Page 281 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 281
262 ParT TwO Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
+
−
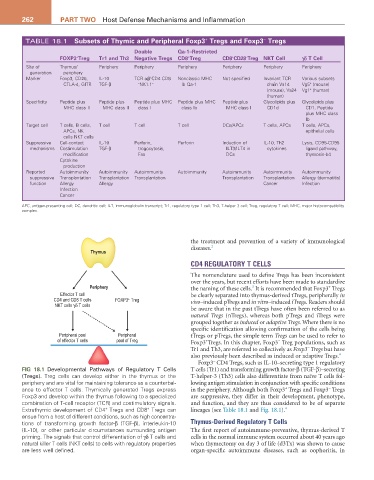
TABLE 18.1 Subsets of Thymic and Peripheral Foxp3 Tregs and Foxp3 Tregs
Double Qa-1–restricted
−
+
+
FOXP3 Treg Tr1 and Th3 Negative Tregs CD8 Treg CD8 CD28 Treg NKT Cell γδ T Cell
+
Site of Thymus/ Periphery Periphery Periphery Periphery Periphery Periphery
generation periphery
Marker Foxp3, CD25, IL-10 TCR αβ CD4 CD8 Nonclassic MHC Not specified Invariant TCR Various subsets
+
−
CTLA-4, GITR TGF-β − NK1.1 − Ib Qa-1 chain Va14 Vg5 (mouse)
+
(mouse), Va24 Vg1 (human)
+
(human)
Specificity Peptide plus Peptide plus Peptide plus MHC Peptide plus MHC Peptide plus Glycolipids plus Glycolipids plus
MHC class II MHC class II class I class Ib MHC class I CD1d CD1, Peptide
plus MHC class
Ib
Target cell T cells, B cells, T cell T cell T cell DCs/APCs T cells, APCs T cells, APCs,
APCs, NK epithelial cells
cells NKT cells
Suppressive Cell-contact IL-10 Perforin, Perforin Induction of IL-10, Th2 Lysis, CD95-CD95
mechanisms Costimulation TGF-β trogocytosis, ILT3/ILT4 in cytokines ligand pathway,
modification Fas DCs thymosin-b4
Cytokine
production
Reported Autoimmunity Autoimmunity Autoimmunity Autoimmunity Autoimmunity Autoimmunity Autoimmunity
suppressive Transplantation Transplantation Transplantation Transplantation Transplantation Allergy (dermatitis)
function Allergy Allergy Cancer Infection
Infection
Cancer
APC, antigen-presenting cell; DC, dendritic cell; ILT, immunoglobulin transcript; Tr1, regulatory type 1 cell; Th3, T-helper 3 cell; Treg, regulatory T cell; MHC, major histocompatibility
complex.
the treatment and prevention of a variety of immunological
diseases. 2
Thymus
CD4 REGULATORY T CELLS
The nomenclature used to define Tregs has been inconsistent
over the years, but recent efforts have been made to standardize
Periphery the naming of these cells. It is recommended that Foxp3 Tregs
+
3
Effector T cell be clearly separated into thymus-derived tTregs, peripherally in
+
CD4 and CD8 T cells FOXP3 Treg vivo–induced pTregs and in vitro–induced iTregs. Readers should
NKT cells γδ T cells
be aware that in the past tTregs have often been referred to as
natural Tregs (nTregs), whereas both pTregs and iTregs were
grouped together as induced or adaptive Tregs. Where there is no
specific identification allowing confirmation of the cells being
Peripheral pool Peripheral tTregs or pTregs, the simple term Tregs can be used to refer to
of effector T cells pool of Treg Foxp3 Tregs. In this chapter, Foxp3 Treg populations, such as
−
+
−
Tr1 and Th3, are referred to collectively as Foxp3 Tregs but have
also previously been described as induced or adaptive Tregs. 4
−
Foxp3 CD4 Tregs, such as IL-10–secreting type 1 regulatory
FIG 18.1 Developmental Pathways of Regulatory T Cells T cells (Tr1) and transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)–secreting
(Tregs). Treg cells can develop either in the thymus or the T-helper-3 (Th3) cells also differentiate from naïve T cells fol-
periphery and are vital for maintaining tolerance as a counterbal- lowing antigen stimulation in conjunction with specific conditions
+
−
ance to effector T cells. Thymically generated Tregs express in the periphery. Although both Foxp3 Tregs and Foxp3 Tregs
Foxp3 and develop within the thymus following to a specialized are suppressive, they differ in their development, phenotype,
combination of T-cell receptor (TCR) and costimulatory signals. and function, and they are thus considered to be of separate
Extrathymic development of CD4 Tregs and CD8 Tregs can lineages (see Table 18.1 and Fig. 18.1). 4
+
+
ensue from a host of different conditions, such as high concentra-
tions of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), interleukin-10 Thymus-Derived Regulatory T Cells
(IL-10), or other particular circumstances surrounding antigen The first report of autoimmune-preventive, thymus-derived T
priming. The signals that control differentiation of γδ T cells and cells in the normal immune system occurred about 40 years ago
natural killer T cells (NKT cells) to cells with regulatory properties when thymectomy on day 3 of life (d3Tx) was shown to cause
are less well defined. organ-specific autoimmune diseases, such as oophoritis, in