Page 1252 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1252
CHAPTER 91: TTP, HUS, and Other Thrombotic Microangiopathies 859
MECHANISMS OF THE DISEASES the UL-VWF multimers anchored on endothelial cell surface 72-74 or
■ HISTOLOGIC FINDINGS in the identification and molecular cloning of ADAMTS13 has greatly
those circulating in blood under arterial shear stress.
The success
75,76
TMA, a pathologic term, describes histologic findings of hyaline accelerated our understanding of pathogenesis of TTP, HUS, and other
condition/disease-related TMAs.
thrombi in the terminal arterioles and capillaries, 1,66,67 which is the hall-
mark of TTP and HUS. However, the organ involvement and thrombus Hereditary and Acquired Idiopathic TTP: Levy et al first reported
7
composition in cases of TTP may differ from those of HUS. Hosler 12 mutations in the ADAMTS13 gene, accounting for 14 of the 15
et al performed histology analysis in 56 autopsied cases of TTP and disease alleles studied. Subsequently, more mutations in ADAMTS13
67
HUS. In 25 cases of diagnosed TTP, platelet-rich thrombi were present, were identified in cases of hereditary TTP. 16,23,77-82 Mutations were
in decreasing severity, in heart, pancreas, kidney, adrenal gland, and found throughout the ADAMTS13 gene including point mutations,
brain. In 31 cases of diagnosed HUS, fibrin/red cell-rich thrombi were frame shifts, deletion, and alternative splicing. A majority of these
predominant, largely confined to the kidney and often severe, and only mutations are compound heterozygous, but a few are in homozygous
6 cases showed pancreas involvement, 4 adrenal gland involvement, form. Nearly all mutations in ADAMTS13 cause protein misfolding
83
2 brain involvement, and 1 heart involvement. Immunohistochemical and intracellular retention of the mutants, leading to severe deficiency
studies have confirmed these findings: the predominance of VWF/ of plasma ADAMTS13 activity. 77,81
platelets thrombi in cases of TTP, but fibrin in cases of HUS or dissemi- In 1998, Tsai and Lian first reported the presence of inhibitory auto-
84
nated intravascular coagulation. 68-70 These differences in the propensity of antibodies against ADAMTS13 protein in most adult cases of acquired
organ involvement and thrombus composition underscore the potential TTP; these inhibitory autoantibodies are immunoglobulin Gs (IgGs) in
difference in the mechanisms between TTP and HUS (or other TMAs). nature. Mapping studies demonstrate that nearly all patients harbor IgGs
■ TTP that target at the Cys-rich/spacer domain of ADAMTS13 protein, 84-88 a
89-94
The initial hint that suggested the deficiency of a plasma protease that critical region for substrate recognition. Mutations in ADAMTS13
or inhibition of ADAMTS13 activity by anti-ADAMTS13 IgGs results
breaks down VWF polymers came from the seminal observation by in an accumulation of hyperactive ULVWF multimers, leading to exces-
Dr Joel Moake in 1982. He and his colleagues reported that ultra- sive platelet aggregation and disseminated microvascular thromboses
71
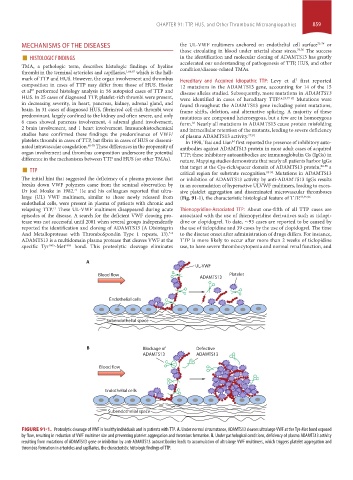
large (UL) VWF multimers, similar to those newly released from (Fig. 91-1), the characteristic histological feature of TTP. 93,95,96
endothelial cells, were present in plasma of patients with chronic and
relapsing TTP. These UL-VWF multimers disappeared during acute Thienopyridine-Associated TTP: About one-fifth of all TTP cases are
71
episodes of the disease. A search for the deficient VWF cleaving pro- associated with the use of thienopyridine derivatives such as ticlopi-
tease was not successful until 2001 when several groups independently dine or clopidogrel. To date, ∼93 cases are reported to be caused by
reported the identification and cloning of ADAMTS13 (A Disintegrin the use of ticlopidine and 39 cases by the use of clopidogrel. The time
And Metalloprotease with ThromboSpondin Type 1 repeats, 13). to the disease onset after administration of drugs differs. For instance,
5-8
ADAMTS13 is a multidomain plasma protease that cleaves VWF at the TTP is more likely to occur after more than 2 weeks of ticlopidine
specific Tyr 1605 -Met 1606 bond. This proteolytic cleavage eliminates use, to have severe thrombocytopenia and normal renal function, and
A
UL-VWF
Blood flow Platelet
ADAMTS13
Endothelial cells
Subendothelial space
B Blockage of Defective
ADAMTS13 ADAMTS13
Blood flow
Endothelial cells
Subendothelial space
FIGURE 91-1. Proteolytic cleavage of VWF in healthy individuals and in patients with TTP. A. Under normal circumstance, ADAMTS13 cleaves ultralarge VWF at the Tyr-Met bond exposed
by flow, resulting in reduction of VWF multimer size and preventing platelet aggregation and thrombus formation. B. Under pathological conditions, deficiency of plasma ADAMTS13 activity
resulting from mutations of ADAMTS13 gene or inhibition by anti-ADAMTS13 autoantibodies leads to accumulation of ultralarge VWF multimers, which triggers platelet aggregation and
thrombus formation in arterioles and capillaries, the characteristic histologic findings of TTP.
section07.indd 859 1/21/2015 7:42:47 AM