Page 612 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 612
CHaPTEr 42 Urticaria, Angioedema, and Anaphylaxis 589
acute urticaria; atopic diseases are found in about half the patients
3
with acute urticaria. Most acute urticaria resolves spontaneously
within 3 weeks, but in 10% of patients, it may progress to CSU.
Infections are the most common identifiable cause of acute
urticaria, with some cases resulting from foods or drugs. A specific
cause of acute urticaria will not be found in about 50% of patients.
Foods are the most common cause of acute urticaria in young
children but are rarely responsible for acute urticaria in adults.
In infancy, cow’s milk allergy may cause acute allergic urticaria.
Drug-induced urticaria is the most common presentation of
drug hypersensitivity, accounting for a quarter of all adverse
drug reactions, with penicillin and NSAIDs being the most
common causes of allergic and nonallergic drug-induced urticaria,
respectively. Drug-induced urticaria is more likely in older adults,
perhaps reflecting polypharmacy and age-related pharmacokinetic
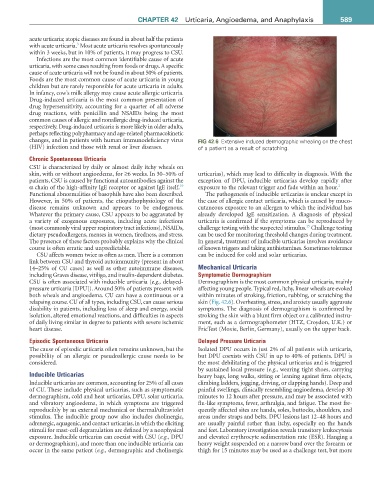
changes, and in patients with human immunodeficiency virus fiG 42.6 Extensive induced dermographic whealing on the chest
(HIV) infection and those with renal or liver diseases. of a patient as a result of scratching.
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
CSU is characterized by daily or almost daily itchy wheals on
skin, with or without angioedema, for ≥6 weeks. In 30–50% of urticarias), which may lead to difficulty in diagnosis. With the
patients, CSU is caused by functional autoantibodies against the exception of DPU, inducible urticarias develop rapidly after
10
α chain of the high-affinity IgE receptor or against IgE itself. exposure to the relevant trigger and fade within an hour. 2
Functional abnormalities of basophils have also been described. The pathogenesis of inducible urticarias is unclear except in
However, in 50% of patients, the etiopathophysiology of the the case of allergic contact urticaria, which is caused by muco-
disease remains unknown and appears to be endogenous. cutaneous exposure to an allergen to which the individual has
Whatever the primary cause, CSU appears to be aggravated by already developed IgE sensitization. A diagnosis of physical
a variety of exogenous exposures, including acute infections urticaria is confirmed if the symptoms can be reproduced by
15
(most commonly viral upper respiratory tract infections), NSAIDs, challenge testing with the suspected stimulus. Challenge testing
dietary pseudoallergens, menses in women, tiredness, and stress. can be used for monitoring threshold changes during treatment.
The presence of these factors probably explains why the clinical In general, treatment of inducible urticarias involves avoidance
course is often erratic and unpredictable. of known triggers and taking antihistamines. Sometimes tolerance
CSU affects women twice as often as men. There is a common can be induced for cold and solar urticarias.
link between CSU and thyroid autoimmunity (present in about
14–25% of CU cases) as well as other autoimmune diseases, Mechanical Urticaria
including Graves disease, vitiligo, and insulin-dependent diabetes. Symptomatic Dermographism
CSU is often associated with inducible urticaria (e.g., delayed- Dermographism is the most common physical urticaria, mainly
pressure urticaria [DPU]). Around 50% of patients present with affecting young people. Typical red, itchy, linear wheals are evoked
both wheals and angioedema. CU can have a continuous or a within minutes of stroking, friction, rubbing, or scratching the
relapsing course. CU of all types, including CSU, can cause serious skin (Fig. 42.6). Overheating, stress, and anxiety usually aggravate
disability in patients, including loss of sleep and energy, social symptoms. The diagnosis of dermographism is confirmed by
isolation, altered emotional reactions, and difficulties in aspects stroking the skin with a blunt firm object or a calibrated instru-
of daily living similar in degree to patients with severe ischemic ment, such as a dermographometer (HTZ, Croydon, U.K.) or
heart disease. FricTest (Moxie, Berlin, Germany), usually on the upper back.
Episodic Spontaneous Urticaria Delayed Pressure Urticaria
The cause of episodic urticaria often remains unknown, but the Isolated DPU occurs in just 2% of all patients with urticaria,
possibility of an allergic or pseudoallergic cause needs to be but DPU coexists with CSU in up to 40% of patients. DPU is
considered. the most debilitating of the physical urticarias and is triggered
by sustained local pressure (e.g., wearing tight shoes, carrying
Inducible Urticarias heavy bags, long walks, sitting or leaning against firm objects,
Inducible urticarias are common, accounting for 25% of all cases climbing ladders, jogging, driving, or clapping hands). Deep and
of CU. These include physical urticarias, such as symptomatic painful swellings, clinically resembling angioedema, develop 30
dermographism, cold and heat urticarias, DPU, solar urticaria, minutes to 12 hours after pressure, and may be associated with
and vibratory angioedema, in which symptoms are triggered flu-like symptoms, fever, arthralgia, and fatigue. The most fre-
reproducibly by an external mechanical or thermal/ultraviolet quently affected sites are hands, soles, buttocks, shoulders, and
stimulus. The inducible group now also includes cholinergic, areas under straps and belts. DPU lesions last 12–48 hours and
adrenergic, aquagenic, and contact urticarias, in which the eliciting are usually painful rather than itchy, especially on the hands
stimuli for mast-cell degranulation are defined by a nonphysical and feet. Laboratory investigation reveals transitory leukocytosis
exposure. Inducible urticarias can coexist with CSU (e.g., DPU and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Hanging a
or dermographism), and more than one inducible urticaria can heavy weight suspended on a narrow band over the forearm or
occur in the same patient (e.g., dermographic and cholinergic thigh for 15 minutes may be used as a challenge test, but more