Page 778 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 778
CHaPtEr 55 Scleroderma–Systemic Sclerosis 749
with loss of body hair, reduced production of skin oils, and a disease, severe GI dysfunction, SRC, progressive heart disease,
decline in sweating capacity as these cutaneous structures atrophy. and recurrent digital ulcers during the initial active inflammatory
Gradually, the subcutaneous tissue becomes affected, with atrophy and fibrotic phases of the skin disease. In practical terms, this
of subcutaneous fat and fibrosis extending to the underlying means that in dcSSc, the initial 3–4 years is the period that the
fascia, muscle, and other soft tissue structures. During the fibrotic systemic process is most active; if organ failure does not occur
phase, patients note pain, progressive loss of flexibility, distressing during this period, the systemic process may stabilize without
disfigurement, and profound weight loss. Progressive flexion further progression.
contractures of the finger joints ensue. Other joints, including
wrist, elbow, shoulder, hip girdle, knees, and ankle, can also be Limited Cutaneous SSc
affected as a result of fibrosis of the supporting joint structures The disease course in the limited cutaneous variant of SSc is
(see Fig. 55.3). Thick ridges at the neck caused by firm adherence more indolent and often relatively benign. After the onset of
of skin to the underlying platysma muscle interfere with neck Raynaud phenomenon, several years may pass before additional
extension. Tendon friction rub is a prominent crepitation that symptoms or signs are recognized. The most common non-
can be felt or even heard over tendons of the lower and upper Raynaud symptoms in patients with lcSSc are those of upper
extremities. Tendon friction rubs are caused by fibrosis in the GI disease with dysphagia and gastroesophageal reflux. Dilated
tissues surrounding the affected joints; they are associated with capillaries form visible erythematous vascular lesions (telangi-
rapidly progressive skin disease and are linked to an overall poor ectasia), seen most commonly on the fingertips, nailfold areas
prognosis. Fibrosis of the skin of the face yields a characteristic of the digits, palms, face, lips, and inside the oral cavity (Fig.
facial appearance with diminished oral aperture, loss of facial 55.6). CREST (subcutaneous calcinosis, Raynaud phenomenon,
expression, vertical lines around the lips, loss of lip thickness, esophageal dysfunction, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia) syn-
and protrusion of teeth. drome is a subtype of lcSSc, with distinctive features, an overall
The natural history of skin disease in dcSSc tends to be good prognosis, and an association with the presence of anti-
monophasic, and relapse is uncommon after the edematous and centromere antibodies. Subcutaneous calcinosis caused by
active fibrotic phase. The duration of active skin disease from deposition of calcium hydroxyapatite crystals occurs commonly
the first signs of skin involvement to its maximal extent is at sites of tissue ischemia and recurrent trauma, such as the
characteristically less than 3 years; cutaneous inflammation and fingertips, forearm, or elbow.
progressive fibrosis gradually subside, and regression of skin Although significant internal organ disease occurs with lower
involvement begins. However, this time frame is highly variable frequency in patients with lcSSc, isolated pulmonary arterial
from one patient to another, with many patients demonstrating hypertension (PAH) develops in 10–15% of patients and may
14
rapid skin regression and others showing chronically active disease be life-threatening. Significant interstitial lung disease can
over years. In the late stages of dcSSc, skin remodeling can be occur in about 20% of patients with lcSSc. Severe Raynaud
dramatic, with return to normal-appearing skin in those areas phenomenon with macrovascular occlusive involvement occurs
spared from severe end-stage fibrosis. In more severely affected more frequently in lcSSc than in dcSSc and can be associated
areas, the skin becomes thin or atrophic and can be bound down with critical digital ischemia, ischemic ulcerations, gangrene,
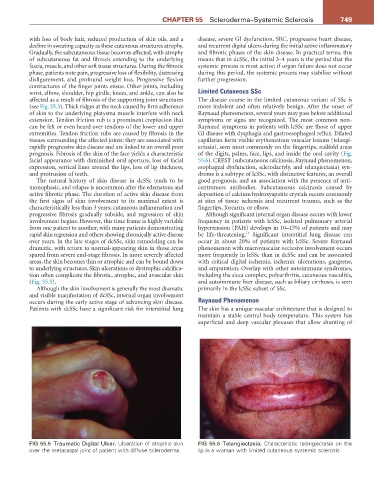
to underlying structures. Skin ulcerations or dystrophic calcifica- and amputation. Overlap with other autoimmune syndromes,
tion often complicate the fibrotic, atrophic, and avascular skin including the sicca complex, polyarthritis, cutaneous vasculitis,
(Fig. 55.5). and autoimmune liver disease, such as biliary cirrhosis, is seen
Although the skin involvement is generally the most dramatic primarily in the lcSSc subset of SSc.
and visible manifestation of dcSSc, internal organ involvement
occurs during the early active stage of advancing skin disease. Raynaud Phenomenon
Patients with dcSSc have a significant risk for interstitial lung The skin has a unique vascular architecture that is designed to
maintain a stable central body temperature. This system has
superficial and deep vascular plexuses that allow shunting of
FIG 55.5 Traumatic Digital Ulcer. Ulceration of atrophic skin FIG 55.6 Telangiectasia. Characteristic telangiectasia on the
over the metacarpal joint of patient with diffuse scleroderma. lip in a woman with limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis.