Page 680 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 680
CHaPTEr 48 Drug Hypersensitivity 653
Autologous HLA T cell
risk allele
1 2
3
Primary HHV
infection
T EM cells persist
in tissue
Patient is exposed
to drug
Model of Effector
heterologous Immunity memory T cell
4
Cross-reactive HHV or other Endogenous
TCR pathogen peptide
HHV peptide Drug 5
HHV-specific T cells
EM
recognize endogonous peptide
presented in context of HLA +
drug to elicit T cell response
T EM cell
A
Antiviral sensitization phase Antiviral T cell proliferation Antiviral effector phase
T cell membrane Effector T cell Virus specific memory T cell
T cell receptor T cell receptor T cell receptor
Viral peptide Viral peptide
MHC MHC
Virus specific memory T cell
APC membrane Infected cell
T cell receptor
T cell membrane
T cell receptor
T cell membrane T cell membrane
T cell receptor T cell receptor
Self peptide Self peptide Self peptide
MHC MHC MHC
APC membrane APC membrane APC membrane
Hapten/prohapten and heterologous p-i model and Altered peptide repertoire model and
B immunity model heterologous immunity model heterologous immunity
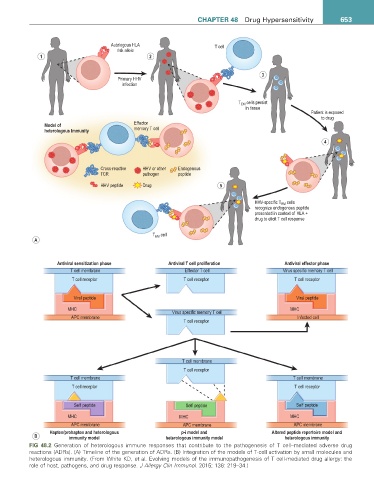
FiG 48.2 Generation of heterologous immune responses that contribute to the pathogenesis of T cell–mediated adverse drug
reactions (ADRs). (A) Timeline of the generation of ADRs. (B) Integration of the models of T-cell activation by small molecules and
heterologous immunity. (From White KD, et al. Evolving models of the immunopathogenesis of T cell-mediated drug allergy: the
role of host, pathogens, and drug response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015; 136: 219–34.)