Page 534 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 534
CHaPTEr 36 Immunodeficiencies at the Interface of Innate and Adaptive Immunity 513
IFN-γ IFN-α/β other infectious agents. In two other patients with a history of
pure MSMD, the same heterozygous mutation, T80A, was found
23
in IRF8, defining an AD IRF8 deficiency. The mutation was
severely hypomorphic and dominant negative. Interestingly, the
IFN-γ circuit did not appear to be disrupted in tests on whole
blood. Nevertheless, the two unrelated patients with AD IRF8
23
cytoplasmic deficiency lacked circulating CD1c CD11c DCs. This population
membrane of cells produces large amounts of IL-12 in normal individuals,
and its absence therefore probably contributed to the MSMD
phenotype.
AR Complete ISG15 Deficiency
STAT-1/STAT-1 STAT-1/STAT-2/IRF-9 Recently, six patients with complete AR ISG15 deficiency have
(GAF) (ISGF-3) nucleus been identified (OMIM 616126). 34,35 Three of the six patients
membrane
suffered from clinical disease caused by BCG vaccine. The only
features common to all patients were calcifications of the basal
ganglia in the brain. The cellular phenotype was characterized
by an impaired, but not abolished, IFN-γ production upon whole
GAS ISRE blood activation by BCG plus IL-12, as seen in patients with
antimycobacterial immunity antiviral immunity IL-12p40 or IL-12Rβ1 deficiency. 1,34,35 The addition of recom-
binant ISG15 rescued the production of IFN-γ by T and NK
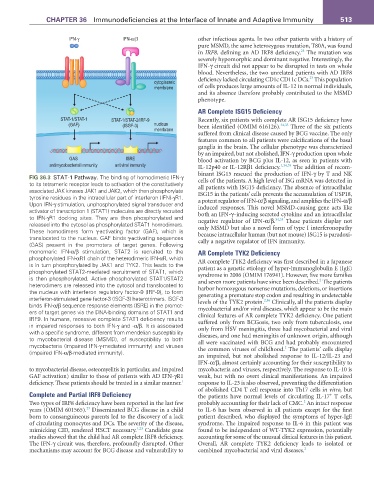
fIG 36.3 STAT-1 Pathway. The binding of homodimeric IFN-γ
to its tetrameric receptor leads to activation of the constitutively cells of the patients. A high level of ISG mRNA was detected in
associated JAK kinases JAK1 and JAK2, which then phosphorylate all patients with ISG15 deficiency. The absence of intracellular
tyrosine residues in the intracellular part of interferon (IFN)-γR1. ISG15 in the patients’ cells prevents the accumulation of USP18,
Upon IFN-γ stimulation, unphosphorylated signal transducer and a potent regulator of IFN-α/β signaling, and amplifies the IFN-α/β
activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) molecules are directly recruited induced responses. This novel MSMD-causing gene acts like
to IFN-γR1 docking sites. They are then phosphorylated and both an IFN-γ–inducing secreted cytokine and an intracellular
34,35
released into the cytosol as phosphorylated STAT1 homodimers. negative regulator of IFN-α/β. These patients display not
These homodimers form γ-activating factor (GAF), which is only MSMD but also a novel form of type I interferonopathy
translocated to the nucleus. GAF binds γ-activating sequences because intracellular human (but not mouse) ISG15 is paradoxi-
(GAS) present in the promoters of target genes. Following cally a negative regulator of IFN immunity.
monomeric IFN-α/β stimulation, STAT2 is recruited to the AR Complete TYK2 Deficiency
phosphorylated IFN-αR1 chain of the heterodimeric IFN-αR, which
is in turn phosphorylated by JAK1 and TYK2. This leads to the AR complete TYK2 deficiency was first described in a Japanese
phosphorylated STAT2-mediated recruitment of STAT1, which patient as a genetic etiology of hyper-immunoglobulin E (IgE)
is then phosphorylated. Active phosphorylated STAT1/STAT2 syndrome in 2006 (OMIM 176941). However, five more families
2
heterodimers are released into the cytosol and translocated to and seven more patients have since been described. The patients
the nucleus with interferon regulatory factor-9 (IRF-9), to form harbor homozygous nonsense mutations, deletions, or insertions
interferon-stimulated gene factor-3 (ISGF-3) heterotrimers. ISGF-3 generating a premature stop codon and resulting in undetectable
2,36
binds IFN-α/β sequence response elements (ISRE) in the promot- levels of the TYK2 protein. Clinically, all the patients display
ers of target genes via the DNA-binding domains of STAT1 and mycobacterial and/or viral diseases, which appear to be the main
IRF9. In humans, recessive complete STAT1 deficiency results clinical features of AR complete TYK2 deficiency. One patient
in impaired responses to both IFN-γ and -α/β. It is associated suffered only from BCGosis, two only from tuberculosis, one
with a specific syndrome, different from mendelian susceptibility only from HSV meningitis, three had mycobacterial and viral
to mycobacterial disease (MSMD), of susceptibility to both diseases, and one had meningitis of unknown origin, although
mycobacteria (impaired IFN-γ-mediated immunity) and viruses all were vaccinated with BCG and had probably encountered
2
(impaired IFN-α/β-mediated immunity). the common viruses of childhood. The patients’ cells display
an impaired, but not abolished response to IL-12/IL-23 and
IFN-α/β, almost certainly accounting for their susceptibility to
to mycobacterial disease, osteomyelitis in particular, and impaired mycobacteria and viruses, respectively. The response to IL-10 is
GAF activation) similar to those of patients with AD IFN-γR1 weak, but with no overt clinical manifestations. An impaired
deficiency. These patients should be treated in a similar manner. 1 response to IL-23 is also observed, preventing the differentiation
of abolished CD4 T cell response into Th17 cells in vitro, but
Complete and Partial IRF8 Deficiency the patients have normal levels of circulating IL-17 T cells,
+
2
Two types of IRF8 deficiency have been reported in the last few probably accounting for their lack of CMC. An intact response
23
years (OMIM 601565). Disseminated BCG disease in a child to IL-6 has been observed in all patients except for the first
born to consanguineous parents led to the discovery of a lack patient described, who displayed the symptoms of hyper-IgE
of circulating monocytes and DCs. The severity of the disease, syndrome. The impaired response to IL-6 in this patient was
mimicking CID, rendered HSCT necessary. 1,23 Candidate gene found to be independent of WT-TYK2 expression, potentially
studies showed that the child had AR complete IRF8 deficiency. accounting for some of the unusual clinical features in this patient.
The IFN-γ circuit was, therefore, profoundly disrupted. Other Overall, AR complete TYK2 deficiency leads to isolated or
mechanisms may account for BCG disease and vulnerability to combined mycobacterial and viral diseases. 2