Page 682 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 682
CHaPTEr 48 Drug Hypersensitivity 655
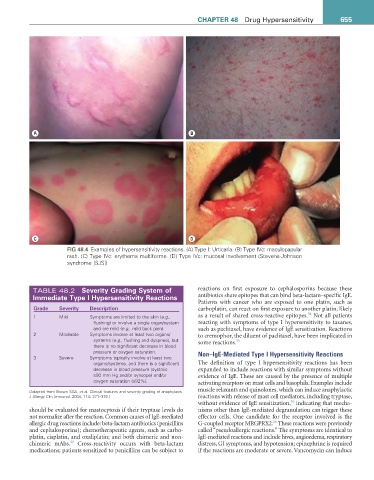
A B
C D
FiG 48.4 Examples of hypersensitivity reactions. (A) Type I: Urticaria. (B) Type IVc: maculopapular
rash. (C) Type IVc: erythema multiforme. (D) Type IVc: mucosal involvement (Stevens-Johnson
syndrome [SJS])
TABLE 48.2 Severity Grading System of reactions on first exposure to cephalosporins because these
immediate Type i Hypersensitivity reactions antibiotics share epitopes that can bind beta-lactam–specific IgE.
Patients with cancer who are exposed to one platin, such as
Grade Severity Description carboplatin, can react on first exposure to another platin, likely
34
1 Mild Symptoms are limited to the skin (e.g., as a result of shared cross-reactive epitopes. Not all patients
flushing) or involve a single organ/system reacting with symptoms of type I hypersensitivity to taxanes,
and are mild (e.g., mild back pain). such as paclitaxel, have evidence of IgE sensitization. Reactions
2 Moderate Symptoms involve at least two organs/ to cremophor, the diluent of paclitaxel, have been implicated in
systems (e.g., flushing and dyspnea), but some reactions. 35
there is no significant decrease in blood
pressure or oxygen saturation. Non–IgE-Mediated Type I Hypersensitivity Reactions
3 Severe Symptoms typically involve at least two
organs/systems, and there is a significant The definition of type I hypersensitivity reactions has been
decrease in blood pressure (systolic expanded to include reactions with similar symptoms without
≤90 mm Hg and/or syncope) and/or evidence of IgE. These are caused by the presence of multiple
oxygen saturation (≤92%). activating receptors on mast cells and basophils. Examples include
(Adapted from Brown SGA, et al. Clinical features and severity grading of anaphylaxis. muscle relaxants and quinolones, which can induce anaphylactic
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 114: 371–376.) reactions with release of mast cell mediators, including tryptase,
36
without evidence of IgE sensitization, indicating that mecha-
should be evaluated for mastocytosis if their tryptase levels do nisms other than IgE-mediated degranulation can trigger these
not normalize after the reaction. Common causes of IgE-mediated effector cells. One candidate for the receptor involved is the
26
allergic drug reactions include: beta-lactam antibiotics (penicillins G-coupled receptor MRGPRX2. These reactions were previously
and cephalosporins); chemotherapeutic agents, such as carbo- called “pseudoallergic reactions.” The symptoms are identical to
platin, cisplatin, and oxaliplatin; and both chimeric and non- IgE-mediated reactions and include hives, angioedema, respiratory
33
chimeric mAbs. Cross-reactivity occurs with beta-lactam distress, GI symptoms, and hypotension; epinephrine is required
medications; patients sensitized to penicillins can be subject to if the reactions are moderate or severe. Vancomycin can induce