Page 1343 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1343
1304 ParT ElEvEN Diagnostic Immunology
Solid phase Anchor primer
G G C A G T
Incorporation 4-color fluorescent-labeled dNTPs
Nucleotide incorporates
into DNA H+
Hydrogen ion released
Imaging Ion sensitive layer Sensor layer
Electrochemical signal
T G A C GG
B Sequence call
Deprotection
A
ZMW array
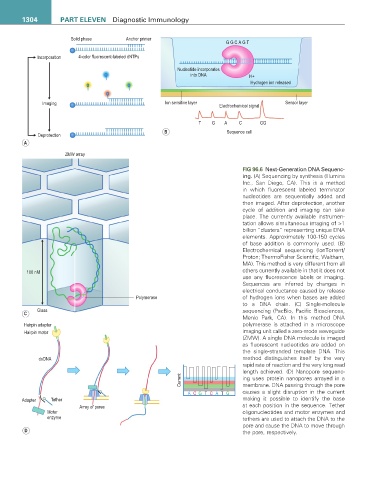
FIG 96.6 Next-Generation DNA Sequenc-
ing. (A) Sequencing by synthesis (Illumina
Inc., San Diego, CA). This is a method
in which fluorescent labeled terminator
nucleotides are sequentially added and
then imaged. After deprotection, another
cycle of addition and imaging can take
place. The currently available instrumen-
tation allows simultaneous imaging of >1
billion “clusters” representing unique DNA
elements. Approximately 100-150 cycles
of base addition is commonly used. (B)
Electrochemical sequencing (IonTorrent/
Proton; ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham,
MA). This method is very different from all
100 nM others currently available in that it does not
use any fluorescence labels or imaging.
Sequences are inferred by changes in
electrical conductance caused by release
Polymerase of hydrogen ions when bases are added
to a DNA chain. (C) Single-molecule
Glass sequencing (PacBio, Pacific Biosciences,
C
Menlo Park, CA). In this method DNA
Hairpin adapter polymerase is attached in a microscope
Hairpin motor imaging unit called a zero-mode waveguide
(ZMW). A single DNA molecule is imaged
as fluorescent nucleotides are added on
the single-stranded template DNA. This
dsDNA method distinguishes itself by the very
rapid rate of reaction and the very long read
length achieved. (D) Nanopore sequenc-
Current ing uses protein nanopores arrayed in a
membrane. DNA passing through the pore
A C G T C A T G causes a slight disruption in the current
Adapter Tether making it possible to identify the base
Array of pores at each position in the sequence. Tether
Motor oligonucleotides and motor enzymes and
enzyme tethers are used to attach the DNA to the
pore and cause the DNA to move through
D the pore, respectively.