Page 590 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 590
566 ParT FOur Immunological Deficiencies
MANAGEMENT
Therapies directed at the syndromes of pathogenic autoantibodies
have focused either on treating the disease consequences or
B lymphocytes
targeting the autoantibody itself. Therapeutic BAL removes
proteinaceous alveolar material from the lungs of patients with
1
PAP, and antimycobacterials treat the disseminated NTM infec-
tion in patients with autoantibodies to IFN-γ. 9,29 Approaches
ranging from physical removal of the antibody, to immuno-
modulatory therapy, to induction of immune tolerance or
suppression of the population of cells that produce the pathogenic
autoantibodies have also been employed.
Epithelial PAP and disseminated NTM associated with anti–IFN-γ
IL-22 IL-22 20,21
Th17 cell cell autoantibodies have been treated with exogenous GM-CSF
receptor and IFN-γ, respectively, resulting in clinical improvement,
29
although PAP has been studied more rigorously in this regard.
IL-17A Autoantibody levels after therapy were not routinely evaluated
IL-17F across diseases, nor are they performed in a standardized fashion,
IL-17
receptor although, at least in the PAP cohorts, it appears they do not
change in response to exogenous cytokine. 20,21
Anti-IL-22, anti-IL17A and anti-IL-17F In cases that are refractory to treatment, attempts have been
autoantibodies associated with mucocutaneous made to alleviate the blockade by reducing anticytokine–
candidiasis in APECED and thymoma patients autoantibody levels. One patient with anti–IFN-γ autoantibodies
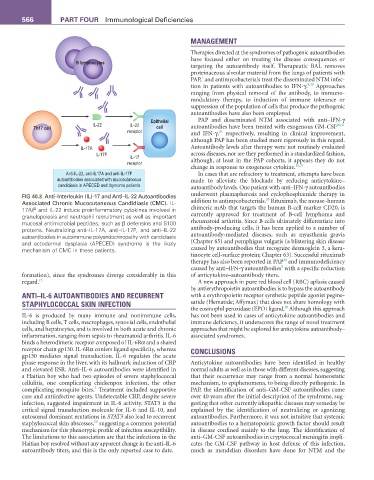
FIG 40.3 Anti–Interleukin (IL)-17 and Anti–IL-22 Autoantibodies underwent plasmapheresis and cyclophosphamide therapy in
26
Associated Chronic Mucocutaneous Candidiasis (CMC). IL- addition to antimycobacterials. Rituximab, the mouse–human
17A/F and IL-22 induce proinflammatory cytokines involved in chimeric mAb that targets the human B-cell marker CD20, is
granulopoiesis and neutrophil recruitment as well as important currently approved for treatment of B-cell lymphoma and
mucosal antimicrobial peptides, such as β defensins and S100 rheumatoid arthritis. Since B cells ultimately differentiate into
proteins. Neutralizing anti–IL-17A, anti–IL-17F, and anti–IL-22 antibody-producing cells, it has been applied to a number of
autoantibodies in autoimmune polyendocrinopathy with candidiasis autoantibody-mediated diseases, such as myasthenia gravis
and ectodermal dysplasia (APECED) syndrome is the likely (Chapter 65) and pemphigus vulgaris (a blistering skin disease
mechanism of CMC in these patients. caused by autoantibodies that recognize desmoglein 3, a kera-
tinocyte cell-surface protein; Chapter 63). Successful rituximab
22
therapy has also been reported in PAP and immunodeficiency
8
caused by anti–IFN-γ autoantibodies with a specific reduction
formation), since the syndromes diverge considerably in this of anticytokine–autoantibody titers.
regard. 13 A new approach in pure red blood cell (RBC) aplasia caused
by antierythropoietin autoantibodies is to bypass the autoantibody
ANTI–IL-6 AUTOANTIBODIES AND RECURRENT with a erythropoietin receptor synthetic peptide agonist pegine-
STAPHYLOCOCCAL SKIN INFECTION satide (Hematide; Affymax) that does not share homology with
30
the eosinophil peroxidase (EPO) ligand. Although this approach
IL-6 is produced by many immune and nonimmune cells, has not been used in cases of anticytokine autoantibodies and
including B cells, T cells, macrophages, synovial cells, endothelial immune deficiency, it underscores the range of novel treatment
cells, and hepatocytes, and is involved in both acute and chronic approaches that might be explored for anticytokine autoantibody–
inflammation, ranging from sepsis to rheumatoid arthritis. IL-6 associated syndromes.
binds a heterodimeric receptor composed of IL-6Rα and a shared
receptor chain gp130. IL-6Rα confers ligand specificity, whereas CONCLUSIONS
gp130 mediates signal transduction. IL-6 regulates the acute
phase response in the liver, with its hallmark induction of CRP Anticytokine autoantibodies have been identified in healthy
and elevated ESR. Anti–IL-6 autoantibodies were identified in normal adults as well as in those with different diseases, suggesting
a Haitian boy who had two episodes of severe staphylococcal that their occurrence may range from a normal homeostatic
cellulitis, one complicating chickenpox infection, the other mechanism, to epiphenomena, to being directly pathogenic. In
5
complicating mosquito bites. Treatment included supportive PAP, the identification of anti–GM-CSF autoantibodies came
care and antiinfective agents. Undetectable CRP, despite severe over 40 years after the initial description of the syndrome, sug-
infection, suggested impairment in IL-6 activity. STAT3 is the gesting that other currently idiopathic diseases may someday be
critical signal transduction molecule for IL-6 and IL-10, and explained by the identification of neutralizing or agonizing
autosomal dominant mutations in STAT3 also lead to recurrent autoantibodies. Furthermore, it was not intuitive that systemic
28
staphylococcal skin abscesses, suggesting a common potential autoantibodies to a hematopoietic growth factor should result
mechanism for this phenotypic profile of infection susceptibility. in disease confined mainly to the lung. The identification of
The limitations to this association are that the infections in the anti–GM-CSF autoantibodies in cryptococcal meningitis impli-
Haitian boy resolved without any apparent change in the anti–IL-6 cates the GM-CSF pathway in host defense of this infection,
autoantibody titers, and this is the only reported case to date. much as mendelian disorders have done for NTM and the