Page 1318 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1318
1280 Part ElEvEn Diagnostic Immunology
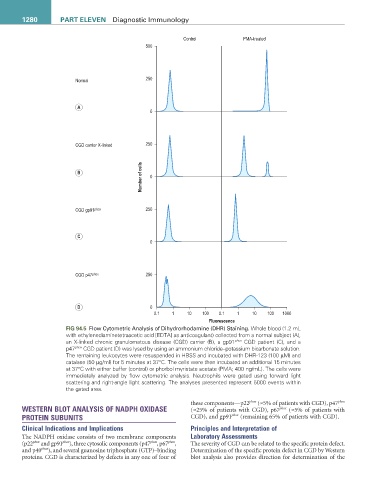
Control PMA-treated
500
Normal 250
A
0
CGD carrier X-linked 250
Number of cells 0
B
CGD gp91 phox 250
C
0
CGD p47 phox 250
D 0
0.1 1 10 100 0.1 1 10 100 1000
Fluorescence
FIG 94.5 Flow Cytometric Analysis of Dihydrorhodamine (DHR) Staining. Whole blood (1.2 mL
with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid [EDTA] as anticoagulant) collected from a normal subject (A),
an X-linked chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) carrier (B), a gp91 phox CGD patient (C), and a
p47 phox CGD patient (D) was lysed by using an ammonium chloride–potassium bicarbonate solution.
The remaining leukocytes were resuspended in HBSS and incubated with DHR-123 (100 µM) and
catalase (50 µg/ml) for 5 minutes at 37°C. The cells were then incubated an additional 15 minutes
at 37°C with either buffer (control) or phorbol myristate acetate (PMA; 400 ng/mL). The cells were
immediately analyzed by flow cytometric analysis. Neutrophils were gated using forward light
scattering and right-angle light scattering. The analyses presented represent 5000 events within
the gated area.
these components—p22 phox (≈5% of patients with CGD), p47 phox
WESTERN BLOT ANALYSIS OF NADPH OXIDASE (≈25% of patients with CGD), p67 phox (≈5% of patients with
PROTEIN SUBUNITS CGD), and gp91 phox (remaining 65% of patients with CGD).
Clinical Indications and Implications Principles and Interpretation of
The NADPH oxidase consists of two membrane components Laboratory Assessments
(p22 phox and gp91 phox ), three cytosolic components (p47 phox , p67 phox , The severity of CGD can be related to the specific protein defect.
and p40 phox ), and several guanosine triphosphate (GTP)–binding Determination of the specific protein defect in CGD by Western
proteins. CGD is characterized by defects in any one of four of blot analysis also provides direction for determination of the