Page 204 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 204
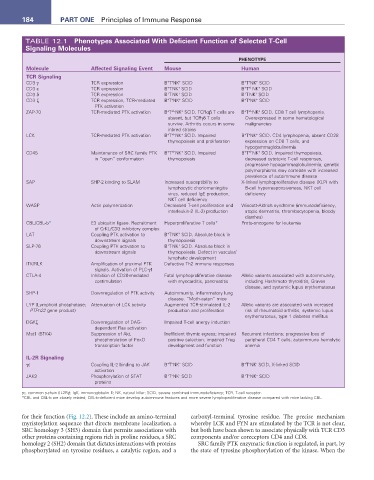
184 PART ONE Principles of Immune Response
TABLE 12.1 Phenotypes Associated With Deficient Function of Selected T-Cell
Signaling Molecules
PHENOTYPE
Molecule Affected Signaling Event Mouse Human
TCR Signaling
+ +
CD3 γ TCR expression B T NK SCID B T NK SCID
+
+
+ +
+ +/−
CD3 ε TCR expression B T NK SCID B T NK SCID
+
+ -
+
+ -
+
+ -
CD3 δ TCR expression B T NK SCID B T NK SCID
+
+
+
+ +
+ +
CD3 ζ TCR expression, TCR-mediated B T NK SCID B T NK SCID
PTK activation
+ +/−
+
+ +/−
+
ZAP-70 TCR-mediated PTK activation B T NK SCID. TCRαβ T cells are B T NK SCID. CD8 T cell lymphopenia.
absent, but TCRγδ T cells Overexpressed in some hematological
survive. Arthritis occurs in some malignancies
inbred strains
+
+
+ +/−
+ +
LCK TCR-mediated PTK activation B T NK SCID. Impaired B T NK SCID. CD4 lymphopenia, absent CD28
thymopoiesis and proliferation expression on CD8 T cells, and
hypogammaglobulinemia
+ +/−
+ +/−
+
+
CD45 Maintenance of SRC family PTK B T NK SCID. Impaired B T NK SCID. Impaired thymopoiesis,
in “open” conformation thymopoiesis decreased cytotoxic T-cell responses,
progressive hypogammaglobulinemia, genetic
polymorphisms may correlate with increased
prevalence of autoimmune disease
SAP SHP-2 binding to SLAM Increased susceptibility to X-linked lymphoproliferative disease (XLP) with
lymphocytic choriomeningitis B-cell hyperresponsiveness, NKT cell
virus, reduced IgE production, deficiency
NKT cell deficiency
WASP Actin polymerization Decreased T-cell proliferation and Wiscott-Aldrich syndrome (immunodeficiency,
interleukin-2 (IL-2) production atopic dermatitis, thrombocytopenia, bloody
diarrhea)
CBL/CBL-b* E3 ubiquitin ligase. Recruitment Hyperproliferative T cells* Proto-oncogene for leukemia
of CrKL/C3G inhibitory complex
+
LAT Coupling PTK activation to B T NK SCID. Absolute block in
+ -
downstream signals thymopoiesis
+
SLP-76 Coupling PTK activation to B T NK SCID. Absolute block in
+ -
downstream signals thymopoiesis. Defect in vascular/
lymphatic development
ITK/RLK Amplification of proximal PTK Defective Th2 immune responses
signals. Activation of PLC-γ1
CTLA-4 Inhibition of CD28-mediated Fatal lymphoproliferative disease Allelic variants associated with autoimmunity,
costimulation with myocarditis, pancreatitis including Hashimoto thyroiditis, Graves
disease, and systemic lupus erythematosus
SHP-1 Downregulation of PTK activity Autoimmunity, inflammatory lung
disease. “Moth-eaten” mice
LYP (Lymphoid phosphatase; Attenuation of LCK activity Augmented TCR-stimulated IL-2 Allelic variants are associated with increased
PTPn22 gene product) production and proliferation risk of rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus
erythematosus, type 1 diabetes mellitus
DGKζ Downregulation of DAG- Impaired T-cell anergy induction
dependent Ras activation
Mst1 (STK4) Suppression of Akt, Inefficient thymic egress; impaired Recurrent infections; progressive loss of
phosphorylation of FoxO positive selection; impaired Treg peripheral CD4 T cells; autoimmune hemolytic
transcription factor development and function anemia
IL-2R Signaling
-
−
+ −
γc Coupling IL-2 binding to JAK B T NK SCID B T NK SCID, X-linked SCID
+ −
activation
+ −
JAK3 Phosphorylation of STAT B T NK SCID B T NK SCID
+ −
−
-
proteins
γc, common γ-chain (IL2Rγ); IgE, immunoglobulin E; NK, natural killer; SCID, severe combined immunodeficiency; TCR, T-cell receptor.
*CBL and CBL-b are closely related; CBL-b-deficient mice develop autoimmune features and more severe lymphoproliferative disease compared with mice lacking CBL.
for their function (Fig. 12.2). These include an amino-terminal carboxyl-terminal tyrosine residue. The precise mechanism
myristoylation sequence that directs membrane localization, a whereby LCK and FYN are stimulated by the TCR is not clear,
SRC homology 3 (SH3) domain that permits associations with but both have been shown to associate physically with TCR CD3
other proteins containing regions rich in proline residues, a SRC components and/or coreceptors CD4 and CD8.
homology 2 (SH2) domain that dictates interactions with proteins SRC family PTK enzymatic function is regulated, in part, by
phosphorylated on tyrosine residues, a catalytic region, and a the state of tyrosine phosphorylation of the kinase. When the