Page 1313 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1313
CHaPtEr 94 Assessment of Neutrophil Function 1275
NEUTROPHIL ADHERENCE
Clinical Indications and Implications
Adherence of neutrophils to the endothelium is a prerequisite
step to the migration of neutrophils into the tissues. Neutrophils
isolated from patients with leukocyte adhesion defect-1 (LAD-1)
who lack the common β 2 integrin subunit CD18 exhibit abnormal
A B 19
adherence to the endothelium and therefore are not able to
migrate efficiently into the surrounding tissues, often resulting
20
in marked granulocytosis. LAD-2 is a milder form of the disease,
in which patients exhibit a defect in fucose metabolism and
21
glycoprotein biosynthesis. Neutrophils from patients with LAD-2
exhibit abnormal expression of the glycoprotein l-selectin and
fail to roll along the endothelium. However, they do exhibit
normal β 2 integrin–mediated adherence.
C D
Principles and Interpretation of Laboratory Assessment
Adherence of neutrophils can be assessed by measuring binding
to plastic using a 96-well plate either uncoated or coated with
fetal bovine serum or a specific extracellular matrix (ECM)
protein, such as fibrinogen or fibronectin. Endothelial cell
monolayers harvested from human umbilical veins may serve
as a more physiological substrate for the measurement of cell
E F adhesion. Isolated neutrophils are preloaded with the cell perme-
ant acetoxymethyl ester derivative of the fluorescent dye calcein
(calcein-AM). Nonspecific esterases in the cytosol cleave the ester
linkage, trapping the fluorescent probe in the cytosol. The labeled
neutrophils are added to each well and incubated in the absence
or presence of phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) to promote
adherence through activation of the integrins. At the end of the
incubation, the wells are washed three times to remove nonadher-
G ent cells. The fluorescence of each well is determined with a
fluorescent microplate reader and compared with the fluorescence
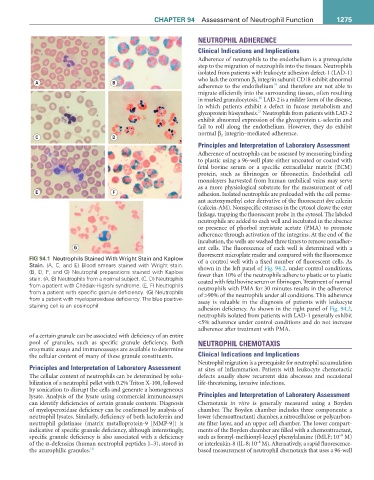
FIG 94.1 Neutrophils Stained With Wright Stain and Kaplow
Stain. (A, C, and E) Blood smears stained with Wright stain. of a control well with a fixed number of fluorescent cells. As
(B, D, F, and G) Neutrophil preparations stained with Kaplow shown in the left panel of Fig. 94.2, under control conditions,
stain. (A, B) Neutrophils from a normal subject. (C, D) Neutrophils fewer than 10% of the neutrophils adhere to plastic or to plastic
from a patient with Chédiak-Higashi syndrome. (E, F) Neutrophils coated with fetal bovine serum or fibrinogen. Treatment of normal
from a patient with specific granule deficiency. (G) Neutrophils neutrophils with PMA for 30 minutes results in the adherence
from a patient with myeloperoxidase deficiency. The blue positive- of >90% of the neutrophils under all conditions. This adherence
staining cell is an eosinophil. assay is valuable in the diagnosis of patients with leukocyte
adhesion deficiency. As shown in the right panel of Fig. 94.2,
neutrophils isolated from patients with LAD-1 generally exhibit
<5% adherence under control conditions and do not increase
adherence after treatment with PMA.
of a certain granule can be associated with deficiency of an entire
pool of granules, such as specific granule deficiency. Both NEUTROPHIL CHEMOTAXIS
enzymatic assays and immunoassays are available to determine
the cellular content of many of these granule constituents. Clinical Indications and Implications
Neutrophil migration is a prerequisite for neutrophil accumulation
Principles and Interpretation of Laboratory Assessment at sites of inflammation. Patients with leukocyte chemotactic
The cellular content of neutrophils can be determined by solu- defects usually show recurrent skin abscesses and occasional
bilization of a neutrophil pellet with 0.2% Triton X-100, followed life-threatening, invasive infections.
by sonication to disrupt the cells and generate a homogeneous
lysate. Analysis of the lysate using commercial immunoassays Principles and Interpretation of Laboratory Assessment
can identify deficiencies of certain granule contents. Diagnosis Chemotaxis in vitro is generally measured using a Boyden
of myeloperoxidase deficiency can be confirmed by analysis of chamber. The Boyden chamber includes three components: a
neutrophil lysates. Similarly, deficiency of both lactoferrin and lower (chemoattractant) chamber, a nitrocellulose or polycarbon-
neutrophil gelatinase (matrix metalloprotein-9 [MMP-9]) is ate filter layer, and an upper cell chamber. The lower compart-
indicative of specific granule deficiency, although interestingly, ments of the Boyden chamber are filled with a chemoattractant,
−8
specific granule deficiency is also associated with a deficiency such as formyl-methionyl-leucyl phenylalanine (fMLF; 10 M)
−8
of the α-defensins (human neutrophil peptides 1–3), stored in or interleukin-8 (IL-8; 10 M). Alternatively, a rapid fluorescence-
the azurophilic granules. 18 based measurement of neutrophil chemotaxis that uses a 96-well