Page 824 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 824
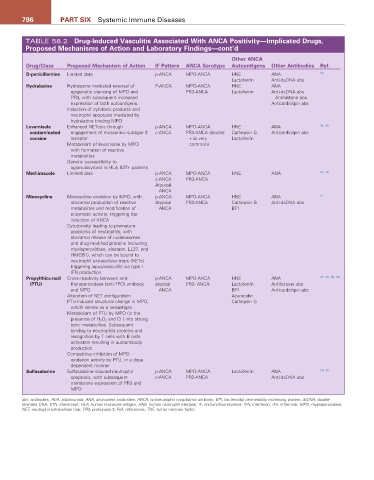
796 Part SIX Systemic Immune Diseases
TABLE 58.2 Drug-Induced Vasculitis associated With aNCa Positivity—Implicated Drugs,
Proposed Mechanisms of action and Laboratory Findings—cont’d
Other aNCa
Drug/Class Proposed Mechanism of action IF Pattern aNCa Serotype autoantigens Other antibodies ref.
D-penicillamine Limited data p-ANCA MPO-ANCA HNE ANA 53
Lactoferrin Anti-dsDNA abs
Hydralazine Hydralazine mediated reversal of P-ANCA MPO-ANCA HNE ANA
epigenetic silencing of MPO and PR3-ANCA Lactoferrin Anti-dsDNA abs
PR3, with subsequent increased Antihistone abs
expression of both autoantigens. Anticardiolipin abs
Induction of cytotoxic products and
neutrophil apoptosis mediated by
hydralazine binding MPO
Levamisole Enhanced NETosis through p-ANCA MPO-ANCA HNE ANA 54, 40
contaminated engagement of muscarinic subtype 3 c-ANCA PR3-ANCA (double Cathepsin G Anticardiolipin abs
cocaine receptor + is very Lactoferrin
Metabolism of levamisole by MPO common)
with formation of reactive
metabolites
Genetic susceptibility to
agranulocytosis in HLA B27+ patients
Methimazole Limited data p-ANCA MPO-ANCA HNE ANA 55, 56
c-ANCA PR3-ANCA
Atypical
ANCA
Minocycline Minocycline oxidation by MPO, with p-ANCA MPO-ANCA HNE ANA 57
abnormal production of reactive Atypical PR3-ANCA Cathepsin G Anti-dsDNA abs
metabolites and modification of ANCA BPI
enzymatic activity, triggering the
induction of ANCA
Cytotoxicity leading to premature
apoptosis of neutrophils, with
abnormal release of nucleosomes
and drug-modified proteins (including
myeloperoxidase, elastase, LL37, and
HMGB1), which can be bound to
neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs)
triggering lupus/vasculitis via type I
IFN production
Propylthiouracil Cross-reactivity between anti- p-ANCA MPO-ANCA HNE ANA 27, 55, 95, 58
(PtU) thyroperoxidase (anti-TPO) antibody atypical PR3- ANCA Lactoferrin Antihistone abs
and MPO ANCA BPI Anticardiolipin abs
Alteration of NET configuration Azurocidin
PTU-induced structural change in MPO, Cathepsin G
which serves as a neoantigen
Metabolism of PTU by MPO (in the
−
presence of H 2 O 2 and Cl ) into strong
toxic metabolites. Subsequent
binding to neutrophils proteins and
recognition by T cells with B cells
activation resulting in autoantibody
production
Competitive inhibition of MPO
oxidation activity by PTU, in a dose
dependent manner
Sulfasalazine Sulfasalazine-induced neutrophil p-ANCA MPO-ANCA Lactoferrin ANA 50, 59
apoptosis, with subsequent c-ANCA PR3-ANCA Anti-dsDNA abs
membrane expression of PR3 and
MPO
abs, antibodies; ADA, adalimumab; ANA, antinuclear antibodies; ANCA, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; BPI, bactericidal permeability increasing protein; dsDNA, double-
stranded DNA; ETN, etanercept; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; HNE, human neutrophil elastase; IF, immunofluorescence; IFN, interferon; IFX, infliximab; MPO, myeloperoxidase;
NET, neutrophil extracellular trap; PR3, proteinase 3; Ref, references; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.