Page 532 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 532
CHaPTEr 36 Immunodeficiencies at the Interface of Innate and Adaptive Immunity 511
ISG15
p19 IL-12Rβ1 TYK2
Mycobacteria IL-23R JAK2
p40 IL-12Rβ1 TYK2
gp91phox IL-12 p35 IL-12Rβ2 JAK2
NF-κB NEMO
CD40 CD40L
IRF-8 IRF-1
IFNγR1 IFNγ
STAT1 IFNγR2 IFNγR1
IFNγ IFNγR2
Antigen presenting cell T lymphocyte and NK cell
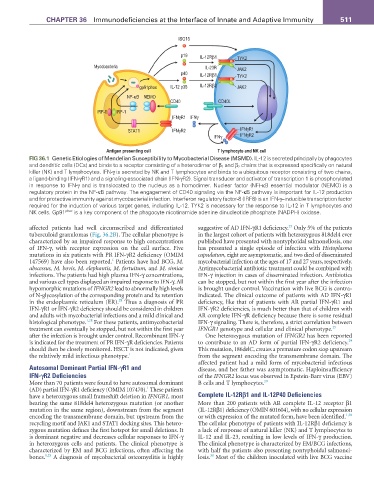
fIG 36.1 Genetic Etiologies of Mendelian Susceptibility to Mycobacterial Disease (MSMD). IL-12 is secreted principally by phagocytes
and dendritic cells (DCs) and binds to a receptor consisting of a heterodimer of β 1 and β 2 chains that is expressed specifically on natural
killer (NK) and T lymphocytes. IFN-γ is secreted by NK and T lymphocytes and binds to a ubiquitous receptor consisting of two chains,
a ligand-binding (IFN-γR1) and a signaling-associated chain (IFN-γR2). Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 is phosphorylated
in response to IFN-γ and is translocated to the nucleus as a homodimer. Nuclear factor (NF)-κB essential modulator (NEMO) is a
regulatory protein in the NF-κB pathway. The engagement of CD40 signaling via the NF-κB pathway is important for IL-12 production
and for protective immunity against mycobacterial infection. Interferon regulatory factor-8 (IRF8) is an IFN-γ–inducible transcription factor
required for the induction of various target genes, including IL-12. TYK2 is necessary for the response to IL-12 in T lymphocytes and
NK cells. Gp91 phox is a key component of the phagocyte nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase.
25
affected patients had well circumscribed and differentiated suggestive of AD IFN-γR1 deficiency. Only 5% of the patients
tuberculoid granulomas (Fig. 36.2B). The cellular phenotype is in the largest cohort of patients with heterozygous 818del4 ever
characterized by an impaired response to high concentrations published have presented with nontyphoidal salmonellosis, one
of IFN-γ, with receptor expression on the cell surface. Five has presented a single episode of infection with Histoplasma
mutations in six patients with PR IFN-γR2 deficiency (OMIM capsulatum, eight are asymptomatic, and two died of disseminated
1
147569) have also been reported. Patients have had BCG, M. mycobacterial infection at the ages of 17 and 27 years, respectively.
abscessus, M. bovis, M. elephantis, M. fortuitum, and M. simiae Antimycobacterial antibiotic treatment could be combined with
infections. The patients had high plasma IFN-γ concentrations, IFN-γ injection in cases of disseminated infection. Antibiotics
and various cell types displayed an impaired response to IFN-γ. All can be stopped, but not within the first year after the infection
hypomorphic mutations of IFNGR2 lead to abnormally high levels is brought under control. Vaccination with live BCG is contra-
of N-glycosylation of the corresponding protein and its retention indicated. The clinical outcome of patients with AD IFN-γR1
28
in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Thus a diagnosis of PR deficiency, like that of patients with AR partial IFN-γR1 and
IFN-γR1 or IFN-γR2 deficiency should be considered in children IFN-γR2 deficiencies, is much better than that of children with
and adults with mycobacterial infections and a mild clinical and AR complete IFN-γR deficiency because there is some residual
histological phenotype. 1,28 For these patients, antimycobacterial IFN-γ signaling. There is, therefore, a strict correlation between
treatment can eventually be stopped, but not within the first year IFNGR1 genotype and cellular and clinical phenotype. 25
after the infection is brought under control. Recombinant IFN-γ One heterozygous mutation of IFNGR2 has been reported
29
is indicated for the treatment of PR IFN-γR deficiencies. Patients to contribute to an AD form of partial IFN-γR2 deficiency.
should then be closely monitored. HSCT is not indicated, given This mutation, 186delC, creates a premature codon stop upstream
the relatively mild infectious phenotype. 1 from the segment encoding the transmembrane domain. The
affected patient had a mild form of mycobacterial infectious
Autosomal Dominant Partial IFN-γR1 and disease, and her father was asymptomatic. Haploinsufficiency
IFN-γR2 Deficiencies of the IFNGR2 locus was observed in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
More than 70 patients were found to have autosomal dominant B cells and T lymphocytes. 29
1
(AD) partial IFN-γR1 deficiency (OMIM 107470). These patients
have a heterozygous small frameshift deletion in IFNGR1, most Complete IL-12Rβ1 and IL-12P40 Deficiencies
bearing the same 818del4 heterozygous mutation (or another More than 200 patients with AR complete IL-12 receptor β1
mutation in the same region), downstream from the segment (IL-12Rβ1) deficiency (OMIN 601604), with no cellular expression
encoding the transmembrane domain, but upstream from the or with expression of the mutated form, have been identified. 1,30
recycling motif and JAK1 and STAT1 docking sites. This hetero- The cellular phenotype of patients with IL-12Rβ1 deficiency is
zygous mutation defines the first hotspot for small deletions. It a lack of response of natural killer (NK) and T lymphocytes to
is dominant negative and decreases cellular responses to IFN-γ IL-12 and IL-23, resulting in low levels of IFN-γ production.
in heterozygous cells and patients. The clinical phenotype is The clinical phenotype is characterized by EM/BCG infections,
characterized by EM and BCG infections, often affecting the with half the patients also presenting nontyphoidal salmonel-
30
bones. 1,25 A diagnosis of mycobacterial osteomyelitis is highly losis. Most of the children inoculated with live BCG vaccine