Page 803 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 803
774 Part six Systemic Immune Diseases
CD4 positive
T lymphocyte
Natural killer
CD8 positive (NK) cell
T lymphocyte
αβ KIR receptor
T cell B2
receptor
Free B27 HLA-class II
heavy chain (DR, DQ, DP) HLA-B27 homodimers
A2 presenting at cell surface A2
HLA-B27:B2microglobulin:peptide HLA-B27 peptide
trimolecular complex
Endoplasmic reticulum BiP BiP ERAD
BiP BiP
B B27 misfolding,
homodimerization UPR
Golgi
B1 A1
B27 folding, assembly and HLA-B27:B2M:peptide trimolecular
loading of peptide Tapasin
B27 heavy chain (HC) complex transported to the cell
B2 microglobulin surface via the golgi apparatus
B27 HC folding (B2m) loading peptide loading
Calnexin Calreticulum
A BiP B2m Macrophage
Ribosome
TAP 1,2
proteolytic degradation
within proteasome peptide fragments
Viral, bacterial or
tumor protein
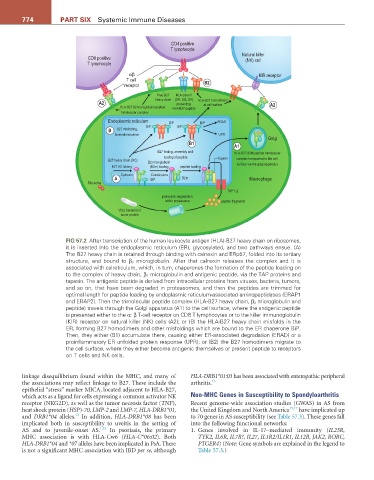
FiG 57.2 After transcription of the human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-B27 heavy chain on ribosomes,
it is inserted into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), glycosylated, and two pathways ensue. (A)
The B27 heavy chain is retained through binding with calnexin and ERp57, folded into its tertiary
structure, and bound to β 2 microglobulin. After that calnexin releases the complex and it is
associated with calreticulum, which, in turn, chaperones the formation of the peptide loading on
to the complex of heavy chain, β 2 microglobulin and antigenic peptide, via the TAP proteins and
tapasin. The antigenic peptide is derived from intracellular proteins from viruses, bacteria, tumors,
and so on, that have been degraded in proteasomes, and then the peptides are trimmed for
optimal length for peptide loading by endoplasmic reticulum-associated aminopeptidases (ERAP1
and ERAP2). Then the trimolecular peptide complex (HLA-B27 heavy chain, β 2 microglobulin and
peptide) travels through the Golgi apparatus (A1) to the cell surface, where the antigenic peptide
is presented either to the α: β T-cell receptor on CD8 T lymphocytes or to the killer immunoglobulin
(KIR) receptor on natural killer (NK) cells (A2); or (B) the HLA-B27 heavy chain misfolds in the
ER, forming B27 homodimers and other misfoldings which are bound to the ER chaperone BiP.
Then, they either (B1) accumulate there, causing either ER-associated degradation (ERAD) or a
proinflammatory ER unfolded protein response (UPR); or (B2) the B27 homodimers migrate to
the cell surface, where they either become antigenic themselves or present peptide to receptors
on T cells and NK cells.
linkage disequilibrium found within the MHC, and many of HLA-DRB1*01:03 has been associated with enteropathic peripheral
the associations may reflect linkage to B27. These include the arthritis. 13
epithelial “stress” marker MICA, located adjacent to HLA-B27,
which acts as a ligand for cells expressing a common activator NK Non-MHC Genes in Susceptibility to Spondyloarthritis
receptor (NKG2D), as well as the tumor necrosis factor (TNF), Recent genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in AS from
heat shock protein (HSP)-70, LMP-2 and LMP-7, HLA-DRB1*01, the United Kingdom and North America 15,17 have implicated up
13
and DRB1*04 alleles. In addition, HLA-DRB1*08 has been to 70 genes in AS susceptibility (see Table 57.3). These genes fall
implicated both in susceptibility to uveitis in the setting of into the following functional networks:
AS and to juvenile-onset AS. 1,13 In psoriasis, the primary 1. Genes involved in IL-17–mediated immunity (IL23R,
MHC association is with HLA-Cw6 (HLA-C*06:02). Both TYK2, IL6R, IL7R?, IL27, IL1R2/IL1R1, IL12B, JAK2, RORC,
HLA-DRB1*04 and *07 alleles have been implicated in PsA. There PTGER4) (Note: Gene symbols are explained in the legend to
is not a significant MHC association with IBD per se, although Table 57.3.)