Page 677 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 677
650 ParT FivE Allergic diseases
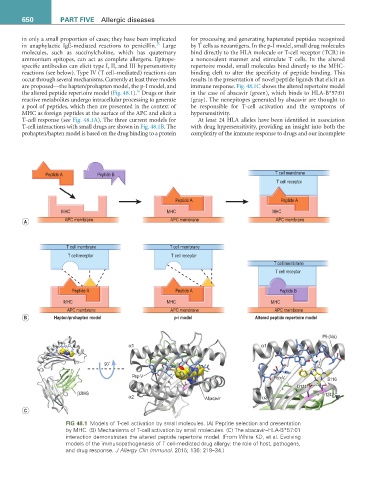
in only a small proportion of cases; they have been implicated for processing and generating haptenated peptides recognized
15
in anaphylactic IgE-mediated reactions to penicillin. Large by T cells as neoantigens. In the p-I model, small drug molecules
molecules, such as succinylcholine, which has quaternary bind directly to the HLA molecule or T-cell receptor (TCR) in
ammonium epitopes, can act as complete allergens. Epitope- a noncovalent manner and stimulate T cells. In the altered
specific antibodies can elicit type I, II, and III hypersensitivity repertoire model, small molecules bind directly to the MHC-
reactions (see below). Type IV (T cell–mediated) reactions can binding cleft to alter the specificity of peptide binding. This
occur through several mechanisms. Currently at least three models results in the presentation of novel peptide ligands that elicit an
are proposed—the hapten/prohapten model, the p-I model, and immune response. Fig. 48.1C shows the altered repertoire model
16
the altered peptide repertoire model (Fig. 48.1). Drugs or their in the case of abacavir (green), which binds to HLA-B*57:01
reactive metabolites undergo intracellular processing to generate (gray). The neoepitopes generated by abacavir are thought to
a pool of peptides, which then are presented in the context of be responsible for T-cell activation and the symptoms of
MHC as foreign peptides at the surface of the APC and elicit a hypersensitivity.
T-cell response (see Fig. 48.1A). The three current models for At least 24 HLA alleles have been identified in association
T-cell interactions with small drugs are shown in Fig. 48.1B. The with drug hypersensitivity, providing an insight into both the
prohapten/hapten model is based on the drug binding to a protein complexity of the immune response to drugs and our incomplete
Peptide A Peptide B T cell membrane
T cell receptor
Peptide A Peptide A
MHC MHC MHC
A APC membrane APC membrane APC membrane
T cell membrane T cell membrane
T cell receptor T cell receptor
T cell membrane
T cell receptor
Peptide A Peptide A Peptide B
MHC MHC MHC
APC membrane APC membrane APC membrane
B Hapten/prohapten model p-i model Altered peptide repertoire model
P9 (Val)
α1 α1
90˚
Pep-V Pep-V S116
V
Pe Pe Pe P P P Pep-V
p
V
V
D11 1 4 4 4 4 4
D114
D114
D11
β2MG I124 4 4 4
12 12 124
2
α2 Abacavir α2
C
FiG 48.1 Models of T-cell activation by small molecules. (A) Peptide selection and presentation
by MHC. (B) Mechanisms of T-cell activation by small molecules. (C) The abacavir–HLA-B*57:01
interaction demonstrates the altered peptide repertoire model. (From White KD, et al. Evolving
models of the immunopathogenesis of T cell-mediated drug allergy: the role of host, pathogens,
and drug response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 136: 219–34.)