Page 589 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 589
CHaPTEr 40 Autoantibody-Mediated Phenocopies of Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases 565
and IL-17RC heterodimeric receptor complexes, ultimately
activating NF-κB. IL-22, produced by T lymphocytes and NK
cells, also signals via a heterodimeric receptor composed of
IL-22R1 and IL-10R2 subunits, expressed mainly on epithelial
B lymphocytes and other nonimmune cells. IL-17A/F and IL-22 cooperate to
induce proinflammatory cytokines involved in granulopoiesis
and neutrophil recruitment as well as antimicrobial peptides,
such as β defensins and S100 proteins, which are thought to be
important in mucosal immunity. Clinical evidence for a protective
role of IL-17 in CMC arose from the observation of this infectious
complication in diseases with varying degrees of Th17 impairment,
including STAT3-deficient hyper-IgE syndrome (HIES, or Job’s
Monocyte/ IFN-γ syndrome), dectin-1 deficiency, CARD9 deficiency, and, to a
macrophage Th1 cell lesser degree, IL-12 receptor β 1 deficiency. Strong support of
27
IFN-γ
receptor this hypothesis came via instances of two families that demon-
strated inherited susceptibility to mucosal candidiasis: one with
IL-12 an autosomal recessive mutation in IL-17RA, and another with
receptor an autosomal dominant negative mutation in IL-17F. 27
IL-12
APECED syndrome is another mendelian disorder associated
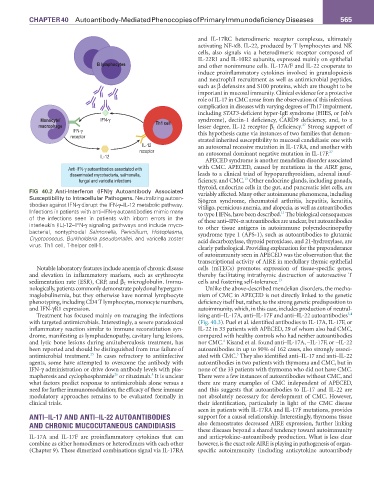
Anti-IFN-γ autoantibodies associated with with CMC. APECED, caused by mutations in the AIRE gene,
disseminated mycobacteria, salmonella, leads to a clinical triad of hypoparathyroidism, adrenal insuf-
13
fungal and varicella infections ficiency, and CMC. Other endocrine glands, including gonads,
thyroid, endocrine cells in the gut, and pancreatic islet cells, are
FIG 40.2 Anti-Interferon (IFN)γ Autoantibody Associated variably affected. Many other autoimmune phenomena, including
Susceptibility to Intracellular Pathogens. Neutralizing autoan- Sjögren syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, hepatitis, keratitis,
tibodies against IFN-γ disrupt the IFN-γ–IL-12 metabolic pathway. vitiligo, pernicious anemia, and alopecia, as well as autoantibodies
Infections in patients with anti–IFN-γ autoantibodies mimic many to type I IFNs, have been described. The biological consequences
13
of the infections seen in patients with inborn errors in the of these anti–IFN-α autoantibodies are unclear, but autoantibodies
interleukin (IL)-12–IFN-γ signaling pathways and include myco- to other tissue antigens in autoimmune polyendocrinopathy
bacterial, nontyphoidal Salmonella, Penicillium, Histoplasma, syndrome type 1 (APS-1), such as autoantibodies to glutamic
Cryptococcus, Burkholderia pseudomallei, and varicella zoster acid decarboxylase, thyroid peroxidase, and 21-hydroxylase, are
virus. Th1 cell, T-helper cell-1.
clearly pathological. Providing explanation for the preponderance
of autoimmunity seen in APECED was the observation that the
transcriptional activity of AIRE in medullary thymic epithelial
Notable laboratory features include anemia of chronic disease cells (mTECs) promotes expression of tissue-specific genes,
and elevation in inflammatory markers, such as erythrocyte thereby facilitating intrathymic destruction of autoreactive T
sedimentation rate (ESR), CRP, and β 2 microglobulin. Immu- cells and fostering self-tolerance. 13
nologically, patients commonly demonstrate polyclonal hypergam- Unlike the above-described mendelian disorders, the mecha-
maglobulinemia, but they otherwise have normal lymphocyte nism of CMC in APECED is not directly linked to the genetic
phenotyping, including CD4 T lymphocytes, monocyte numbers, deficiency itself but, rather, to the strong genetic predisposition to
and IFN-γR1 expression. autoimmunity, which, in this case, includes production of neutral-
3,4
Treatment has focused mainly on managing the infections izing anti–IL-17A, anti–IL-17F and anti–IL-22 autoantibodies
with targeted antimicrobials. Interestingly, a severe paradoxical (Fig. 40.3). Puel et al. identified antibodies to IL-17A, IL-17F, or
inflammatory reaction similar to immune reconstitution syn- IL-22 in 33 patients with APECED, 29 of whom also had CMC,
drome, manifesting as lymphadenopathy, cavitary lung lesions, compared with healthy controls who had neither autoantibodies
4
and lytic bone lesions during antituberculosis treatment, has nor CMC. Kisand et al. found anti–IL-17A, –IL-17F, or –IL-22
been reported and should be distinguished from true failure of autoantibodies in up to 90% of 162 cases, also strongly associ-
3
25
antimicrobial treatment. In cases refractory to antiinfective ated with CMC. They also identified anti–IL-17 and anti–IL-22
agents, some have attempted to overcome the antibody with autoantibodies in two patients with thymoma and CMC, but in
IFN-γ administration or drive down antibody levels with plas- none of the 33 patients with thymoma who did not have CMC.
8
26
mapheresis and cyclophosphamide or rituximab. It is unclear There were a few instances of autoantibodies without CMC, and
what factors predict response to antimicrobials alone versus a there are many examples of CMC independent of APECED,
need for further immunomodulation; the efficacy of these immune and this suggests that autoantibodies to IL-17 and IL-22 are
modulatory approaches remains to be evaluated formally in not absolutely necessary for development of CMC. However,
clinical trials. their identification, particularly in light of the CMC disease
seen in patients with IL-17RA and IL-17F mutations, provides
ANTI–IL-17 AND ANTI–IL-22 AUTOANTIBODIES support for a causal relationship. Interestingly, thymoma tissue
AND CHRONIC MUCOCUTANEOUS CANDIDIASIS also demonstrates decreased AIRE expression, further linking
these diseases beyond a shared tendency toward autoimmunity
IL-17A and IL-17F are proinflammatory cytokines that can and anticytokine–autoantibody production. What is less clear
combine as either homodimers or heterodimers with each other however, is the exact role AIRE is playing in pathogenesis of organ-
(Chapter 9). These dimerized combinations signal via IL-17RA specific autoimmunity (including anticytokine autoantibody