Page 492 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 492
472 PARt fouR Immunological Deficiencies
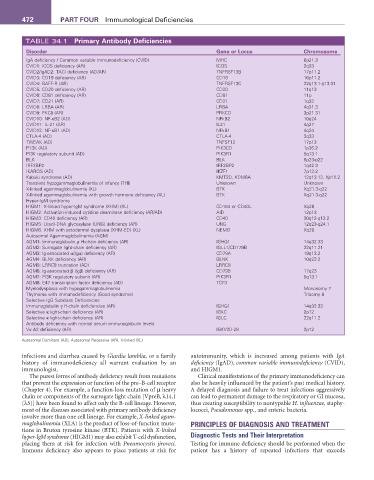
TABLE 34.1 Primary Antibody Deficiencies
Disorder Gene or Locus Chromosome
IgA deficiency / Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) MHC 6p21.3
CVID1: ICOS deficiency (AR) ICOS 2q33
CVID2/IgAD2: TACI deficiency (AD/AR) TNFRSF13B 17p11.2
CVID3: CD19 deficiency (AR) CD19 16p11.2
CVID4: BAFF-R (AR) TNFRSF13C 22q13.1-q13.31
CVID5: CD20 deficiency (AR) CD20 11q13
CVID6: CD81 deficiency (AR) CD81 11p
CVID7: CD21 (AR) CD21 1q32
CVID8: LRBA (AR) LRBA 4q31.3
CVID9: PKCδ (AR) PRKCD 3p21.31
CVID10: NF-κB2 (AD) NFkB2 10q24
CVID11: IL-21 (AR) IL21 4q27
CVID12: NF-κB1 (AD) NFkB1 4q24
CTLA-4 (AD) CTLA-4 2q33
TWEAK (AD) TNFSF12 17p13
P13K (AD) PIK3CD 1p36.2
PI3K regulatory subunit (AD) PIK3R1 5q13.1
BLK BLK 8p23-p22
IRF2BP2 IRF2BP2 1q42.3
IKAROS (AD) IKZF1 7p12.2
Kabuki syndrome (AD) KMT2D, KDM6A 12q13.12, Xp11.2
Transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy (THI) Unknown Unknown
X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XL) BTK Xq21.3-q22
X-linked agammaglobulinemia with growth hormone deficiency (XL) BTK Xq21.3-q22
Hyper-IgM syndrome
HIGM1: X-linked hyper-IgM syndrome (XHM) (XL) CD154 or CD40L Xq26
HIGM2: Activation-induced cytidine deaminase deficiency (AR/AD) AID 12p13
HIGM3: CD40 deficiency (AR) CD40 20q12-q13.2
HIGM5: Uracil-DNA glycosylase (UNG) deficiency (AR) UNG 12q23-q24.1
HIGM6: XHM with ectodermal dysplasia (XHM-ED) (XL) NEMO Xq28
Autosomal Agammaglobulinemia (AGM)
AGM1: Immunoglobulin µ H-chain deficiency (AR) IGHG1 14q32.33
AGM2: Surrogate light-chain deficiency (AR) IGLL1/CD179B 22q11.21
AGM3: Ig-associated α(Igα) deficiency (AR) CD79A 19q13.2
AGM4: BLNK deficiency (AR) BLNK 10q23.2
AGM5: LRRC8 truncation (AD) LRRC8
AGM6: Ig-associated β (Igβ) deficiency (AR) CD79B 17q23
AGM7: PI3K regulatory subunit (AR) PIK3R1 5q13.1
AGM8: E47 transcription factor deficiency (AD) TCF3
Myelodysplasia with hypogammaglobulinemia Monosomy 7
Thymoma with immunodeficiency (Good syndrome) Trisomy 8
Selective IgG Subclass Deficiencies
Immunoglobulin γ H-chain deficiencies (AR) IGHG1 14q32.33
Selective κ light-chain deficiency (AR) IGKC 2p12
Selective κ light-chain deficiency (AR) IGLC 22q11.2
Antibody deficiency with normal serum immunoglobulin levels
Vκ A2 deficiency (AR) IGKV2D-29 2p12
Autosomal Dominant (AD), Autosomal Recessive (AR), X-linked (XL)
infections and diarrhea caused by Giardia lamblia, or a family autoimmunity, which is increased among patients with IgA
history of immunodeficiency all warrant evaluation by an deficiency (IgAD), common variable immunodeficiency (CVID),
immunologist. and HIGM1.
The purest forms of antibody deficiency result from mutations Clinical manifestations of the primary immunodeficiency can
that prevent the expression or function of the pre–B-cell receptor also be heavily influenced by the patient’s past medical history.
(Chapter 4). For example, a function-loss mutation of µ heavy A delayed diagnosis and failure to treat infections aggressively
chain or components of the surrogate light chain [VpreB, λ14.1 can lead to permanent damage to the respiratory or GI mucosa,
(λ5)] have been found to affect only the B-cell lineage. However, thus creating susceptibility to nontypable H. influenzae, staphy-
most of the diseases associated with primary antibody deficiency lococci, Pseudomonas spp., and enteric bacteria.
involve more than one cell lineage. For example, X-linked agam-
maglobulinemia (XLA) is the product of loss-of-function muta- PRINCIPLES OF DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
tions in Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK). Patients with X-linked
hyper-IgM syndrome (HIGM1) may also exhibit T-cell dysfunction, Diagnostic Tests and Their Interpretation
placing them at risk for infection with Pneumocystis jiroveci. Testing for immune deficiency should be performed when the
Immune deficiency also appears to place patients at risk for patient has a history of repeated infections that exceeds