Page 586 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 586
562 ParT FOur Immunological Deficiencies
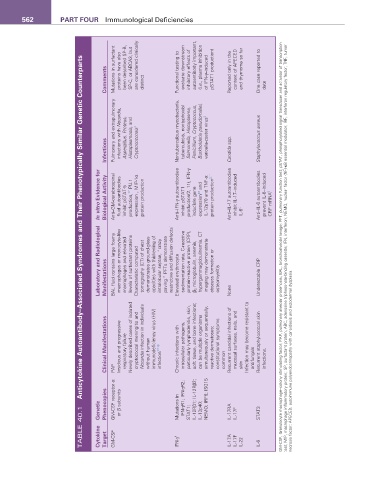
anticytokine autoantibody–associated Syndromes and Their Phenotypically Similar Genetic Counterparts
Comments Mutations in surfactant proteins have also been described SP-B, SP-C, or ABCA3, but are considered clinically distinct Functional testing to evaluate downstream inhibitory effects of autoantibody important, (i.e., plasma inhibition of IFN-γ–induced pSTAT1 production) Reported only in the context of APECED and thymoma so far One case reported to date
Pulmonary and extrapulmonary infections with Nocardia, Aspergillus, Proteus, Histoplasmosis, and Nontuberculous mycobacteria, tuberculosis, nontyphoidal Salmonella, Histoplasma, Penicillium, Cryptococcus, Burkholderia pseudomallei, varicella-zoster virus 2 Staphylococcus aureus
Infections Cryptococcosis 1 Candida spp.
In vitro Evidence for Biological activity Anti–GM-cerebrospinal fluid autoantibodies inhibit pSTAT-5 production, 17 PU.1 expression , MIP-1α protein production Anti–IFN-γ autoantibodies inhibit pSTAT1 production(2, 11), IFN-γ inducible gene expression 29 and IL-12p70 and TNF-α protein production 2,11 Anti–IL-17 autoantibodies inhibit IL-17–induced IL-6 4 Anti–IL-6 autoantibodies prevent IL-6–induced CRP mRNA 5
Laboratory and radiological Manifestations BAL fluid contains large foamy macrophages or monocyte-like macrophages and elevated levels of surfactant proteins Characteristic computed tomography (CT) of chest demonstrates ground-glass opacities with thickening of intralobular septae, “crazy paving.” PFTs demonstrate restrictive and diffusion defects 1 Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein-reactive protein (CRP), β
Clinical Manifestations PAP Insidious and progressive respiratory failure Newly described cases of isolated cryptococcal meningitis and Nocardia infection in individuals without human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection 17-19 Chronic infections with intracellular pathogens, particularly lymphadenitis, skin, soft tissue, and bone infections; can be multiple organisms simultaneously or sequentially; reactive dermatoses; constit
TABLE 40.1 Genetic Cytokine Phenocopies Target GM-CSF receptor α GM-CSF or β subunits Mutations in IFN-γ h IFN-γR1; IFN-γR2; STAT1; IL-12Rβ1; IL-12Rβ2; IL-12p40; NEMO; IRF8; ISG15 IL-17RA IL-17A IL-17F IL-17F IL-22 STAT3 IL-6