Page 531 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 531
510 ParT fOur Immunological Deficiencies
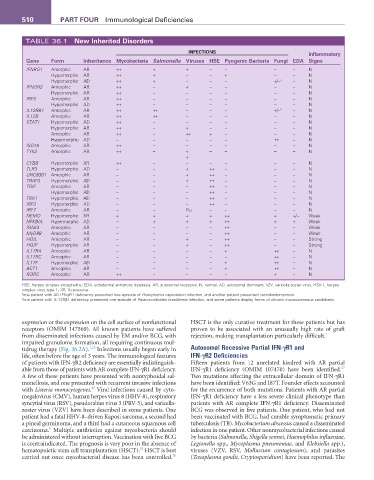
TABLE 36.1 New Inherited Disorders
INfECTIONS Inflammatory
Gene form Inheritance Mycobacteria Salmonella Viruses HSE Pyogenic Bacteria fungi EDa Signs
IFNRG1 Amorphic AR ++ + + − − − − N
Hypomorphic AR ++ + − − + − − N
Hypomorphic AD ++ + − − − +/− a − N
IFNGR2 Amorphic AR ++ − + − − − − N
Hypomorphic AR ++ − − − − − − N
IRF8 Amorphic AR ++ − − − − − − N
Hypomorphic AD ++ − − − − − − N
IL12RB1 Amorphic AR ++ ++ − − − +/− b − N
IL12B Amorphic AR ++ ++ − − − − − N
STAT1 Hypomorphic AD ++ − − − − − − N
Hypomorphic AR ++ − + − − − − N
Amorphic AR ++ − ++ + − − − N
Hypermorphic AD − − − − − ++ − N
ISG15 Amorphic AR ++ − − − − − − N
TYK2 Amorphic AR ++ − + − − − − N
+
CYBB Hypomorphic XR ++ − − − − − − N
TLR3 Hypomorphic AD − − + ++ − − − N
UNC93B1 Amorphic AR − − + ++ − − − N
TRAF3 Hypomorphic AD − − + ++ − − − N
TRIF Amorphic AR − − − ++ − − − N
Hypomorphic AD − − − ++ − − − N
TBK1 Hypomorphic AD − − − ++ − − − N
IRF3 Hypomorphic AD − − − ++ − − − N
IRF7 Amorphic AR − − Flu − − − − N
NEMO Hypomorphic XR + + + + ++ + +/− Weak
NFKBIA Hypermorphic AD − + + + ++ + + Weak
IRAK4 Amorphic AR − − − − ++ − − Weak
MyD88 Amorphic AR − − − − ++ − − Weak
HOIL Amorphic AR − − + − ++ − − Strong
HOIP Hypomorphic AR − − + − ++ − − Strong
IL17RA Amorphic AR − − − − + ++ − N
IL17RC Amorphic AR − − − − − ++ − N
IL17F Hypomorphic AD − − − − + ++ − N
ACT1 Amorphic AR − − − − + ++ − N
RORC Amorphic AR ++ − − − − + − N
HSE, herpes simplex encephalitis; EDA, ectodermal anhidrotic dysplasia; AR, autosomal recessive; N, normal; AD, autosomal dominant; VZV, varicella-zoster virus; HSV-1, herpes
simplex virus type 1; XR, X-recessive.
a one patient with AD IFN-γR1 deficiency presented one episode of Histoplasma capsulatum infection, and another patient presented coccidioidomycosis.
b one patient with IL-12Rβ1 deficiency presented one episode of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis infection, and some patients display forms of chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis.
expression or the expression on the cell surface of nonfunctional HSCT is the only curative treatment for these patients but has
receptors (OMIM 147569). All known patients have suffered proven to be associated with an unusually high rate of graft
from disseminated infections caused by EM and/or BCG, with rejection, making transplantation particularly difficult. 1
impaired granuloma formation, all requiring continuous mul-
tidrug therapy (Fig. 36.2A). 1,25 Infections usually began early in Autosomal Recessive Partial IFN-γR1 and
life, often before the age of 3 years. The immunological features IFN-γR2 Deficiencies
of patients with IFN-γR2 deficiency are essentially indistinguish- Fifteen patients from 12 unrelated kindred with AR partial
27
able from those of patients with AR complete IFN-γR1 deficiency. IFN-γR1 deficiency (OMIM 107470) have been identified.
A few of these patients have presented with nontyphoidal sal- Two mutations affecting the extracellular domain of IFN-γR1
monellosis, and one presented with recurrent invasive infections have been identified: V63G and I87T. Founder effects accounted
25
with Listeria monocytogenes. Viral infections caused by cyto- for the recurrence of both mutations. Patients with AR partial
megalovirus (CMV), human herpes virus 8 (HHV-8), respiratory IFN-γR1 deficiency have a less severe clinical phenotype than
syncytial virus (RSV), pseudorabies virus 3 (PRV-3), and varicella- patients with AR complete IFN-γR1 deficiency. Disseminated
zoster virus (VZV) have been described in some patients. One BCG was observed in five patients. One patient, who had not
patient had a fatal HHV-8–driven Kaposi sarcoma, a second had been vaccinated with BCG, had curable symptomatic primary
a pineal germinoma, and a third had a cutaneous squamous cell tuberculosis (TB). Mycobacterium abscessus caused a disseminated
1
carcinoma. Multiple antibiotics against mycobacteria should infection in one patient. Other nonmycobacterial infections caused
be administered without interruption. Vaccination with live BCG by bacteria (Salmonella, Shigella sonnei, Haemophilus influenzae,
is contraindicated. The prognosis is very poor in the absence of Legionella spp., Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Klebsiella spp.),
25
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). HSCT is best viruses (VZV, RSV, Molluscum contagiosum), and parasites
26
carried out once mycobacterial disease has been controlled. (Toxoplasma gondii, Cryptosporidium) have been reported. The