Page 518 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 518
498 ParT fOur Immunological Deficiencies
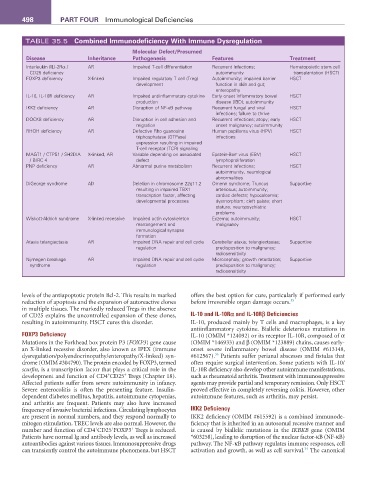
TABLE 35.5 Combined Immunodeficiency With Immune Dysregulation
Molecular Defect/Presumed
Disease Inheritance Pathogenesis features Treatment
Interleukin (IL)-2Rα / AR Impaired T-cell differentiation Recurrent infections; Hematopoietic stem cell
CD25 deficiency autoimmunity transplantation (HSCT)
FOXP3 deficiency X-linked Impaired regulatory T cell (Treg) Autoimmunity; impaired barrier HSCT
development function in skin and gut;
enteropathy
IL-10, IL-10R deficiency AR Impaired antiinflammatory cytokine Early onset inflammatory bowel HSCT
production disease (IBD); autoimmunity
IKK2 deficiency AR Disruption of NF-κB pathway Recurrent fungal and viral HSCT
infections; failure to thrive
DOCK8 deficiency AR Disruption in cell adhesion and Recurrent infections; atopy; early HSCT
migration onset malignancy; autoimmunity
RHOH deficiency AR Defective Rho guanosine Human papilloma virus (HPV) HSCT
triphosphatase (GTPase) infections
expression resulting in impaired
T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling
MAGT1 / CTPS1 / SH2DIA X-linked, AR Variable depending on associated Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) HSCT
/ BIRC 4 defect lymphoproliferation
PNP deficiency AR Abnormal purine metabolism Recurrent infections; HSCT
autoimmunity, neurological
abnormalities
DiGeorge syndrome AD Deletion in chromosome 22q11.2 Omenn syndrome; Truncus Supportive
resulting in impaired TBX1 arteriosus; autoimmunity;
transcription factor, affecting cardiac defects; hypocalcemia;
developmental processes dysmorphism; cleft palate; short
stature; neuropsychiatric
problems
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome X-linked recessive Impaired actin cytoskeleton Eczema; autoimmunity; HSCT
rearrangement and malignancy
immunological synapse
formation
Ataxia telangiectasia AR Impaired DNA repair and cell cycle Cerebellar ataxia; telangiectasias; Supportive
regulation predisposition to malignancy;
radiosensitivity
Nijmegen breakage AR Impaired DNA repair and cell cycle Microcephaly; growth retardation; Supportive
syndrome regulation predisposition to malignancy;
radiosensitivity
levels of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2. This results in marked offers the best option for cure, particularly if performed early
reduction of apoptosis and the expansion of autoreactive clones before irreversible organ damage occurs. 35
in multiple tissues. The markedly reduced Tregs in the absence
of CD25 explains the uncontrolled expansion of these clones, IL-10 and IL-10Rα and IL-10Rβ Deficiencies
resulting in autoimmunity. HSCT cures this disorder. IL-10, produced mainly by T cells and macrophages, is a key
antiinflammatory cytokine. Biallelic deleterious mutations in
FOXP3 Deficiency IL-10 (OMIM *124092) or its receptor IL-10R, composed of α
Mutations in the Forkhead box protein P3 (FOXP3) gene cause (OMIM *146933) and β (OMIM *123889) chains, causes early-
an X-linked recessive disorder, also known as IPEX (immune onset severe inflammatory bowel disease (OMIM #613148,
36
dysregulation/polyendocrinopathy/enteropathy/X-linked) syn- #612567). Patients suffer perianal abscesses and fistulas that
drome (OMIM #304790). The protein encoded by FOXP3, termed often require surgical intervention. Some patients with IL-10/
scurfin, is a transcription factor that plays a critical role in the IL-10R deficiency also develop other autoimmune manifestations,
+
+
development and function of CD4 CD25 Tregs (Chapter 18). such as rheumatoid arthritis. Treatment with immunosuppressive
Affected patients suffer from severe autoimmunity in infancy. agents may provide partial and temporary remission. Only HSCT
Severe enterocolitis is often the presenting feature. Insulin- proved effective in completely reversing colitis. However, other
dependent diabetes mellitus, hepatitis, autoimmune cytopenias, autoimmune features, such as arthritis, may persist.
and arthritis are frequent. Patients may also have increased
frequency of invasive bacterial infections. Circulating lymphocytes IKK2 Deficiency
are present in normal numbers, and they respond normally to IKK2 deficiency (OMIM #615592) is a combined immunode-
mitogen stimulation. TREC levels are also normal. However, the ficiency that is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner and
+
+
+
number and function of CD4 CD25 FOXP3 Tregs is reduced. is caused by biallelic mutations in the IKBKB gene (OMIM
Patients have normal Ig and antibody levels, as well as increased *603258), leading to disruption of the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)
autoantibodies against various tissues. Immunosuppressive drugs pathway. The NF-κB pathway regulates immune responses, cell
34
can transiently control the autoimmune phenomena, but HSCT activation and growth, as well as cell survival. The canonical