Page 541 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 541
520 ParT fOur Immunological Deficiencies
C. albicans IL-17A
IL-17F
IL-17RA
PRR
IL-17RC
CARD9 ACT1
RORyt
NF-κB MAPK
STAT-3 STAT1
IL-6R IFN-R
IL-6
IL-23
IL-23R IL-27R
Phagocytes, epithelial cells T lymphocytes
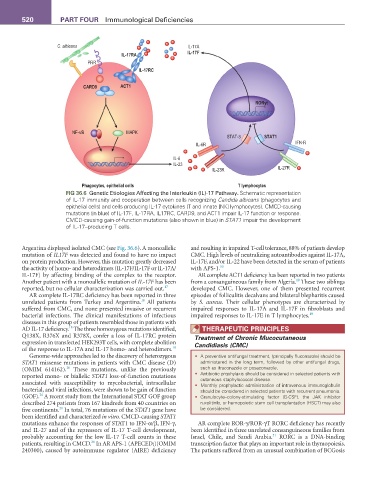
fIG 36.6 Genetic Etiologies Affecting the Interleukin (IL)-17 Pathway. Schematic representation
of IL-17 immunity and cooperation between cells recognizing Candida albicans (phagocytes and
epithelial cells) and cells producing IL-17 cytokines (T and innate [NK] lymphocytes). CMCD-causing
mutations (in blue) of IL-17F, IL-17RA, IL17RC, CARD9, and ACT1 impair IL-17 function or response.
CMCD-causing gain-of-function mutations (also shown in blue) in STAT1 impair the development
of IL-17–producing T cells.
Argentina displayed isolated CMC (see Fig. 36.6). A monoallelic and resulting in impaired T-cell tolerance, 88% of patients develop
mutation of IL17F was detected and found to have no impact CMC. High levels of neutralizing autoantibodies against IL-17A,
on protein production. However, this mutation greatly decreased IL-17F, and/or IL-22 have been detected in the serum of patients
the activity of homo- and heterodimers (IL-17F/IL-17F or IL-17A/ with APS-1. 50
IL-17F) by affecting binding of the complex to the receptor. AR complete ACT1 deficiency has been reported in two patients
19
Another patient with a monoallelic mutation of IL-17F has been from a consanguineous family from Algeria. These two siblings
reported, but no cellular characterization was carried out. 17 developed CMC. However, one of them presented recurrent
AR complete IL-17RC deficiency has been reported in three episodes of folliculitis decalvans and bilateral blepharitis caused
18
unrelated patients from Turkey and Argentina. All patients by S. aureus. Their cellular phenotypes are characterized by
suffered from CMC, and none presented invasive or recurrent impaired responses to IL-17A and IL-17F in fibroblasts and
bacterial infections. The clinical manifestations of infectious impaired responses to IL-17E in T lymphocytes. 19
diseases in this group of patients resembled those in patients with
18
AD IL-17 deficiency. The three homozygous mutations identified, THEraPEuTIC PrINCIPLES
Q138X, R376X and R378X, confer a loss of IL-17RC protein Treatment of Chronic Mucocutaneous
expression in transfected HEK293T cells, with complete abolition Candidiasis (CMC)
of the response to IL-17A and IL-17 homo- and heterodimers. 18
Genome-wide approaches led to the discovery of heterozygous • A preventive antifungal treatment, (principally fluconazole) should be
STAT1 missense mutations in patients with CMC disease (D) administered in the long term, followed by other antifungal drugs,
20
(OMIM 614162). These mutations, unlike the previously such as itraconazole or posaconazole.
reported mono- or biallelic STAT1 loss-of-function mutations • Antibiotic prophylaxis should be considered in selected patients with
cutaneous staphylococcal disease.
associated with susceptibility to mycobacterial, intracellular • Monthly prophylactic administration of intravenous immunoglobulin
bacterial, and viral infections, were shown to be gain of function should be considered in selected patients with recurrent pneumonia.
24
(GOF). A recent study from the International STAT GOF group • Granulocyte–colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), the JAK inhibitor
described 274 patients from 167 kindreds from 40 countries on ruxolitinib, or hemopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) may also
20
five continents. In total, 76 mutations of the STAT1 gene have be considered.
been identified and characterized in vitro. CMCD-causing STAT1
mutations enhance the responses of STAT1 to IFN-α/β, IFN-γ, AR complete ROR-γ/ROR-γT RORC deficiency has recently
and IL-27 and of the repressors of IL-17 T-cell development, been identified in three unrelated consanguineous families from
51
probably accounting for the low IL-17 T-cell counts in these Israel, Chile, and Saudi Arabia. RORC is a DNA-binding
20
patients, resulting in CMCD. In AR APS-1 (APECED;)(OMIM transcription factor that plays an important role in thymopoiesis.
240300), caused by autoimmune regulator (AIRE) deficiency The patients suffered from an unusual combination of BCGosis