Page 533 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 533
512 ParT fOur Immunological Deficiencies
produce abnormally low levels of IFN-γ because of a lack of
stimulation through the IL-12R. This defect can be partially
corrected, in a dose-dependent manner, with exogenous recom-
binant IFN-γ. 1,33 All children inoculated with live BCG vaccine
developed clinical infection, and infections caused by EM or M.
tuberculosis have also been reported. Other infections, such as
salmonellosis, klebsiellosis, and nocardiosis, have been described.
Five of the reported patients are asymptomatic. Thirteen of the
50 patients died before the age of 8 years, and one patient died
at the age of 34 years. 1,33
For IL-12p40 and IL-12Rβ1 deficiencies, antibiotic treatment
can be combined with IFN-γ injection in cases of disseminated
1
infection. Antibiotics can be stopped, but not within the first
year after the infection is brought under control. Infectious
Salmonella disease should be treated with antibiotics or with
IFN-γ and antibiotics in patients with recurrent salmonellosis.
Thus a diagnosis of IL-12p40 or IL-12Rβ1 deficiency should be
considered in children and adults with mycobacterial and Sal-
A
monella infections or mycobacterial infections and CMC with
a mild clinical and histological phenotype. The vaccination of
1,33
these patients with live BCG is contraindicated. The prognosis
is, nevertheless, good, partly because of the incomplete clinical
penetrance of primary mycobacterial infection, the favorable
response of infections to treatment, and the rarity of recurrent
or multiple mycobacterial infections. Indeed, children with
primary mycobacterial disease can mount a fully protective
immune response against a secondary mycobacterial disease.
THEraPEuTIC PrINCIPLES
Treatment of Mendelian Susceptibility to
Mycobacterial Disease (MSMD) Patients
• Vaccination with live Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is contraindicated.
• Multiple antibiotics against mycobacteria should be administered
without interruption in patients with complete interferon (IFN)-γR1 or
B IFN-γR2 deficiency.
• Antimycobacterial antibiotics may be associated with IFN-γ injections
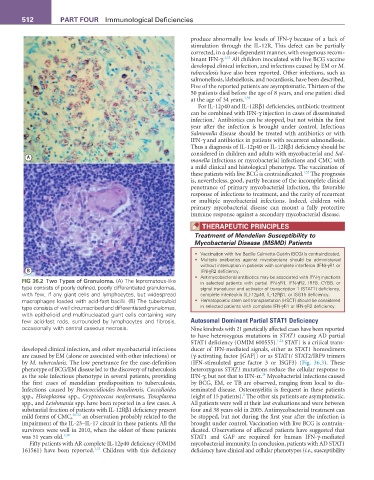
fIG 36.2 Two Types of Granuloma. (A) The lepromatous-like in selected patients with partial IFN-γR1, IFN-γR2, IRF8, CYBB, or
type consists of poorly defined, poorly differentiated granulomas, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) deficiency,
with few, if any giant cells and lymphocytes, but widespread complete interleukin (IL)-12p40, IL-12Rβ1, or ISG15 deficiency.
macrophages loaded with acid-fast bacilli. (B) The tuberculoid • Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) should be considered
type consists of well circumscribed and differentiated granulomas, in selected patients with complete IFN-γR1 or IFN-γR2 deficiency.
with epithelioid and multinucleated giant cells containing very
few acid-fast rods, surrounded by lymphocytes and fibrosis, Autosomal Dominant Partial STAT1 Deficiency
occasionally with central caseous necrosis. Nine kindreds with 21 genetically affected cases have been reported
to have heterozygous mutations in STAT1 causing AD partial
STAT1 deficiency (OMIM 600555). 1,24 STAT1 is a critical trans-
developed clinical infection, and other mycobacterial infections ducer of IFN-mediated signals, either as STAT1 homodimers
are caused by EM (alone or associated with other infections) or (γ-activating factor [GAF]) or as STAT1/ STAT2/IRF9 trimers
by M. tuberculosis. The low penetrance for the case-definition (IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 or ISGF3) (Fig. 36.3). These
phenotype of BCG/EM disease led to the discovery of tuberculosis heterozygous STAT1 mutations reduce the cellular response to
24
as the sole infectious phenotype in several patients, providing IFN-γ, but not that to IFN-α. Mycobacterial infections caused
the first cases of mendelian predisposition to tuberculosis. by BCG, EM, or TB are observed, ranging from local to dis-
Infections caused by Paracoccidioides brasiliensis, Coccidioides seminated disease. Osteomyelitis is frequent in these patients
1
spp., Histoplasma spp., Cryptococcus neoformans, Toxoplasma (eight of 15 patients). The other six patients are asymptomatic.
spp., and Leishmania spp. have been reported in a few cases. A All patients were well at their last evaluations and were between
substantial fraction of patients with IL-12Rβ1 deficiency present four and 38 years old in 2005. Antimycobacterial treatment can
mild forms of CMC, 30-32 an observation probably related to the be stopped, but not during the first year after the infection is
impairment of the IL-23–IL-17 circuit in these patients. All the brought under control. Vaccination with live BCG is contrain-
survivors were well in 2010, when the oldest of these patients dicated. Observations of affected patients have suggested that
was 51 years old. 1,30 STAT1 and GAF are required for human IFN-γ-mediated
Fifty patients with AR complete IL-12p40 deficiency (OMIM mycobacterial immunity. In conclusion, patients with AD STAT1
161561) have been reported. 1,33 Children with this deficiency deficiency have clinical and cellular phenotypes (i.e., susceptibility