Page 284 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 284
CHaPTEr 18 Regulatory Immune Cells 265
+
+
+
+
−
+
low
CD25 CD4 T cells and CD25 CD4 CD8 thymocytes specifically into two subsets: CD45RA FOXP3 naïve Tregs (nTregs) and
−
express Foxp3 mRNA in contrast to the cell surface markers used CD45RA FOXP3 high effector Tregs (eTregs) (see Fig. 18.3).
until now. In addition, other thymocytes/T cells, Th1, or Th2 In addition to tTregs, there is abundant evidence from mouse
9
cells scarcely express Foxp3 even after stimulation. Intranuclear studies supporting the peripheral development of T cells with
+
+
staining of the Foxp3 protein shows that although the majority suppressive properties. For example, Foxp3-expressing CD25 CD4
+
+
+
of Foxp3 cells in mice reside in the CD4 CD25 T-cell population, Tregs, functionally and phenotypically similar to tTregs, can be
+
−
some can also be found in the CD4 CD25 population (see Fig. induced from naïve T cells by in vitro or in vivo antigenic stimula-
11
18.3). Importantly, retroviral transduction of Foxp3 in naïve tion in the presence of TGF-β. However, it should be noted
−
CD25 T cells can convert them to regulatory cells with at least that in vitro–induced Tregs lack the Treg-type epigenetic pattern
some of the suppressive functions of true Tregs. However, although and so may not be stable Tregs, making it important to differenti-
it is essential, it has also become clear that Foxp3 alone is not ate between in vivo peripherally induced pTregs and in vitro-
10
sufficient to stably maintain the full Treg identity. Another critical induced iTregs. Recent findings indicate that both murine and
factor is the presence of a Treg-type epigenetic pattern in which human thymus-derived Treg cells express Helios, an Ikaros family
genes, such as Foxp3, CTLA-4, and GITR, have stably demethylated transcription factor, and Neuropilin-1, whereas most induced
CpG residues and a permissive chromatin structure allowing Foxp3-expressing CD4 T cells do not. However, some highly
−
them to be constitutively expressed by Tregs. These epigenetic activated pTregs and Foxp3 T cells express these markers to
modifications occur independently of Foxp3 expression and some extent, making them useful, but not of themselves conclusive,
12
maintain a significant proportion of the Treg gene expression to differentiate between tTregs and pTregs. Recent work has
10
even in the absence of Foxp3 itself. However, at the same time, demonstrated that tTregs are sufficient for the prevention of
Foxp3 expression is still essential, as shown by the severe diseases widespread autoimmunity but that pTregs have a more specialized
seen in humans or mice lacking functional Foxp3. A similar function in the prevention of type-2 immune responses in mucosal
pattern of FOXP3 expression can be observed in humans, with sites, such as the gastrointestinal tract and the lungs. 11
+
+
most FOXP3 cells among CD4 CD25 high T cells, and a few being +
−
low
CD25 or CD25 (see Fig. 18.3). However, in humans, but not Maintenance of Foxp3 Tregs
in mice, low levels of FOXP3 can be transiently induced by TCR In addition to TCR interaction, it seems that accessory signals,
stimulation in conventional T cells. These T cells can be detected such as costimulation through CD28-B7 or CD40-CD40L, play
+
+
directly in blood as CD4 T cells with a memory phenotype and an important role in the production of Foxp3 Tregs in the thymus,
8
a weak expression of FOXP3, but with no suppressive function. since animals that lack CD28 or CD40 expression generate only
+
+
Human FOXP3 Tregs with suppressive function can be divided minute numbers of Foxp3 T cells in the thymus (Table 18.2). 6
+
In the periphery, the maintenance of Foxp3 Tregs requires
+
CLINICaL rELEVaNCE antigenic priming and cytokines. It is vital that Foxp3 Tregs
Infections and Immune Dysfunction/ encounter specific antigens to remain in the Treg pool. For
example, cell transfer experiments in mice thymectomized on
Polyendocrinopathy/Enteropathy/X-Linked (IPEX) day 3 (d3Tx) have demonstrated that Tregs from donors of the
Syndrome Is a Result of FOXP3 Treg Deficiency same sex are better at protecting against orchitis or oophoritis
+
compared with Tregs from donors of the opposite sex and that
When the Foxp3/FOXP3 gene has a loss-of-function mutation, FOXP3 +
regulatory T cells (Tregs) fail to develop, or Foxp3 protein is dysfunctional, Tregs from ovariectomized mice are less competent in preventing
5
and a fatal autoimmune/autoinflammatory disease develops. This oophoritis compared with those from normal females.
monogenic X-linked disease directly demonstrates how crucial FOXP3 + IL-2 is vital for the maintenance of natural Tregs, and
Tregs are for maintaining self-tolerance and immune homeostasis. accordingly, CD25 is not only a marker but also a functionally
Cardinal features of IPEX are: indispensable molecule for Tregs as a key component of the
• Autoimmune diseases (type 1 diabetes, thyroiditis, hemolytic anemia) high-affinity IL-2 receptor. Mice genetically deficient in IL-2
• Allergy (dermatitis, hyperimmunoglobulinemia E, food allergy) or IL-2 receptor α chain (CD25) or β chain (CD122) develop
• Inflammatory bowel disease
severe lymphoproliferative disease with lymphocyte infiltration
+
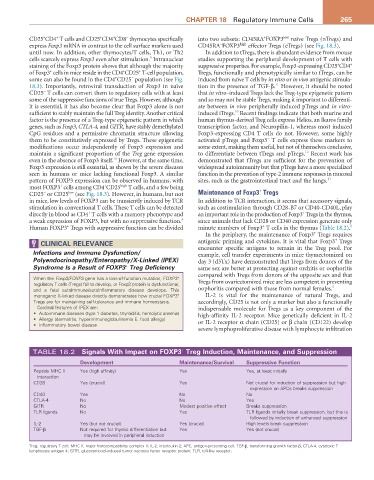
TABLE 18.2 Signals with Impact on FOXP3 Treg Induction, Maintenance, and Suppression
Development Maintenance/Survival Suppressive Function
Peptide MHC II Yes (high affinity) Yes Yes, at least initially
interaction
CD28 Yes (crucial) Yes Not crucial for induction of suppression but high
expression on APCs breaks suppression
CD40 Yes No No
CTLA-4 No No Yes
GITR No Modest positive effect Breaks suppression
TLR ligands No Yes TLR ligands initially break suppression, but this is
followed by induction of enhanced suppression
IL-2 Yes (but not crucial) Yes (crucial) High levels break suppression
TGF-β Not required for thymic differentiation but Yes Yes (not crucial)
may be involved in peripheral induction
Treg, regulatory T cell; MHC II, major histocompatibility complex II; IL-2, interleukin 2; APC, antigen-presenting cell; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T
lymphocyte antigen 4; GITR, glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor protein; TLR, toll-like receptor.