Page 689 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 689
662 ParT FivE Allergic diseases
with exacerbation of chronic urticaria. Anaphylaxis can occur such as with rituximab. Infusion-related reactions to mAbs
to a single NSAID with tolerance to all others, but usually present as cytokine storm-like reactions, with such symptoms
there is complete cross-reactivity. Desensitization protocols are as nausea, chills, fever, and malaise. These are thought to be
available for AERD to ameliorate nasal polyps and increase the caused by release of proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1, IL-6,
sense of smell. Desensitization has also been tried for urticarial and TNF-α) and respond to NSAIDs and steroids. Hypersensitivity
reactions. reactions to cetuximab on first exposure have been attributed
to sensitization to the galactose-α-1,3-galactose epitope caused
Biological Agents and Monoclonal Antibodies by exposure to the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum).
The use of mAbs to target cancer and chronic inflammatory The carbohydrate galactose-α-1,3-galactose is expressed on
diseases has become widespread over the past decade. Inevitably nonprimate mammalian proteins and also on the cetuximab
this has led to adverse reactions, which sometimes prevent the heavy chain.
use of first-line therapies. Some of the most frequently used HSRs to mAbs can also be caused by IgE against antibody
mAbs are presented in Table 48.5, including their targets, moieties, as in some patients sensitized to rituximab. Both
incidence of overall injection/infusion site reactions, and rates immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions (skin lesions
51
of severe immediate hypersensitivity reactions (HSRs). The with CD4 T cells and eosinophilic infiltrates) can occur with
immunogenicity of mAbs varies, depending on whether they tocilizumab.
are chimeric mouse–human, humanized, or fully human mAbs given subcutaneously can elicit injection-site reactions,
mAbs, such as adalimumab and ofatumumab. Reactions to with symptoms including local redness, warmth, burning,
mAbs can occur during the first exposure, as has been reported stinging, itching, urticaria, pain, and induration. Such reactions
with cetuximab and trastuzumab or after multiple exposures, can start within 1 hour of the injection and usually resolve
over a few days, but large and persistent reactions can lead to
discontinuation of the mAb; desensitization protocols have been
developed for patients who have no alternative medications
(see Table 48.5).
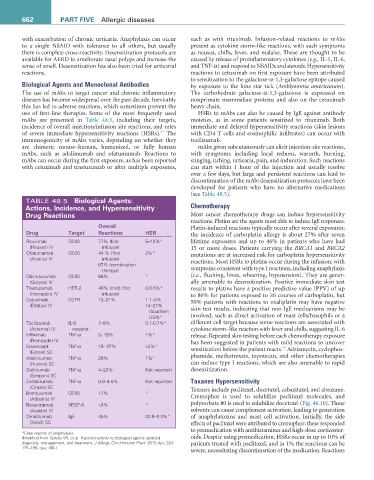
TABLE 48.5 Biological agents:
actions, incidence, and Hypersensitivity Chemotherapy
Drug reactions Most cancer chemotherapy drugs can induce hypersensitivity
reactions. Platins are the agents most able to induce IgE responses.
Overall Platin-induced reactions typically occur after several exposures;
Drug Target reactions HSr the incidence of carboplatin allergy is about 27% after seven
Rituximab CD20 77% (first 5–10%* lifetime exposures and up to 46% in patients who have had
(Rituxan) IV infusion) 15 or more doses. Patients carrying the BRCA1 and BRCA2
Ofatumumab CD20 44 % (first 2%* mutations are at increased risk for carboplatin hypersensitivity
(Arzerra) IV infusion) reactions. Most HSRs to platins occur during the infusion, with
67% (combination
therapy) symptoms consistent with type I reactions, including anaphylaxis
Obinutuzumab CD20 66% * (i.e., flushing, hives, wheezing, hypotension). They are gener-
(Gazyva) IV ally amenable to desensitization. Positive immediate skin test
Trastuzumab HER-2 40% (mild; first 0.6-5%* results to platins have a positive predictive value (PPV) of up
(Herceptin) IV infusion) to 86% for patients exposed to ≥6 courses of carboplatin, but
Cetuximab EGFR 15–21% 1.1–5% 50% patients with reactions to oxaliplatin may have negative
(Erbitux) IV 14–27%
(Southern skin test results, indicating that non-IgE mechanisms may be
USA)* involved, such as direct activation of mast cells/basophils or a
Tocilizumab IL-6 7–8% 0.1-0.7%* different cell target because some reactions are associated with
(Actemra) IV receptor cytokine storm–like reaction with fever and chills, suggesting IL-6
Infliximab TNF-α 5- 18% 1%* release. Repeated skin testing before each chemotherapy exposure
(Remicade) IV has been suggested in patients with mild reactions to uncover
Etanercept TNF-α 15- 37% <2%* sensitization before the patient reacts. Adriamycin, cyclophos-
52
(Enbrel) SC
Adalimumab TNF-α 20% 1%* phamide, methotrexate, topotecan, and other chemotherapies
(Humira) SC can induce type I reactions, which are also amenable to rapid
Golimumab TNF-α 4–20% Not reported desensitization.
(Simponi) SC
Certolizumab TNF-α 0.8–4.5% Not reported Taxanes Hypersensitivity
(Cimzia) SC Taxanes include paclitaxel, docetaxel, cabazitaxel, and abraxane.
Brentuximab CD30 12% *
(Adcetris) IV Cremophor is used to solubilize paclitaxel molecules, and
Bevacizumab VEGF-A <3% * polysorbate 80 is used to solubilize docetaxel (Fig. 48.10). These
(Avastin) IV solvents can cause complement activation, leading to generation
Omalizumab IgE 45% 00.9–0.2%* of anaphylatoxins and mast cell activation. Initially, the side
(Xolair) SC effects of paclitaxel were attributed to cremophor; these responded
to premedication with antihistamines and high-dose corticoster-
*Case reports of anaphylaxis.
(Modified from Galvão VR, et al. Hypersensitivity to biological agents-updated oids. Despite using premedication, HSRs occur in up to 10% of
diagnosis, management, and treatment. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2015 Apr; 3(2): patients treated with paclitaxel, and in 1% the reactions can be
175–185; quiz 186.)
severe, necessitating discontinuation of the medication. Reactions