Page 1348 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1348
CHaPTEr 96 Molecular Methods 1309
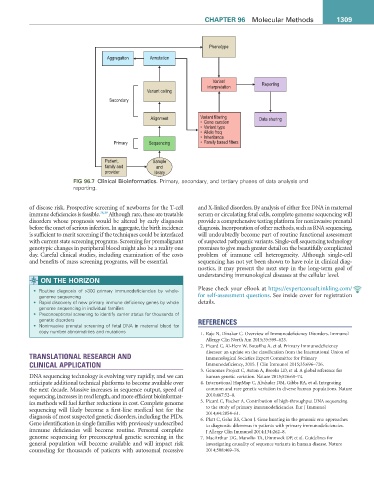
Phenotype
Aggregation Annotation
Variant
interpretation Reporting
Variant calling
Secondary
Alignment Variant filtering Data sharing
• Gene curation
• Variant type
• Allele freq
• Inheritance
Primary Sequencing • Family based filters
Patient, Sample
family and and
provider library
FIG 96.7 Clinical Bioinformatics. Primary, secondary, and tertiary phases of data analysis and
reporting.
of disease risk. Prospective screening of newborns for the T-cell and X-linked disorders. By analysis of either free DNA in maternal
immune deficiencies is feasible. 38,39 Although rare, these are treatable serum or circulating fetal cells, complete genome sequencing will
disorders whose prognosis would be altered by early diagnosis provide a comprehensive testing platform for noninvasive prenatal
before the onset of serious infection. In aggregate, the birth incidence diagnosis. Incorporation of other methods, such as RNA sequencing,
is sufficient to merit screening if the techniques could be interfaced will undoubtedly become part of routine functional assessment
with current state screening programs. Screening for premalignant of suspected pathogenic variants. Single-cell sequencing technology
genotypic changes in peripheral blood might also be a reality one promises to give much greater detail on the beautifully complicated
day. Careful clinical studies, including examination of the costs problem of immune cell heterogeneity. Although single-cell
and benefits of mass screening programs, will be essential. sequencing has not yet been shown to have role in clinical diag-
nostics, it may present the next step in the long-term goal of
understanding immunological diseases at the cellular level.
ON THE HOrIZON
• Routine diagnosis of >300 primary immunodeficiencies by whole- Please check your eBook at https://expertconsult.inkling.com/
genome sequencing for self-assessment questions. See inside cover for registration
• Rapid discovery of new primary immune deficiency genes by whole details.
genome sequencing in individual families
• Preconceptional screening to identify carrier status for thousands of
genetic disorders REFERENCES
• Noninvasive prenatal screening of fetal DNA in maternal blood for
copy number abnormalities and mutations 1. Raje N, Dinakar C. Overview of Immunodeficiency Disorders. Immunol
Allergy Clin North Am 2015;35:599–623.
2. Picard C, Al-Herz W, Bousfiha A, et al. Primary Immunodeficiency
diseases: an update on the classification from the International Union of
TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH AND Immunological Societies Expert Committee for Primary
CLINICAL APPLICATION Immunodeficiency, 2015. J Clin Immunol 2015;35:696–726.
3. Genomes Project C, Auton A, Brooks LD, et al. A global reference for
DNA sequencing technology is evolving very rapidly, and we can human genetic variation. Nature 2015;526:68–74.
anticipate additional technical platforms to become available over 4. International HapMap C, Altshuler DM, Gibbs RA, et al. Integrating
the next decade. Massive increases in sequence output, speed of common and rare genetic variation in diverse human populations. Nature
sequencing, increases in read length, and more efficient bioinformat- 2010;467:52–8.
ics methods will fuel further reductions in cost. Complete genome 5. Picard C, Fischer A. Contribution of high-throughput DNA sequencing
sequencing will likely become a first-line medical test for the to the study of primary immunodeficiencies. Eur J Immunol
2014;44:2854–61.
diagnosis of most suspected genetic disorders, including the PIDs. 6. Platt C, Geha RS, Chou J. Gene hunting in the genomic era: approaches
Gene identification in single families with previously undescribed to diagnostic dilemmas in patients with primary immunodeficiencies.
immune deficiencies will become routine. Personal complete J Allergy Clin Immunol 2014;134:262–8.
genome sequencing for preconceptual genetic screening in the 7. MacArthur DG, Manolio TA, Dimmock DP, et al. Guidelines for
general population will become available and will impact risk investigating causality of sequence variants in human disease. Nature
counseling for thousands of patients with autosomal recessive 2014;508:469–76.