Page 774 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 774
CHaPtEr 55 Scleroderma–Systemic Sclerosis 745
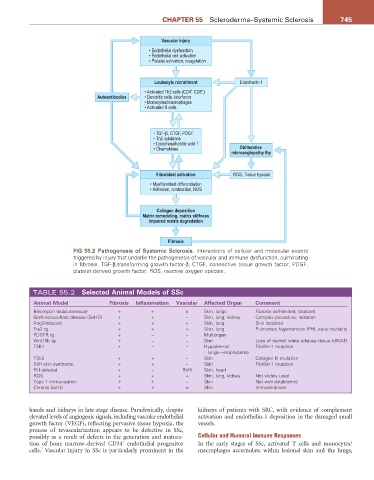
Vascular injury
• Endothelial dysfunction
• Endothelial cell activation
• Platelet activation, coagulation
Leukocyte recruitment Endothelin-1
+
+
• Activated Th2 cells (CD4 CD8 )
Autoantibodies • Dendritic cells, interferon
• Monocytes/macrophages
• Activated B cells
• TGF-β, CTGF, PDGF
• Th2 cytokines
• Lysophosphatidic acid 1
• Chemokines Obliterative
microangiopathy thy
Fibroblast activation ROS, Tissue hypoxia
• Myofibroblast differentiation
• Adhesion, contraction, ROS
Collagen deposition
Matric remodeling, matrix stiffness
Impaired matrix degradation
Fibrosis
FIG 55.2 Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Interactions of cellular and molecular events
triggered by injury that underlie the pathogenesis of vascular and immune dysfunction, culminating
in fibrosis. TGF-β,transforming growth factor-β; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; PDGF,
platelet-derived growth factor; ROS, reactive oxygen species.
TABLE 55.2 Selected animal Models of SSc
animal Model Fibrosis Inflammation Vascular affected Organ Comment
Bleomycin (subcutaneous) + + ± Skin, lungs Fibrosis self-limited; localized
Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) + + − Skin, lung, kidney Complex procedure; radiation
Ang2-induced + + + Skin, lung Skin localized
Fra2 tg + + + Skin, lung Pulmonary hypertension (PH); early mortality
PDGFR tg + − − Multiorgan
Wnt10b tg + − − Skin Loss of dermal white adipose tissue (dWAT)
TSK1 + − − Hypodermal Fibrillin-1 mutation
lungs—emphysema
TSK2 + + − Skin Collagen III mutation
Stiff skin syndrome + + − Skin Fibrillin-1 mutation
Fli1-deleted + − RVH Skin, heart
ROS + + + Skin, lung, kidney Not widely used
Topo 1 immunization + + − Skin Not well established
Chronic GvHD + + ± Skin Immune-driven
hands and kidneys in late-stage disease. Paradoxically, despite kidneys of patients with SRC, with evidence of complement
elevated levels of angiogenic signals, including vascular endothelial activation and endothelin-1 deposition in the damaged small
growth factor (VEGF), reflecting pervasive tissue hypoxia, the vessels.
process of revascularization appears to be defective in SSc,
possibly as a result of defects in the generation and matura- Cellular and Humoral Immune Responses
+
tion of bone marrow–derived CD34 endothelial progenitor In the early stages of SSc, activated T cells and monocytes/
7
cells. Vascular injury in SSc is particularly prominent in the macrophages accumulate within lesional skin and the lungs,