Page 548 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 548
526 Part four Immunological Deficiencies
fIG 37.2 Chest computed tomography (CT) scan of a pneumato-
cele with secondary Mycobacterium abscessus and Pseudomonas
aeruginosa infection in a 25-year-old woman with autosomal
dominant hyper-IgE syndrome (Job’s syndrome; AD-HIES).
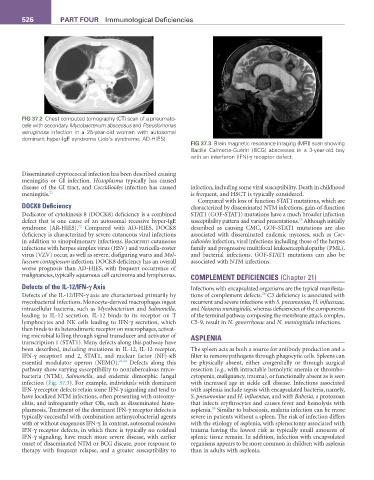
fIG 37.3 Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan showing
Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) abscesses in a 3-year-old boy
with an interferon (IFN)-γ receptor defect.
Disseminated cryptococcal infection has been described causing
meningitis or GI infection. Histoplasma typically has caused
disease of the GI tract, and Coccidioides infection has caused infection, including some viral susceptibility. Death in childhood
meningitis. 21 is frequent, and HSCT is typically considered.
Compared with loss of function STAT1 mutations, which are
DOCK8 Deficiency characterized by disseminated NTM infections, gain-of-function
Dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (DOCK8) deficiency is a combined STAT1 (GOF-STAT1) mutations have a much broader infection
25
defect that is one cause of an autosomal recessive hyper-IgE susceptibility pattern and varied presentations. Although initially
22
syndrome (AR-HIES). Compared with AD-HIES, DOCK8 described as causing CMC, GOF-STAT1 mutations are also
deficiency is characterized by severe cutaneous viral infections associated with disseminated endemic mycoses, such as Coc-
in addition to sinopulmonary infections. Recurrent cutaneous cidioides infection, viral infections including those of the herpes
infections with herpes simplex virus (HSV) and varicella-zoster family and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML),
virus (VZV) occur, as well as severe, disfiguring warts and Mol- and bacterial infections. GOF-STAT1 mutations can also be
luscum contagiosum infection. DOCK8 deficiency has an overall associated with NTM infections.
worse prognosis than AD-HIES, with frequent occurrence of
malignancies, typically squamous cell carcinoma and lymphomas. COMPLEMENT DEFICIENCIES (Chapter 21)
Defects of the IL-12/IFN-γ Axis Infections with encapsulated organisms are the typical manifesta-
26
Defects of the IL-12/IFN-γ axis are characterized primarily by tions of complement defects. C3 deficiency is associated with
mycobacterial infections. Monocyte-derived macrophages ingest recurrent and severe infections with S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae,
intracellular bacteria, such as Mycobacterium and Salmonella, and Neisseria meningitidis, whereas deficiencies of the components
leading to IL-12 secretion. IL-12 binds to its receptor on T of the terminal pathway composing the membrane attack complex,
lymphocytes and NK cells leading to IFN-γ secretion, which C5-9, result in N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis infections.
then binds to its heterodimeric receptor on macrophages, activat-
ing microbial killing through signal transducer and activator of ASPLENIA
transcription 1 (STAT1). Many defects along this pathway have
been described, including mutations in IL-12, IL-12 receptor, The spleen acts as both a source for antibody production and a
IFN-γ receptor1 and 2, STAT1, and nuclear factor (NF)-κB filter to remove pathogens through phagocytic cells. Spleens can
essential modulator operon (NEMO). 23,24 Defects along this be physically absent, either congenitally or through surgical
pathway show varying susceptibility to nontuberculous myco- resection (e.g., with intractable hemolytic anemia or thrombo-
bacteria (NTM), Salmonella, and endemic dimorphic fungal cytopenia, malignancy, trauma), or functionally absent as is seen
infection (Fig. 37.3). For example, individuals with dominant with increased age in sickle cell disease. Infections associated
IFN-γ receptor defects retain some IFN-γ signaling and tend to with asplenia include sepsis with encapsulated bacteria, namely,
have localized NTM infections, often presenting with osteomy- S. pneumoniae and H. influenzae, and with Babesia, a protozoan
elitis, and infrequently other OIs, such as disseminated histo- that infects erythrocytes and causes fever and hemolysis with
26
plasmosis. Treatment of the dominant IFN-γ receptor defects is asplenia. Similar to babesiosis, malaria infection can be more
typically successful with combination antimycobacterial agents severe in patients without a spleen. The risk of infection differs
with or without exogenous IFN-γ. In contrast, autosomal recessive with the etiology of asplenia, with splenectomy associated with
IFN-γ receptor defects, in which there is typically no residual trauma having the lowest risk as typically small amounts of
IFN-γ signaling, have much more severe disease, with earlier splenic tissue remain. In addition, infection with encapsulated
onset of disseminated NTM or BCG disease, poor response to organisms appears to be more common in children with asplenia
therapy with frequent relapse, and a greater susceptibility to than in adults with asplenia.