Page 681 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 681
654 ParT FivE Allergic diseases
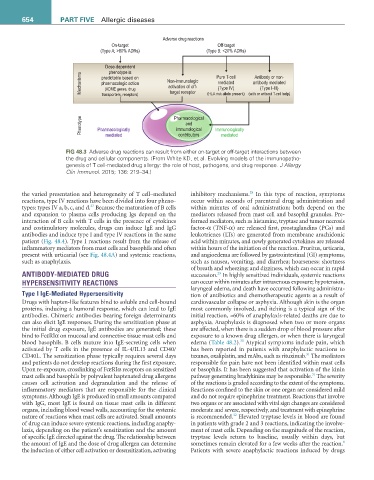
Adverse drug reactions
On-target Off-target
(Type A; >80% ADRs) (Type B; <20% ADRs)
Dose-dependent
phenotype is Pure T-cell Antibody or non-
Mechanisms predictable based on Non-immunologic (HLA risk allele present) (with or without T-cell help)
mediated
antibody mediated
pharmacologic action
activation of off-
(Type I-III)
(Type IV)
(ADME genes, drug
target receptor
transporters, receptors)
Phenotype Pharmacologically Pharmacological Immunologically
and
immunological
contributors
mediated
mediated
FiG 48.3 Adverse drug reactions can result from either on-target or off-target interactions between
the drug and cellular components. (From White KD, et al. Evolving models of the immunopatho-
genesis of T cell-mediated drug allergy: the role of host, pathogens, and drug response. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 2015; 136: 219–34.)
28
the varied presentation and heterogeneity of T cell–mediated inhibitory mechanisms. In this type of reaction, symptoms
reactions, type IV reactions have been divided into four pheno- occur within seconds of parenteral drug administration and
27
types: types IV a, b, c, and d. Because the maturation of B cells within minutes of oral administration; both depend on the
and expansion to plasma cells producing Igs depend on the mediators released from mast cell and basophil granules. Pre-
interaction of B cells with T cells in the presence of cytokines formed mediators, such as histamine, tryptase and tumor necrosis
and costimulatory molecules, drugs can induce IgE and IgG factor-α (TNF-α) are released first, prostaglandins (PGs) and
antibodies and induce type I and type IV reactions in the same leukotrienes (LTs) are generated from membrane arachidonic
patient (Fig. 48.4). Type I reactions result from the release of acid within minutes, and newly generated cytokines are released
inflammatory mediators from mast cells and basophils and often within hours of the initiation of the reaction. Pruritus, urticaria,
present with urticarial (see Fig. 48.4A) and systemic reactions, and angioedema are followed by gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms,
such as anaphylaxis. such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea; hoarseness; shortness
of breath and wheezing; and dizziness, which can occur in rapid
ANTIBODY-MEDIATED DRUG succession. In highly sensitized individuals, systemic reactions
29
HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS can occur within minutes after intravenous exposure; hypotension,
laryngeal edema, and death have occurred following administra-
Type I IgE-Mediated Hypersensitivity tion of antibiotics and chemotherapeutic agents as a result of
Drugs with hapten-like features bind to soluble and cell-bound cardiovascular collapse or asphyxia. Although skin is the organ
proteins, inducing a humoral response, which can lead to IgE most commonly involved, and itching is a typical sign of the
antibodies. Chimeric antibodies bearing foreign determinants initial reaction, ≈60% of anaphylaxis-related deaths are due to
can also elicit IgE responses. During the sensitization phase at asphyxia. Anaphylaxis is diagnosed when two or more organs
the initial drug exposure, IgE antibodies are generated; these are affected, when there is a sudden drop of blood pressure after
bind to FcεRIα on mucosal and connective tissue mast cells and exposure to a known drug allergen, or when there is laryngeal
30
blood basophils. B cells mature into IgE-secreting cells when edema (Table 48.2). Atypical symptoms include pain, which
activated by T cells in the presence of IL-4/IL13 and CD40/ has been reported in patients with anaphylactic reactions to
31
CD40L. The sensitization phase typically requires several days taxanes, oxaliplatin, and mAbs, such as rituximab. The mediators
and patients do not develop reactions during the first exposure. responsible for pain have not been identified within mast cells
Upon re-exposure, crosslinking of FcεRIα receptors on sensitized or basophils. It has been suggested that activation of the kinin
31
mast cells and basophils by polyvalent haptenated drug allergens pathway generating bradykinins may be responsible. The severity
causes cell activation and degranulation and the release of of the reactions is graded according to the extent of the symptoms.
inflammatory mediators that are responsible for the clinical Reactions confined to the skin or one organ are considered mild
symptoms. Although IgE is produced in small amounts compared and do not require epinephrine treatment. Reactions that involve
with IgG, most IgE is found on tissue mast cells in different two organs or are associated with vital sign changes are considered
organs, including blood vessel walls, accounting for the systemic moderate and severe, respectively, and treatment with epinephrine
32
nature of reactions when mast cells are activated. Small amounts is recommended. Elevated tryptase levels in blood are found
of drug can induce severe systemic reactions, including anaphy- in patients with grade 2 and 3 reactions, indicating the involve-
laxis, depending on the patient’s sensitization and the amount ment of mast cells. Depending on the magnitude of the reaction,
of specific IgE directed against the drug. The relationship between tryptase levels return to baseline, usually within days, but
8
the amount of IgE and the dose of drug allergen can determine sometimes remain elevated for a few weeks after the reaction.
the induction of either cell activation or desensitization, activating Patients with severe anaphylactic reactions induced by drugs