Page 1316 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1316
1278 Part ElEvEn Diagnostic Immunology
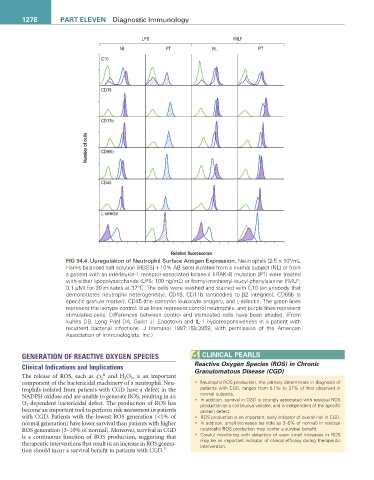
LPS fMLF
NL PT NL PT
C10
CD18
CD11b
Number of cells CD66b
CD45
L-selectin
Relative fluorescence
FIG 94.4 Upregulation of Neutrophil Surface Antigen Expression. Neutrophils (2.5 × 10 /mL
6
Hanks balanced salt solution [HBSS] + 10% AB sera) isolated from a normal subject (NL) or from
a patient with an interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4 (IRAK-4) mutation (PT) were treated
with either lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 100 ng/mL) or formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLF;
0.1 µM) for 30 minutes at 37°C. The cells were washed and stained with C10 (an antibody that
demonstrates neutrophil heterogeneity), CD18, CD11b (antibodies to β2 integrins), CD66b (a
specific granule marker), CD45 (the common leukocyte antigen), and L-selectin. The green lines
represent the isotype control, blue lines represent control neutrophils, and purple lines represent
stimulated cells. Differences between control and stimulated cells have been shaded. (From
Kuhns DB, Long Priel DA, Gallin JI. Endotoxin and IL-1 hyporesponsiveness in a patient with
recurrent bacterial infections. J Immunol 1997;158:3959, with permission of the American
Association of Immunologists, Inc.)
GENERATION OF REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES ClInICal PEarlS
Clinical Indications and Implications Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Chronic
Granulomatous Disease (CGD)
• and H 2 O 2 , is an important
The release of ROS, such as O 2
component of the bactericidal machinery of a neutrophil. Neu- • Neutrophil ROS production, the primary determinate in diagnosis of
trophils isolated from patients with CGD have a defect in the patients with CGD, ranges from 0.1% to 27% of that observed in
normal subjects.
NADPH oxidase and are unable to generate ROS, resulting in an • In addition, survival in CGD is strongly associated with residual ROS
O 2 -dependent bactericidal defect. The production of ROS has production as a continuous variable, and is independent of the specific
become an important tool to perform risk assessment in patients protein defect.
with CGD. Patients with the lowest ROS generation (<1% of • ROS production is an important, early indicator of overall risk in CGD.
normal generation) have lower survival than patients with higher • In addition, small increases (as little as 3–5% of normal) in residual
ROS generation (3–10% of normal). Moreover, survival in CGD neutrophil ROS production may confer a survival benefit.
is a continuous function of ROS production, suggesting that • Careful monitoring with detection of even small increases in ROS
therapeutic interventions that result in an increase in ROS genera- may be an important indicator of clinical efficacy during therapeutic
intervention.
tion should incur a survival benefit to patients with CGD. 25