Page 1159 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1159
798 PART 6: Neurologic Disorders
onset of acute headache, nausea, vomiting, and altered consciousness fibers, together with intractable nausea and vomiting, followed by
in a hypertensive patient indicates intracranial bleeding versus the neurological deficits including visual disturbances associated with late
slow progression of a focal neurological deficit evolving to generalized changes in level of alertness are all typical manifestations of increasing
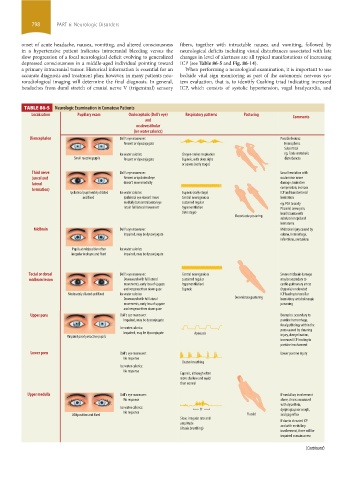
depressed consciousness in a middle-aged individual pointing toward ICP (see Table 86-5 and Fig. 86-14).
a primary intracranial tumor. Historical information is essential for an When performing a neurological examination, it is important to use
accurate diagnosis and treatment plan; however, in many patients neu- bedside vital sign monitoring as part of the autonomic nervous sys-
roradiological imaging will determine the final diagnosis. In general, tem evaluation, that is, to identify Cushing triad indicating increased
headaches from dural stretch of cranial nerve V (trigeminal) sensory ICP, which consists of systolic hypertension, vagal bradycardia, and
TABLE 86-5 Neurologic Examination in Comatose Patients
Localization Pupillary exam Oculocephalic (Doll’s eye) Respiratory patterns Posturing Comments
and
oculovestibular
(ice water calorics)
Diencephalon Doll’s eye maneuver: Possible lesions:
Present or dysconjugate Hemispheric
Subcortical
Ice water calorics: Cheyne-stokes respiration eg, Toxic-metabolic
Small reactive pupils Present or dysconjugate Eupneic, with deep sighs disturbances
or yawns (early stage)
Third nerve Doll’s eye maneuver: Uncal herniation with
(uncal and Present or ipsilateral eye oculomotor nerve
lateral doesn’t move medially damage; brainstem
herniation) compression; increase
Ipsilateral pupil widely dilated Ice water calorics: Eupneic (early stage) ICP and transtentorial
and fixed Ipsilateral eye doesn’t move Central neurogenic or herniation
medially but contralateral eye sustained regular eg, PCA (usually
retain full lateral movement hyperventilation PComm) aneurysm,
(late stage) head trauma with
Decorticate posturing
subdural or epidural
hematoma
Midbrain Doll’s eye maneuver: Midbrain injury caused by
Impaired, may be dysconjugate edema, hemorrhage,
infarctions, contusions
Pupils at midposition often Ice water calorics:
irregular in shape and fixed Impaired, may be dysconjugate
Tectal or dorsal Doll’s eye maneuver: Central neurogenic or Severe midbrain damage
midbrain lesion Downward with full lateral sustained regular may be secondary to
movements, early loss of upgaze hyperventilation/ cardio-pulmonary arrest
and vergence then down gaze Eupneic (hypoxia) or elevated
Moderately dilated and fixed Ice water calorics: ICP leading to tonsillar
Downward with full lateral Decerebrate posturing herniation; anticholinergic
movements, early loss of upgaze poisoning
and vergence then down gaze
Upper pons Doll’s eye maneuver: Examples: secondary to
Impaired, may be dysconjugate pontine hemorrhage,
focal pathology within the
Ice water calorics: pons caused by shearing
Impaired, may be dysconjugate Apneusis
Pinpoint poorly reactive pupils injury, demyelination,
increased ICP leading to
pontine involvement
Lower pons Doll’s eye maneuver: Lower pontine injury
No response
Cluster breathing
Ice water calorics:
No response
Eupneic, although often
more shallow and rapid
than normal
Upper medulla Doll’s eye maneuver: If medullary involvement
No response alone, this is associated
with dysarthria,
Ice water calorics: ?? dysphagia,poor cough,
No response
Midposition and fixed Flaccid and gag reflex
Slow, irregular rate and
amplitude If due to elevated ICP
and with medullary
(Ataxic breathing)
involvement, there will be
impaired consciousness
Cervical spine Doll’s eye maneuver: Disruption of sympathetic
(Continued)
(Avoid with cervical lesion) nervous system caused
by spinal cord lesion
Ice water calorics: above the first thoracic
Present
Horner pupil vertebra
(composed of ptosis,
miosis, and anhidrosis) Nonspecific
section06.indd 798 1/23/2015 12:55:59 PM
Severe Opisthotonus posturing
brainstem seen usually in infants,
lesion/ secondary to disinhibited
extra pyramidal Nonspecific Nonspecific extrapyramidal activity
caused by axial spinal
lesion
Opisthotonus posturing muscles spasm
Summary of important neurological findings seen in comatose patients. ICP, intracranial pressure; PCA, posterior cerebral artery; Pcomm, posterior communicating artery