Page 806 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 806
CHaPtEr 57 Spondyloarthritis 777
A B
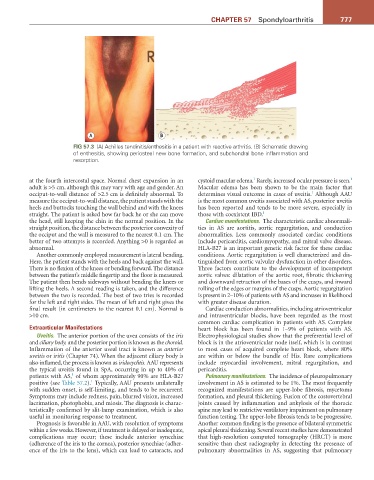
FiG 57.3 (A) Achilles tendinitis/enthesitis in a patient with reactive arthritis. (B) Schematic drawing
of enthesitis, showing periosteal new bone formation, and subchondral bone inflammation and
resorption.
1
1
at the fourth intercostal space. Normal chest expansion in an cystoid macular edema. Rarely, increased ocular pressure is seen.
adult is >5 cm, although this may vary with age and gender. An Macular edema has been shown to be the main factor that
1
occiput-to-wall distance of >2.5 cm is definitely abnormal. To determines visual outcome in cases of uveitis. Although AAU
measure the occiput-to-wall distance, the patient stands with the is the most common uveitis associated with AS, posterior uveitis
heels and buttocks touching the wall behind and with the knees has been reported and tends to be more severe, especially in
straight. The patient is asked how far back he or she can move those with coexistent IBD. 1
the head, still keeping the chin in the normal position. In the Cardiac manifestations. The characteristic cardiac abnormali-
straight position, the distance between the posterior convexity of ties in AS are aortitis, aortic regurgitation, and conduction
the occiput and the wall is measured to the nearest 0.1 cm. The abnormalities. Less commonly associated cardiac conditions
better of two attempts is recorded. Anything >0 is regarded as include pericarditis, cardiomyopathy, and mitral valve disease.
abnormal. HLA-B27 is an important genetic risk factor for these cardiac
Another commonly employed measurement is lateral bending. conditions. Aortic regurgitation is well characterized and dis-
Here, the patient stands with the heels and back against the wall. tinguished from aortic valvular dysfunction in other disorders.
There is no flexion of the knees or bending forward. The distance Three factors contribute to the development of incompetent
between the patient’s middle fingertip and the floor is measured. aortic valves: dilatation of the aortic root, fibrotic thickening
The patient then bends sideways without bending the knees or and downward retraction of the bases of the cusps, and inward
lifting the heels. A second reading is taken, and the difference rolling of the edges or margins of the cusps. Aortic regurgitation
between the two is recorded. The best of two tries is recorded is present in 2–10% of patients with AS and increases in likelihood
for the left and right sides. The mean of left and right gives the with greater disease duration.
final result (in centimeters to the nearest 0.1 cm). Normal is Cardiac conduction abnormalities, including atrioventricular
>10 cm. and intraventricular blocks, have been regarded as the most
common cardiac complication in patients with AS. Complete
Extraarticular Manifestations heart block has been found in 1–9% of patients with AS.
Uveitis. The anterior portion of the uvea consists of the iris Electrophysiological studies show that the preferential level of
and ciliary body, and the posterior portion is known as the choroid. block is in the atrioventricular node itself, which is in contrast
Inflammation of the anterior uveal tract is known as anterior to most cases of acquired complete heart block, where 80%
uveitis or iritis (Chapter 74). When the adjacent ciliary body is are within or below the bundle of His. Rare complications
also inflamed, the process is known as iridocyclitis. AAU represents include myocardial involvement, mitral regurgitation, and
the typical uveitis found in SpA, occurring in up to 40% of pericarditis.
1
patients with AS, of whom approximately 90% are HLA-B27 Pulmonary manifestations. The incidence of pleuropulmonary
1
positive (see Table 57.2). Typically, AAU presents unilaterally involvement in AS is estimated to be 1%. The most frequently
with sudden onset, is self-limiting, and tends to be recurrent. recognized manifestations are upper-lobe fibrosis, mycetoma
Symptoms may include redness, pain, blurred vision, increased formation, and pleural thickening. Fusion of the costovertebral
lacrimation, photophobia, and miosis. The diagnosis is charac- joints caused by inflammation and ankylosis of the thoracic
teristically confirmed by slit-lamp examination, which is also spine may lead to restrictive ventilatory impairment on pulmonary
useful in monitoring response to treatment. function testing. The upper-lobe fibrosis tends to be progressive.
Prognosis is favorable in AAU, with resolution of symptoms Another common finding is the presence of bilateral symmetric
within a few weeks. However, if treatment is delayed or inadequate, apical pleural thickening. Several recent studies have demonstrated
complications may occur; these include anterior synechiae that high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is more
(adherence of the iris to the cornea), posterior synechiae (adher- sensitive than chest radiography in detecting the presence of
ence of the iris to the lens), which can lead to cataracts, and pulmonary abnormalities in AS, suggesting that pulmonary