specific lymphocyte populations at a total BTK pool in BCR-activated B cells. BTK molecules are
40
single-cell level. Phosphoflow assays for the signal transducer singly or doubly tyrosine-phosphorylated, and Y551 phosphoryla-
and activator of transcription (STAT) molecules 41,42 (Fig. 93.12) tion increases BTK activity, whereas Y223 phosphorylation is
have been well described and are discussed in Chapter 92. The use likely more relevant for protein-protein interactions due to its
of phosphoflow assays to assess Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) presence in the SH3 domain. Since the phosphorylation events
phosphorylation in X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) with are sequential (Y551 before Y223), the dephosphorylation event
leaky (hypomorphic) defects as well as to assess radiosensitivity is also successive in the same order. In the flow assay, Y223
and the DNA repair pathway will be covered briefly. phosphorylation is measured after an anti-IgM antibody is used
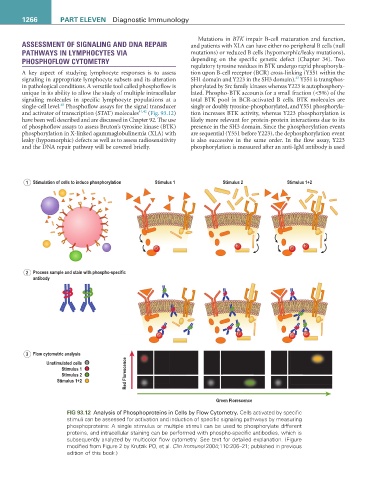
1 Stimulation of cells to induce phosphorylation Stimulus 1 Stimulus 2 Stimulus 1+2
P P
P P
2 Process sample and stain with phospho-specific
antibody
P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P
3 Flow cytometric analysis
Unstimulated cells
Stimulus 1
Stimulus 2 Red Florescence
Stimulus 1+2
Green Florescence
FIG 93.12 Analysis of Phosphoproteins in Cells by Flow Cytometry. Cells activated by specific
stimuli can be assessed for activation and induction of specific signaling pathways by measuring
phosphoproteins: A single stimulus or multiple stimuli can be used to phosphorylate different
proteins, and intracellular staining can be performed with phospho-specific antibodies, which is
subsequently analyzed by multicolor flow cytometry. See text for detailed explanation. (Figure
modified from Figure 2 by Krutzik PO, et al. Clin Immunol 2004;110:206–21; published in previous
edition of this book.)