Page 282 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 282
CHaPTEr 18 Regulatory Immune Cells 263
+
otherwise healthy mice, a finding later attributed to the slightly This dilemma is especially apparent when investigating Foxp3
+
delayed thymic emigration of tTregs in comparison with effector Tregs in humans, where a significant proportion of CD4 T cells
+
5
T cells. Subsequent studies showed that the development of in peripheral blood express CD25, yet only 2%–4% of CD4 T
autoimmune diseases could be inhibited if the thymectomized cells, enriched among cells with the highest expression level of
+
−
+
8
animals were reconstituted with CD4 CD8 thymocytes or CD4 CD25 (CD25 high ), have suppressive properties (Fig. 18.3). The
+
splenocytes from histocompatible immune-uncompromised fact that CD25 Tregs are not a discrete population in humans
animals. Athymic mice transferred with non-Tregs or thymocytes poses a problem both when obtaining cells for experimental
spontaneously develop organ-specific autoimmune diseases, purposes and when evaluating their role in a clinical setting.
+
which can be reversed by cotransfer of tTregs from normal adult Therefore finding more specific cell surface markers of CD4
6,7
mice. Tregs can suppress the proliferation and cytokine produc- natural Tregs remains an important goal.
tion of conventional CD4 or CD8 T cells in vitro. tTregs are
thought to arise from T-cell clones with relatively high reactivity Thymus-Derived Tregs Express the Transcription
to self antigens presented in the thymus. Factor Foxp3
To pinpoint a specific phenotype for CD4 T cells with regula- Specific expression of the transcription factor Foxp3 is closely
9
tory function, surface markers with more restricted expression linked with the development and function of Tregs. The first
patterns have been explored. High and stable expression of the hint as to the significance of Foxp3 was given by studies of the
IL-2 receptor α chain, CD25 has been found to be a useful and Scurfy mutant mouse. This mouse strain suffers from a spontane-
+
specific surface marker of Foxp3 Tregs. Between 5% and 10% ous X-linked mutation of the Foxp3 gene, which leads to fatal
+
of CD4 T cells express CD25 constitutively in the thymus and lymphoproliferative disease associated with multiorgan infiltrates
periphery of mice. Importantly, transfer of CD4 lymphocytes and early death by 3–4 weeks of age in hemizygous males.
+
depleted of CD25 cells induces autoimmunity in athymic nude Similarly, mutations in the human orthologue FOXP3 are linked
+
+
mice, whereas cotransfer of CD4 CD25 cells protects the mice to immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, IBD,
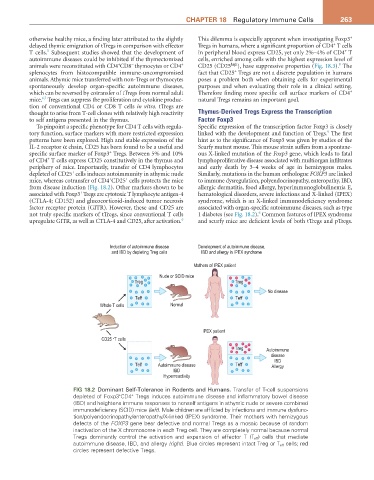
from disease induction (Fig. 18.2). Other markers shown to be allergic dermatitis, food allergy, hyperimmunoglobulinemia E,
+
associated with Foxp3 Tregs are cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 hematological disorders, severe infections and X-linked (IPEX)
(CTLA-4; CD152) and glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis syndrome, which is an X-linked immunodeficiency syndrome
factor receptor protein (GITR). However, these and CD25 are associated with organ-specific autoimmune diseases, such as type
6
not truly specific markers of tTregs, since conventional T cells 1 diabetes (see Fig. 18.2). Common features of IPEX syndrome
6
upregulate GITR, as well as CTLA-4 and CD25, after activation. and scurfy mice are deficient levels of both tTregs and pTregs.
Induction of autoimmune disease Development of autoimmune disease,
and IBD by depleting Treg cells IBD and allergy in IPEX syndrome
Mothers of IPEX patient
Nude or SCID mice
Treg Treg
No disease
Teff Teff
Whole T cells Normal
IPEX patient
-
CD25 T cells
Treg Autoimmune
disease
IBD
Teff Autoimmune disease Teff Allergy
IBD
Hyperreactivity
FIG 18.2 Dominant Self-Tolerance in Rodents and Humans. Transfer of T-cell suspensions
depleted of Foxp3 CD4 Tregs induces autoimmune disease and inflammatory bowel disease
+
+
(IBD) and heightens immune responses to nonself antigens in athymic nude or severe combined
immunodeficiency (SCID) mice (left). Male children are afflicted by infections and immune dysfunc-
tion/polyendocrinopathy/enteropathy/X-linked (IPEX) syndrome. Their mothers with hemizygous
defects of the FOXP3 gene bear defective and normal Tregs as a mosaic because of random
inactivation of the X chromosome in each Treg cell. They are completely normal because normal
Tregs dominantly control the activation and expansion of effector T (T eff ) cells that mediate
autoimmune disease, IBD, and allergy (right). Blue circles represent intact Treg or T eff cells; red
circles represent defective Tregs.