Page 1254 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1254
CHAPTER 91: TTP, HUS, and Other Thrombotic Microangiopathies 861
150
Classical pathway Lectin pathway Alternative inhibitor (TAFI), therefore regulating thrombosis and mediating cyto-
Immune complexes pathway protective activity. Furthermore, TM negatively regulates the comple-
Nonimmune activators Microbial carbohydrates Activating surfaces ment system through accelerating CFI-mediated inactivation of C3b in
the presence of cofactors, CFH, or C4b binding protein. Delvaeye et al
C1q, C1r, C1s CFI first reported identification of TM mutations in a cohort of 152 aHUS
CFH/MCP 151
C3b
TM patients. Most are missense mutations (A43T, D53G, V81I, P495S,
C4 + C2 CFB CFD P501L, and D486Y) in the heterozygous form. TM mutations are found
now in 3% to 5% of aHUS patients worldwide. 141,151,152 These mutations
C4b Bb DAF exhibited defects in suppressing activation of the alternative comple-
C2a C3b CFH ment pathway through CFI-mediated C3b inactivation in vitro and are
associated with the disease after infections. 141,151,152
C3 convertase C3 convertase
C3
TM TAFIa C3a DIAGNOSIS AND DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
CFI ■
CFH/MCP CLINICAL PRESENTATION
C3b
TM
Diagnosis of TTP or HUS should be considered in a patient with follow-
C4b C2a C3b C3b Bb C3b ing findings: thrombocytopenia with a platelet count usually less than
9
C5 convertase C5 convertase 150 × 10 /L, MAHA (with a hemoglobin level less than 10 g/dL, elevated
lactate dehydrogenase, a negative Coombs test, and fragmentation of red
C5 blood cells) with or without organ ischemia resulting in neurological
and/or renal abnormalities. 13,50,52,152 The classic “pentad” of MAHA and
TM TAFIa C5a C6 thrombocytopenia, neurologic and renal abnormalities, and fever was
C5b C9 only found in 7% of patients. 153
C5b C8 Examples of when to suspect hereditary TTP include severe hemolytic
C7
disease in newborn; infant with thrombocytopenia and jaundice 19,154 ;
MAC
episodic “immune mediate thrombocytopenia” in a child with concurrent
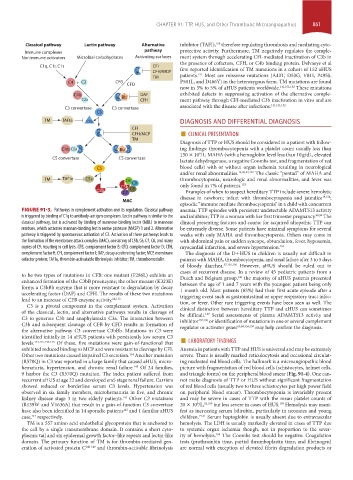
FIGURE 91-3. Pathways in complement activation and its regulation. Classical pathway anemia; TTP episodes with persistent undetectable ADAMTS13 activity
is triggered by binding of C1q to antibody-antigen complexes. Lectin pathway is similar to the and inhibitor; TTP in a woman with her first trimester pregnancy. 98,99 The
classical pathway, but is activated by binding of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) to mannose clinical presenting features and course for acquired idiopathic TTP can
residues, which activates mannan-binding lectin serine protease (MASP) 1 and 2. Alternative be extremely diverse. Some patients have minimal symptoms for several
pathway is triggered by spontaneous activation of C3. Activation of these pathways leads to weeks with only MAHA and thrombocytopenia. Others may come in
the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC), consisting of C5b, C6, C7, C8, and many with abdominal pain or sudden syncope, obtundation, fever, hypoxemia,
copies of C9, resulting in cell lysis. CFB, complement factor B; CFD, complement factor D; CFH, myocardial infarction, and severe hypertension. 153
complement factor H; CFI, complement factor I; DAF, decay accelerating factor; MCP, membrane The diagnosis of the D+HUS in children is usually not difficult in
cofactor protein; TAFIa, thrombin-activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor; TM, thrombomodulin. patients with MAHA, thrombocytopenia, and renal failure after 3 to 5 days
of bloody diarrhea. 57,155,156 However, aHUS should be ruled out in
cases of recurrent disease. In a review of 45 pediatric patients from a
to be two types of mutations in CFB: one mutant (F286L) exhibits an Dutch and Belgium group, the majority of aHUS patients presented
141
enhanced formation of the C3bB proenzyme; the other mutant (K323E) between the age of 1 and 7 years with the youngest patient being only
forms a C3bBb enzyme that is more resistant to degradation by decay 1 month old. Most patients (85%) had their first acute episode after a
accelerating factor (DAF) and CFH. The results of these two mutations triggering event such as gastrointestinal or upper respiratory tract infec-
lead to an increase of CFB enzyme activity. 64,113 tion, or fever. Other rare triggering events have been seen as well. The
C3 is a pivotal component in the complement system. Activation clinical distinction between hereditary TTP and aHUS can sometimes
of the classical, lectin, and alternative pathways results in cleavage of be difficult. Serial assessments of plasma ADAMTS13 activity and
157
C3 to generate C3b and anaphylatoxin C3a. The interaction between inhibitor 157,158 or identification of mutations in one or several complement
C3b and subsequent cleavage of CFB by CFD results in formation of regulator or activator genes 63,64,136,138 may help confirm the diagnosis.
the alternative pathway C3 convertase C3bBb. Mutations in C3 were
Of these, five mutations were gain-of-functional that ■
identified initially in 14 aHUS patients with persistently low serum C3
levels. 114,115,143-145 LABORATORY FINDINGS
exhibited reduced binding to MCP and were resistant to cleavage by CFI. Anemia in patients with TTP and HUS is universal and may be extremely
Other two mutations caused impaired C3 secretion. Another mutation severe. There is usually marked reticulocytosis and occasional circulat-
114
(R570Q) in C3 was reported in a large family that caused aHUS, micro- ing nucleated red blood cells. The hallmark is a microangiopathic blood
hematuria, hypertension, and chronic renal failure. Of 24 families, picture with fragmentation of red blood cells (schistocytes, helmet cells,
145
9 harbor the C3 (R570Q) mutation. The index patient suffered from and triangle forms) on the peripheral blood smear (Fig. 91-4). One can-
recurrent aHUS at age 22 and developed end-stage renal failure. Carriers not make diagnosis of TTP or HUS without significant fragmentation
showed reduced or borderline serum C3 levels. Hypertension was of red blood cells (usually two to three schistocytes per high power field
observed in six family members, microhematuria in five, and chronic on peripheral blood smear). Thrombocytopenia is invariably present
kidney disease stage 3 in two elderly patients. Other C3 mutations and may be severe in cases of TTP with the mean platelet counts of
145
(R139W and V1636A) that result in a gain-of-function C3 convertase 20 × 10 /L, 53,159 but less severe in cases of HUS. Hemolysis may mani-
9
159
have also been identified in 14 sporadic patients and 1 familiar aHUS fest as increasing serum bilirubin, particularly in neonates and young
143
case, respectively. children. 19,21 Serum haptoglobin is usually absent due to extravascular
144
TM is a 557 amino acid endothelial glycoprotein that is anchored to hemolysis. The LDH is usually markedly elevated in cases of TTP due
the cell by a single transmembrane domain. It contains a short cyto- to systemic organ ischemia though, not in proportion to the sever-
plasmic tail and six epidermal growth factor–like repeats and lectin-like ity of hemolysis. The Coombs test should be negative. Coagulation
160
domain. The primary function of TM is for thrombin-mediated gen- tests (prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, and fibrinogen)
eration of activated protein C 146-149 and thrombin-activable fibrinolysis are normal with exception of elevated fibrin degradation products or
section07.indd 861 1/21/2015 7:42:48 AM